Blood Pressure Cross-Country Cross-Language Cross-Paradigm (Demo) IG
0.5.2 - ci-build
Blood Pressure Cross-Country Cross-Language Cross-Paradigm (Demo) IG
0.5.2 - ci-build
Blood Pressure Cross-Country Cross-Language Cross-Paradigm (Demo) IG, published by FO. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 0.5.2 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/frankoemig/bloodpressure/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
Different types of "protocols" exist.
Therefore, the information models should cover all aspects that are needed to specify what to measure exactly.
To separate and distinguish between both, the first is called measurement setup, whereas the second is handled as executable protocol within this guide.
The measurement setup is used to specify the parameters for a single measurement.
| Protocol | Description | Aspects to consider |
|---|---|---|
| AOBP | Automated Office Blood Pressure | measuring blood pressure in a clinical setting that uses an automated device to take multiple readings with the patient alone in a room, thereby eliminating the "white coat effect" and human error associated with manual measurements |
| SMBP | Self-measured Blood Pressure | patient measure BP outside a clinical setting—typically at home—to help diagnose and manage hypertension; use a validated, automated, upper-arm cuff device, untrusted device, typically measured at wrist |
Both settings can be described by their attributes as follows:
| Aspect | AOBP | SMBP |
|---|---|---|
| measurement setting | physician office | home |
| location at body | arm | wrist |
| body position | sitting | unknown |
| exertion | in rest | unknown |
| position of feet | down | unknown |
| device | professional, trusted | untrusted |
| … |
An executable protocol typically should specify a sequence of measurements that are obtained for a certain purpose.
| Protocol | Name | Description | aspects to consider |
|---|---|---|---|
| ABI | Ankle-Brachial Index | quick, non-invasive, and painless diagnostic procedure that compares blood pressure in the arm with blood pressure at the ankle to screen for Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD) | |
| Bruce | Bruce treadmilll test | standardized treadmill stress test (ergometry) used to assess cardiovascular fitness and maximal oxygen uptake. It typically involves 3-minute stages, with speed and incline increasing every three minutes. Commonly used in cardiology, it serves to determine maximal physical performance, measured in METs. | |
| Naughton | treadmill protocol | gently increase work by limiting each stage increase to approximately one metabolic equivalent (3.5 ml/kg/min VO 2 ) | |
| NHANES | National Health and Nutrititon Examination Survey | ||
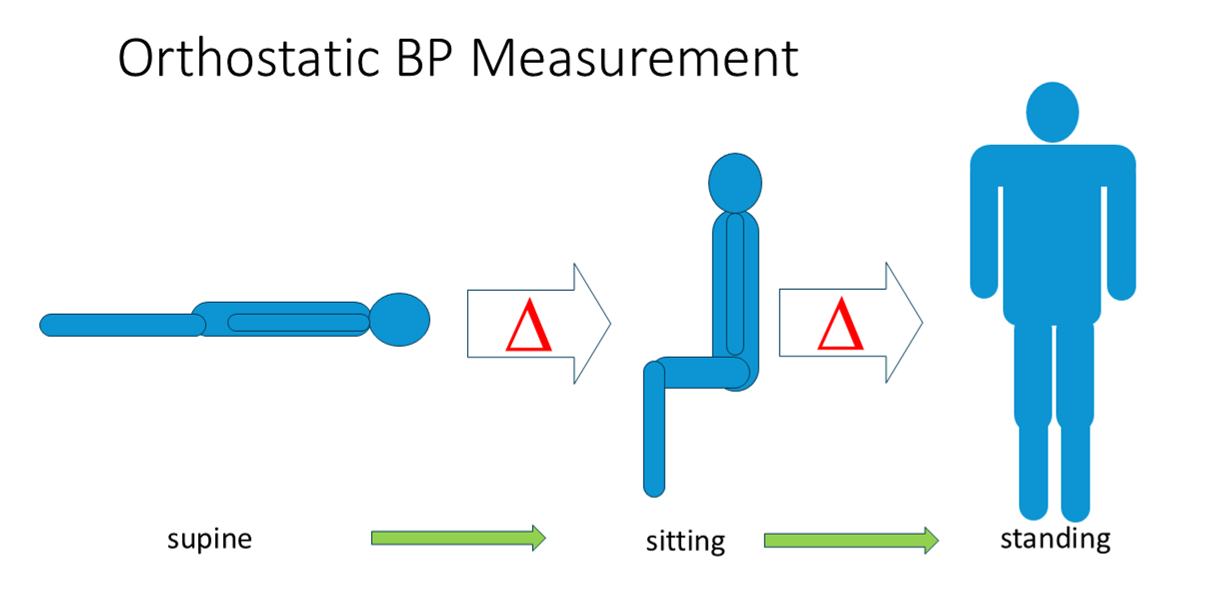
| orthostatic | supine -> sitting -> standing | varying body position to examine what happens if patient stands up; difference is calculated | |
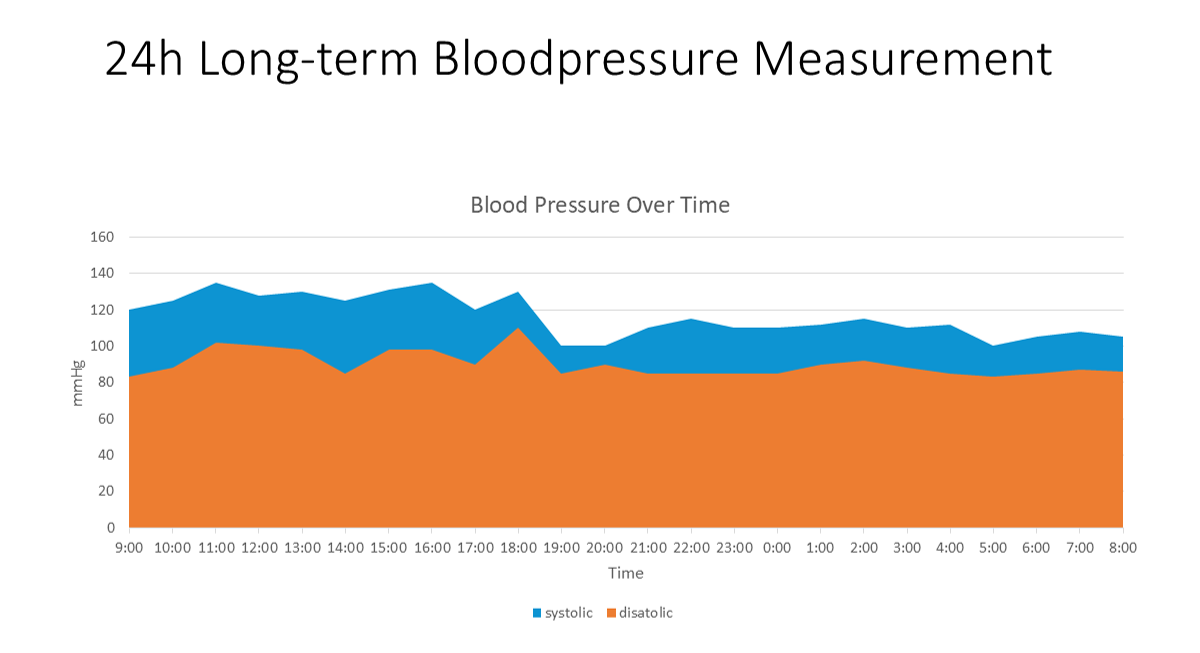
| 24h long-term | sequence of observations during 24 hours | measured all 15 minutes for 24 hours, at arm, arbitrary exertion, activity unclear | |
| SPRINT | Systolic (Blood) Pressure Intervention Trial | clinical trial that found that treating high blood pressure (hypertension) to a lower goal of less than 120 mm Hg significantly reduced the risk of cardiovascular events and death compared to standard treatment (less than 140 mm Hg) in high-risk patients | |
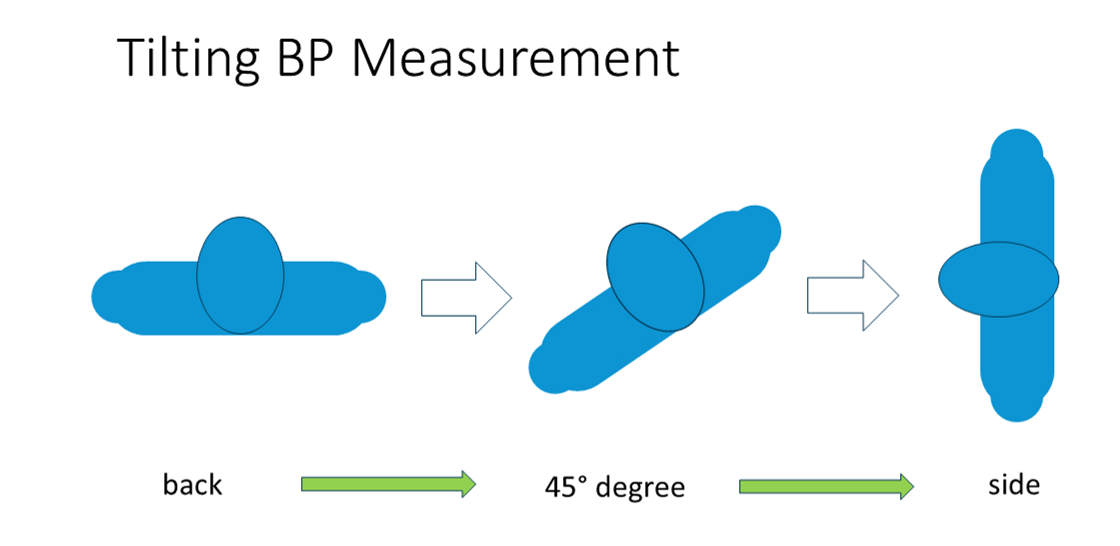
| tilt | sequence of measurements with increasing tilt | tilt angle | |
| .. | .. |
The aspects will be further specified…
For orthostatic evaluations the difference in the sequence of lying (supine), over sitting to standing is calculated:
This protocol examines whether the tilt of the body has an effect on the blood pressure. Therefore, the patient is turned around.
Long-term measurements are usually done during the period of a day, using an automated device that cyclicly measures the blood pressure e.g every 10 or 15 minutes. Instead of providing all values, an average is calculated during special periods of the day, eg. the night.
Different types of devices require different attributes (or properties). The correlation between type of device and attribute is shown in the following table:
| Device | Cuff | Catheter |
|---|---|---|
| Type | x | |
| Size | x | |
| Lumen | x | |
| serial number | x | x |
| … |