Pharmaceutical Quality (Industry), published by HL7 International / Biomedical Research and Regulation. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 1.0.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/uv-dx-pq/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
The Quality sections of regulatory applications are organized into a table of contents that includes sections and sub-sections under the titles “Drug Substance” and “Drug Product”. The structure is defined in the ICH Common Technical Document for the Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use. This Common Technical Document (CTD) structure is designed for unstructured PDF and Word documents.
Rather than recreating the legacy table of contents format in FHIR, pharmaceutical quality data represented by FHIR in this guide are organized into 14 new domains (see figure below). These 14 domains are designed to maximize the use of structured data and deliver benefits in terms of flexibility, efficiency, and data reuse.
Each domain has a page that describes its objective and provides a component diagram (where applicable), description of components, and examples.
The 14 pharmaceutical Quality (PQ) domains and their supporting sub-domains, in which each domain is based on a major Quality concept, such as Stability or Container Closure System. The subdomains contain individual data elements (not pictured) which capture the desired level of granularity needed for effective data exchange and communication of data across multiple parties.
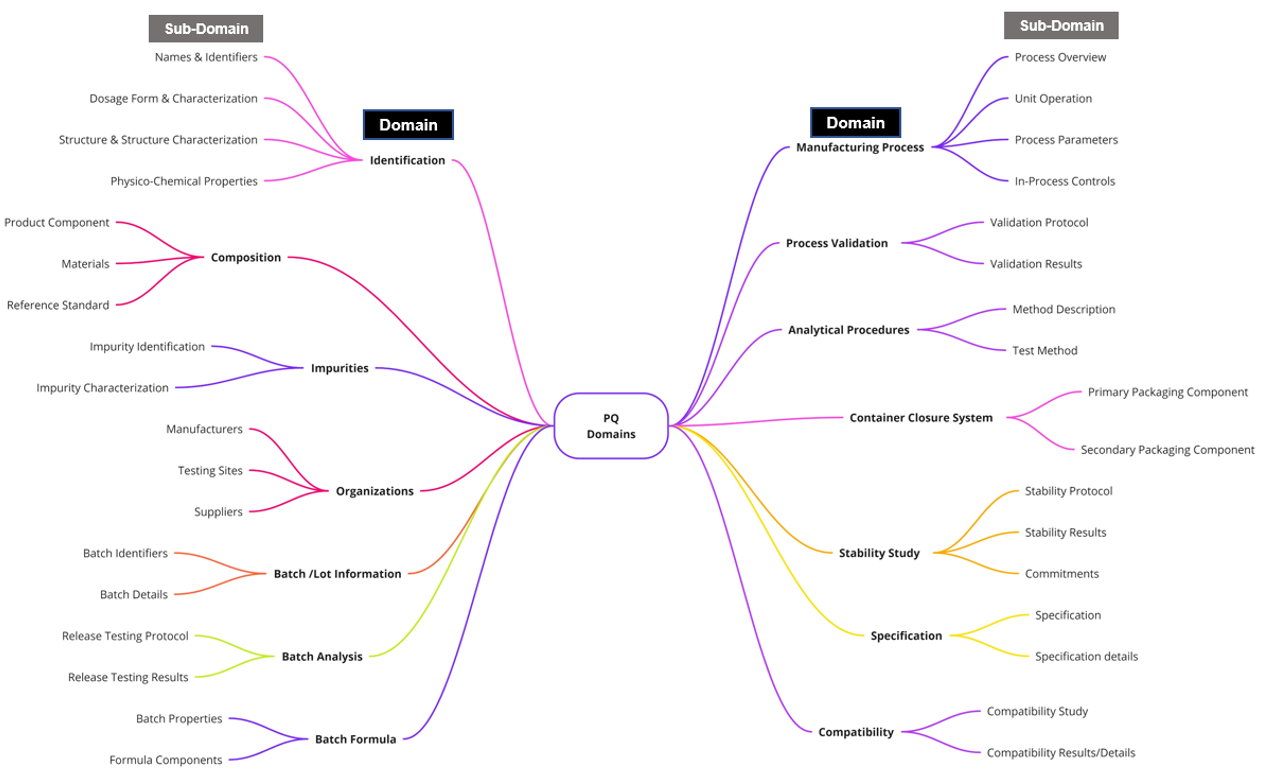 |
| FHIR IG Domain | Drug Product | Drug Substance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Identification | 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development
3.2.P.2.2 Drug Product 3.2.P.2.5 Microbiological Attributes 3.2.P.4 Control of Excipients 3.2.P.4.5 Excipients of Human or Animal Origin 3.2.P.4.6 Novel Excipients |
3.2.S.1 General Information
3.2.S.1.3 General Properties 3.2.S.3 Characterisation 3.2.S.3.1 Elucidation of Structure and Other Characteristics |
| 2. Composition | 3.2.P.1 Description and Composition of the Drug Product
3.2.P.6 Reference Standards or Materials |
3.2.S.5 Reference Standards or Materials |
| 3. Impurities | 3.2.P.5 Control of Drug Product
3.2.P.5.5 Characterisation of Impurities |
3.2.S.3 Characterisation
3.2.S.3.2 Impurities |
| 4. Organizations | 3.2.P.3 Manufacture
3.2.P.3.1 Manufacturer(s) |
3.2.S.2 Manufacture
3.2.S.2.1 Manufacturer(s) |
| 5. Batch or Lot Information | 3.2.P.5 Control of Drug Product
3.2.P.5.4 Batch Analyses |
3.2.S.4 Control of Drug Substance
3.2.S.4.4 Batch Analyses |
| 6. Batch Analysis | 3.2.P.5 Control of Drug Product
3.2.P.5.4 Batch Analyses |
3.2.S.4 Control of Drug Substance
3.2.S.4.4 Batch Analyses |
| 7. Batch Formula | 3.2.P.3 Manufacture
3.2.P.3.2 Batch Formula |
Not Applicable |
| 8. Manufacturing Process | 3.2.P.3 Manufacture
3.2.P.3.3 Description of Manufacturing Process and Process Controls 3.2.P.3.4 Controls of Critical Steps and Intermediates |
3.2.S.2 Manufacture
3.2.S.2.2 Description of Manufacturing Process and Process Controls |
| 9. Process Validation | 3.2.P.3 Manufacture
3.2.P.3.5 Process Validation and/or Evaluation |
3.2.S.2 Manufacture
3.2.S.2.5 Process Validation and/or Evaluation |
| 10. Analytical Procedures | 3.2.P.5 Control of Drug Product
3.2.P.5.2 Analytical Procedures |
3.2.S.4 Control of Drug Substance
3.2.S.4.2 Analytical Procedures |
| 11. Container Closure System | 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development
3.2.P.2.4 Container Closure System 3.2.P.7 Container Closure System |
3.2.S.6 Container Closure System |
| 12. Stability Study | 3.2.P.8 Stability
3.2.P.8.1 Stability Summary and Conclusions 3.2.P.8.3 Stability Data |
3.2.S.7 Stability
3.2.S.7.1 Stability Summary and Conclusions 3.2.S.7.3 Stability Data |
| 13. Drug Specifications | 3.2.P.5 Control of Drug Product
3.2.P.5.1 Specification(s) |
3.2.S.4 Control of Drug Substance
3.2.S.4.1 Specification |
| 14. Compatibility | 3.2.P.2 Pharmaceutical Development
3.2.P.2.6 Compatibility |
Not Applicable |
| Pharmaceutical Quality (Industry) FHIR IG component profiles | 1. Drug Identification | 2. Composition | 3. Impurities | 4. Organizations | 5. Batch/Lot Information | 6. Batch Analysis | 7. Batch Formula | 8. Manufacturing Process | 9. Process Validation | 10. Analytical Procedures | 11. Container Closure System | 12. Stability Study | 13. Drug Specification | 14. Compatibility |
| ActivityDefinition - Test | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Composition - Drug | X | |||||||||||||
| DeviceDefinition - Drug | X | X | X | |||||||||||
| DiagnosticReport - Drug Analysis | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| DocumentReference - Drug | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Ingredient - Drug | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| ManufacturedItemDefinition - Drug | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Medication - Batch Information | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||||
| MedicinalProductDefinition - Drug Product | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |
| Observation - Test Result | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||
| ObservationDefinition - Test Method | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||||
| Organization - Drug | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | |||
| PackagedProductDefinition - Drug | X | X | ||||||||||||
| PlanDefinition - Drug | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | ||||
| Procedure - Drug | X | |||||||||||||
| Specimen - Drug | X | X | ||||||||||||
| SpecimenDefinition - Drug | X | X | ||||||||||||
| Substance - Drug | X | X | X | X | X | |||||||||
| SubstanceDefinition - Component Drug | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X | X |
The resources that are used across all domains are summarized in this diagram:
.png) |