Canonical Resource Management Infrastructure Implementation Guide, published by HL7 International / Clinical Decision Support. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2.0.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/crmi-ig/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
| Page standards status: Informative |
Distribution involves the APIs for searching and retrieving published artifacts. There are a few APIs this IG supports, including:
Like publishing, FHIR Packages are a way to distribute content. This is compatible with IG Publisher, SUSHI and the NPM client.
npm --registry=http://fhir-package-registry install @scope/fhir.uv.test.my-package
This example illustrates the use of an NPM package registry to install IG packages as NPM packages. This example also illustrates the use of NPM Scopes for FHIR packages.
See also Publishing and Downloading FHIR (NPM) Packages for implementation details.
Read and search operations can be used to distribute artifacts, see Artifact Repository and Artifact Terminology Service capability statements. FHIR read and search SHOULD be available for all canonical resources.
Downstream systems MAY require all content dependencies. These dependencies can cross IG/package boundaries, as intended for reusability (e.g. a common Library could be used by two Measures, or an ActivityDefinition could be used by several PlanDefinitions in different content IGs). Furthermore, some content might have been published outside a content IG/FHIR Package.
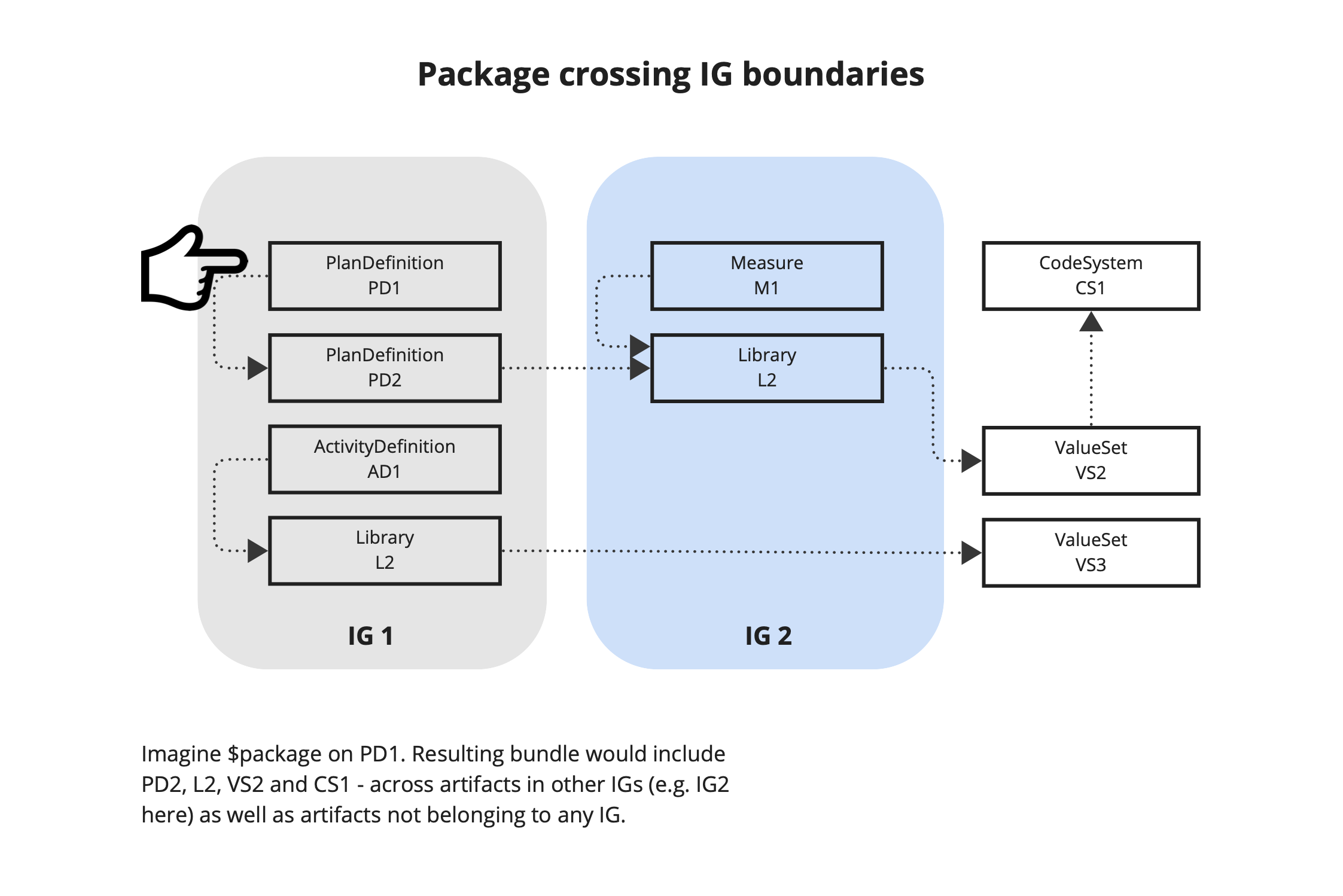
To facilitate this, a downstream system MAY use the $package or $data-requirements operation(s) on a canonical resource to resolve dependencies.
NOTE: $data-requirements allows the client to decide what is needed to download (versus what might already have been downloaded), whereas $package always ships the actual resources.
Both $package and $data-requirements operations are available for all canonical resources and non-canonical-artifacts:
NOTE: To recreate the contents of a FHIR Package, the $package operation could be called on the ImplementationGuide resource with appropriate parameters to only include local resources defined in the package (i.e. packageOnly set to true).
The first entry in the resulting Bundle will be an outcome manifest that completely characterizes the returned bundle, as well as describes any issues that arose during the packaging.
For example, if a ValueSet cannot be expanded as part of the packaging, the following issue may appear in the outcome manifest:
"issue": [
{
"severity": "warning",
"code": "processing",
"details": {
"text": "Could not expand the value set Danger signs Codes Grouper, but the definition of the value set is still included in the resulting package."
},
"expression": "Library.relatedArtifact.where(type='composed-of' and url='http://hl7.org/fhir/uv/crmi/ValueSet/publishable-example').resolve()"
}
]
The expression here is a FHIRPath from the perspective of the Outcome Manifest library.
For a complete example of an outcome manifest, see the Outcome Manifest Example.
It is common for knowledge artifacts to depend on other artifacts, which in turn depend on other artifacts. There may be different copyright owners along this dependency tree of artifacts. To ensure license compliance, we need a way to inventory the license information for an artifact and all of it's dependencies.
All knowledge artifacts (excluding ImplementationGuide, since there is already a .license element, a new extension to be defined) may have a license extension to document the license for the artifact e.g.:
{
"meta": {
"extension": [
{
"url": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/artifact-license",
"valueCode": "not-open-source"
}
]
}
}
All knowledge artifacts may have a license-detail extension to document the license detail for an artifact, especially useful when the licens is not-open-source e.g.:
{
"meta": {
"extension": [
{
"url": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/artifact-license-detail",
"valueMarkdown": "# ACME Restricted License\n\ndetails here"
}
]
}
}
NOTE: During package publishing, a CRMI Artifact Repository may add these extensions to all knowledge artifacts if not already present based on information from the package's ImplementationGuide.
Operation $license-requirements that returns a Parameters resource listing for each resource out:
NOTE: Similar to $package and $data-requirements, this will trace all dependencies, see below.
Request:
GET /Measure/$license-requirements
?url=http://acme.org/Measure/my-measure
&version=1.2.0
Response:
{
"resourceType": "Parameters",
"parameters": [
{
"name": "http://acme.org/Measure/my-measure",
"parameter": [
{
"name": "license",
"valueCode": "CC0-1.0"
},
{
"name": "publisher",
"valueString": "Acme Inc"
},
{
"name": "copyright",
"valueMarkdown": "Copyright notice"
},
{
"name": "canonical",
"valueCanonical": "http://acme.org/Measure/my-measure|1.2.0"
}
]
},
{
"name": "http://acme.org/Library/my-lib",
"parameter": [
{
"name": "license",
"valueCode": "not-open-source"
},
{
"name": "license-details",
"valueMarkdown": "ACME License\nYou have to pay for it."
},
{
"name": "publisher",
"valueString": "Acme Inc"
},
{
"name": "copyright",
"valueMarkdown": "Copyright notice"
},
{
"name": "canonical",
"valueCanonical": "http://acme.org/Library/my-lib|1.2.0"
}
]
}
]
}
Dependency tracing is the process of determining, given a root artifact, what other artifacts are referenced by the artifact, recursively, to produce a complete listing of all the artifacts (or dependencies) required for the artifact to be used. Because FHIR artifacts in general have many different ways of referencing other artifacts, the process needs to be described per resource type. In addition, because new extensions can be introduced and used at any point, the process needs to support a mechanism for allowing new content to indicate whether it constitutes a dependency for this purpose.
In general, the process considers each element of a resource and, if it is a canonical reference, or a reference to an "artifact" resource as described by this implementation guide, it is traced. In addition, extensions used in quality improvement profiles such as Clinical Guidelines and Quality Measures, are considered.
The following sections describe the dependency references for each type of resource. Note that this dependency-listing is not exhaustive, but captures the required dependencies for the quality improvement use case. The cqf-shouldTraceDependency extension can be used in the definition of an extension or profile to indicate whether the element should be traced as a dependency for the purposes of packaging and distribution.
This algorithm implies that all dependencies should be reported, including dependencies on base structure definitions. However, because of the way the base resource structure definitions are built, a dependency on any base specification resource effectively results in a dependency on the entire base specification (because of Extension.value[x] and DomainResource.contained). As a result, dependencies on the base specification resources typically do not add any useful information (because the package in which the base specification resources are defined is typically available in a FHIR-based environment anyway), and should be considered implied.
Each section provides a listing of the paths to each element that should be considered as a reference to an artifact (and recursively traced for dependencies as well) using a FHIRPath-like syntax, with abbreviated references to the names of extensions to be followed.
Note that the following extensions may be safely ignored for the purposes of dependency tracing:
StructureDefinition http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/elementdefinition-type-must-support
StructureDefinition http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/elementdefinition-type-must-support
StructureDefinition http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/codesystem-properties-mode
meta.profile
For structure definitions, only the differential element is considered, on the basis that the baseDefinition will be traced, so anything in the snapshots will be covered by tracing up the hierarchy.
extension[].url
modifierExtension[].url
baseDefinition
differential.element[].type.code
differential.element[].type.profile[]
differential.element[].type.targetProfile[]
differential.element[].binding.valueSet
differential.element[].extension[].url
differential.element[].modifierExtension[].url
extension[cpg-inferenceExpression].reference
extension[cpg-assertionExpression].reference
extension[cpg-featureExpression].reference
structure[].url
import[]
group[].rule[]..source[].defaultValue[x]
compose.include[].valueSet
compose.include[].system
compose.exclude[].valueSet
compose.exclude[].system
valueSet // NOTE: This element may be skipped because if the value set is really used by artifacts it will be referenced
supplements
(none)
sourceCanonical
targetCanonical
group.source
group.target
group[].element[].target[].dependsOn[].system
group[].element[].target[].product[]..system
unmapped.url
derivedFrom
item[]..definition // NOTE: This is not a simple canonical, it will have a fragment to identify the specific element
item[]..answerValueSet
item[]..extension[itemMedia]
item[]..extension[itemAnswerMedia]
item[]..extension[unitValueSet]
item[]..extension[referenceProfile]
item[]..extension[candidateExpression].reference
item[]..extension[lookupQuestionnaire]
extension[cqf-library]
extension[launchContext]
extension[variable].reference
item[]..extension[variable].reference
item[]..extension[initialExpression].reference
item[]..extension[calculatedExpression].reference
item[]..extension[cqf-calculatedValue].reference
item[]..extension[cqf-expression].reference
item[]..extension[sdc-questionnaire-subQuestionnaire]
relatedArtifact[].resource
library[]
profile
location
productReference
specimenRequirement[]
observationRequirement[]
observationResultRequirement[]
transform
extension[cpg-collectWith]
extension[cpg-enrollIn]
extension[cpg-reportWith]
relatedArtifact[].resource
library[]
action[]..trigger[].dataRequirement[].profile[]
action[]..trigger[].dataRequirement[].codeFilter[].valueSet
action[]..condition[].expression.reference
action[]..input[].profile[]
action[]..input[].codeFilter[].valueSet
action[]..output[].profile[]
action[]..output[].codeFilter[].valueSet
action[]..definitionCanonical
action[]..dynamicValue[].expression.reference
extension[cpg-partOf]
relatedArtifact[].resource
dataRequirement[].profile[]
dataRequirement[].codeFilter[].valueSet
relatedArtifact[].resource
library[]
group[].population[].criteria.reference
group[].stratifier[].criteria.reference
group[].stratifier[].component[].criteria.reference
supplementalData[].criteria.reference
extension[cqfm-inputParameters][]
extension[cqfm-expansionParameters][]
extension[cqfm-effectiveDataRequirements]
extension[cqfm-cqlOptions]
extension[cqfm-component][].resource
extension[cpg-relatedArtifact].reference
extension[cpg-relatedArtifact].reference
for
manufacturer
ingredient[].itemReference
ingredient[].substanceReference
parameter[].resource
relatedMedicationKnowledge[].reference
monograph[].source
ingredient[].itemReference
regulatory[].regulatoryAuthority
Canonical references MAY be authored without a version. To ensure consistent versions of resources are used by downstream systems, a manifest parameter to specify canonical versions MAY be passed to FHIR operations that use dynamic requirements: $package and $data-requirements; in addition to execution operations that can use a content endpoint to resolve canonical resources such as $apply from CPG and $evaluate-measure from DEQM IG.
More information on manifest specification
Syndication allows broadcasting of content changes to interested parties. The syndication mechanism proposed in the IG MAY be used by downstream systems, or federated Artifact Repositories so preemptive downloading, or notification message send to interested parties.
The syndication API SHALL be based on ATOM, an example is shown below:
<!-- see: https://validator.w3.org/feed/docs/atom.html -->
<feed xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom" xmlns:hl7="http://hl7.org/fhir/uv/crmi/syndication">
<title>HL7 CRMI Knowledge Artifact Server Feed</title>
<link rel="self" type="application/atom+xml" href="https://crmi-server/syndication/v1/feed.xml" />
<id>urn:uuid:e39958d4-380e-4252-8707-6afeff8b7911</id>
<updated>2023-01-01T01:00:00Z</updated>
<entry>
<id>urn:uuid:2c466218-337c-3367-95d9-57f65cd1a572</id>
<title>SomeMeasure Package</title>
<updated>2020-08-23T23:37:17Z</updated>
<published>2020-08-23T23:37:17Z</published>
<hl7:artifactVersion>0.0.0</hl7:artifactVersion>
<hl7:artifactType>package</hl7:artifactType>
<hl7:fhirVersion>4.0.1</hl7:fhirVersion>
<hl7:publishAction>publish</hl7:publishAction>
<author>
<name>SomeMeasure Agency</name>
<uri>http://www.measure.org</uri>
<email>help@measure.org</email>
</author>
<!-- when publishing a new FHIR package, we expose both the package tarball -->
<link rel="alternate" type="application/fhir+gzip"
href="https://crmi-server/packages/some.fhir.uv.somemeasure/-/some.fhir.uv.somemeasure-0.0.0.tgz" />
<!-- also include a Bundle transaction of all resources in the direct package with conditional create url and version -->
<link rel="alternate" type="application/fhir+json"
href="https://crmi-server/Bundle/f0099e15-3c06-4905-ba65-86749757fe80" />
<summary>Contains updates to SomeMeasure, a quality measure you need in your life.</summary>
<rights>Copyright 2019 SomeMeasure Agency. This content contains information which is protected
by copyright. All Rights Reserved. No part of this work may be reproduced or used in any form
or by any means - graphic, electronic, or mechanical, including photocopying, recording,
taping, or information storage and retrieval systems - without the permission of the
SomeMeasure Agency.</rights>
</entry>
<entry>
<id>urn:uuid:16d8afdf-79d4-4dfe-87ce-cfc6cd186f62</id>
<title>ValueSet ABC Removed</title>
<updated>2020-08-23T23:37:17Z</updated>
<hl7:fhirVersion>4.0.1</hl7:fhirVersion>
<hl7:artifactType>resource</hl7:artifactType>
<hl7:publishAction>unpublish</hl7:publishAction>
<!-- this is a transaction bundle with a conditional delete using the canonical url and version -->
<link rel="alternate" type="application/fhir+json; fhirVersion=4.0"
href="https://crmi-server/Bundle/b8e21acc-a8ee-41d5-acac-b7331d675fbe"/>
</entry>
<entry>
<id>urn:uuid:c4ae3f0f-2aaf-4afc-9752-e5d856b45461</id>
<title>Update FHIR Library</title>
<updated>2020-08-23T23:37:17Z</updated>
<hl7:artifactVersion>0.2.1</hl7:artifactVersion>
<hl7:artifactType>resource</hl7:artifactType>
<hl7:fhirVersion>4.0.1</hl7:fhirVersion>
<hl7:publishAction>publish</hl7:publishAction>
<!-- this is a transaction bundle with a conditional create using the canonical url and version -->
<link rel="alternate" type="application/fhir+json; fhirVersion=4.0"
href="https://crmi-server/Bundle/d654dcde-ba89-4f6e-9024-bced216d58e9"/>
</entry>
</feed>
Uplinks or mirrors are common in software artifact registries. Many times organizations have a virtualized registry that can route installation requests either locally (for local, private packages) or remotely to configured uplinks as show below:
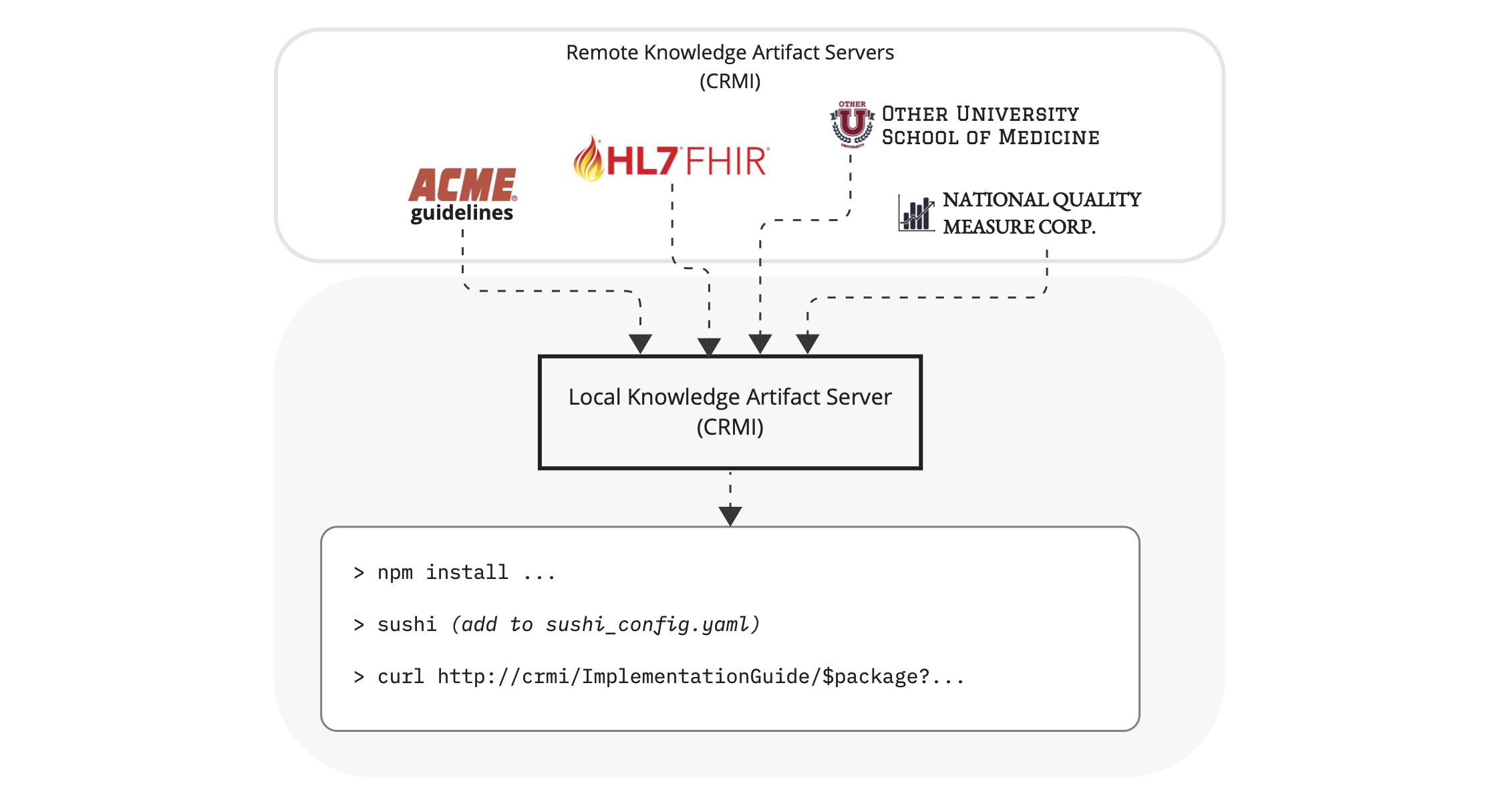
This can simplify tooling for distribution to downstream systems, and can decrease brittleness relying on upstream systems to be available.
Systems using sharable content, including: authoring systems, clinical data repositories, quality measure engines, decision support engines, care management systems, and assessment filler applications.
Distribution clients must be able to consume the artifacts produced by upstream systems, either as IG packages, or as artifact bundles, depending on how the upstream systems choose to distribute artifact content.
For IG packages, the FHIR publishing ecosystem, including the FHIR validation tooling, already provide implementation support for integrating with the FHIR registry to download packaged implementation guide content as published for FHIR implementation guides. Applications can either make use of this existing tooling, or build tooling appropriate for their platform to integrate with the FHIR registry feed (or other upstream feeds as described above).
Note that for artifact bundles that are the result of the $package operation, bundles may be requested that include duplicate artifacts. Client applications that consume artifact bundles must be prepared for this case.
In addition, client applications must ensure that artifact references are resolved correctly. If an artifact reference is unversioned, a version manifest for the artifact should be consulted to determine the appropriate version-binding information. See the Artifact Scope discussion for information on how to identify the version manifest appropriate for a particular artifact.