This is the Continuous Integration Build of FHIR (will be incorrect/inconsistent at times).
See the Directory of published versions 
Responsible Owner: Work Group Clinical Decision Support  & Clinical Quality Information & Clinical Quality Information  | Standards Status: Informative |
The Clinical Reasoning module provides resources and operations to enable the representation, distribution, and evaluation of clinical knowledge artifacts such as clinical decision support rules, quality measures, public health indicators, order sets, clinical protocols, and evidence summaries. In addition, the module describes how expression languages can be used throughout the specification to provide dynamic capabilities.
Clinical Reasoning involves the ability to represent and encode clinical knowledge in a very broad sense so that it can be integrated into clinical systems. This encoding may be as simple as controlling whether or not a particular section of an order set appears based on the conditions that a patient has, or it may be as complex as representing the care pathway for a patient with multiple conditions.
The Clinical Reasoning module focuses on enabling two primary use cases:
To enable these use cases, the module defines several components that can each be used independently, or combined to enable more complex functionality. These components are:
 and Clinical Quality Language (CQL)
and Clinical Quality Language (CQL)  .
.These basic components can then be used to enable a broad variety of clinical decision support and quality measurement use cases, including knowledge sharing, decision support services, and clinical quality assessment and reporting. The topics below provide more detailed discussion on each of these components and uses:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Overview and Background | If you are interested in the background and development of the FHIR Clinical Reasoning module, this topic covers where it came from and why it exists. See also the general FHIR introductions for clinicians, developers or architects |
| Using Expressions | If you want to see how to add dynamic capabilities to FHIR resources using expressions, start here. |
| Definitional Resources | If you want to see how to describe definitional resources using the ActivityDefinition resource, start here. |
| Representing Knowledge Artifacts | If you want to represent knowledge artifacts such as Event-Condition-Action rules, Order Sets, or Clinical Protocols, start here. |
| Sharing Knowledge Artifacts | If you want to share and distribute knowledge artifacts, start here. |
| Clinical Decision Support Service | If you want to use the Clinical Reasoning module to provide or use Clinical Decision Support services, start here. |
| Quality Reporting | If you want to define or report clinical quality measures, start here. |
| Evidence and Statistics | If you want to share and distribute knowledge artifacts about statistical facts, start here. |
From the perspective of a Knowledge Author, this module describes an approach to representing knowledge artifacts within FHIR.
From the perspective of a Knowledge Content Provider, this module defines search functionality for using a FHIR server as a knowledge artifact repository.
From the perspective of a Knowledge Evaluation Service Provider, this module defines operations and profiles in support of evaluating quality measures, and defining and using Decision Support Services  .
.
And finally, from the perspective of a Knowledge Evaluation Service Consumer, this module defines the expected available operations and behavior of a knowledge evaluation service.
| Resource | Description |
|---|---|
| ActivityDefinition | A resource to represent definitional resources. |
| ArtifactAssessment | A resource to capture assessments of knowledge artifacts such as ratings, classifiers, reviews, and comments. |
Citation  |
Represents the identification, location, and contributor attribution for a knowledge artifact. |
| DataRequirement | A datatype that represents a general data requirement for a knowledge asset such as a decision support rule or quality measure. |
| EventDefinition | Represents the definition of an event. |
| Evidence | Represents a single analytic result about a group. |
| EvidenceVariable | Represents the elements that evidence is about, such as the elements of a PICO question. |
| GuidanceResponse | Represents the result from invoking a decision support service. |
| Library | Provides a container for knowledge artifacts that includes logic libraries, model definitions, and asset collections. |
| Measure | Represents a clinical quality measure and provides evaluation through the $evaluate-measure operation. |
| MeasureReport | Represents the response to a specific measure evaluation request returned by the $evaluate-measure operation. |
| ParameterDefinition | Represents the definition of a parameter to logic. |
| PlanDefinition | Represents the description of a plan for accomplishing a particular goal. This resource is used to represent a broad variety of clinical knowledge artifacts including decision support rules, order sets, and protocols. |
| RequestOrchestration | Represents a group of options for a particular subject that can be used to accomplish a particular goal. This resource is often, but not always, the result of applying a PlanDefinition to a particular patient. |
| TriggerDefinition | Represents the definition of a triggering event. Used in EventDefinition and PlanDefinition to define the characteristics of an event. |
The following list details extensions that are commonly used as part of clinical reasoning use cases, either representing or evaluating knowledge artifacts. This is not an exhaustive list of extensions, and when a description of an extension here is inconsistent with the currently published description of an extension in the extensions pack, the extensions pack is the source of truth.
| Extension | Description |
|---|---|
| artifact-author | Allows resources that do not define an author element to provide an author for the artifact. |
| artifact-citeAs | Allow resources to define how they should be cited. |
| artifact-contact | Allow resources that do not define a contact element to provide contact details to assist a user in finding and communicating with the publisher of the artifact. |
| artifact-contactDetailReference | A reference to a resource that is a more detailed representation of the contact detail. |
| artifact-copyright | Allows resources that do not define a copyright element to provide copyright information for the artifact. |
| artifact-copyrightLabel | Allows resources that do not define a copyrightLabel element to provide a copyright label for the artifact. |
| artifact-date | Allows resources that do not define a date element to provide a date for the artifact. |
| artifact-description | Allows resources that do not define a description element to provide a description for the artifact. |
| artifact-editor | Allows resources that do not define an editor element to provide an editor for the artifact. |
| artifact-effectivePeriod | Allows resources that do not define an effectivePeriod element to provide an effectivePeriod for the artifact. |
| artifact-endorser | Allows resources that do not define an endorser element to provide an endorser for the artifact. |
| artifact-experimental | Allows resources that do not define an experimental element to provide an experimental flag for the artifact. |
| artifact-extended-contact-detail | Contact details (including purpose and address) to assist a user in finding and communicating with the publisher. |
| artifact-identifier | Allows resources that do not define an identifier element to provide identifiers for the artifact. |
| artifact-isOwned | Used to indicate whether the referenced resource is owned by the referencing resource (i.e., shares the same lifecycle). |
| artifact-jurisdiction | Allows resources that do not define a jurisdiction element to provide jurisdiction information for the artifact. |
| artifact-name | Allows resources that do not define a name element to provide a name for the artifact. |
| artifact-periodDuration | Allows a period to be specified using a start date and duration rather than specifying an end date. |
| artifact-publisher | Allows resources that do not define a publisher element to provide publisher information for the artifact. |
| artifact-purpose | Allows resources that do not define a purpose element to provide purpose information for the artifact. |
| artifact-relatedArtifact | Allows resources that do not define a relatedArtifact element to provide related artifact information for the artifact. |
| artifact-releaseDescription | Allows artifacts to specify release notes, i.e., a brief description of the contents and updates of a particular artifact release. |
| artifact-releaseLabel | Allows artifacts to specify a release label, i.e., a human-friendly release label assigned for the version of the artifact. |
| artifact-reviewer | Allows resources that do not define a reviewer element to provide reviewer information for the artifact. |
| artifact-status | Allows resources that do not define a status element to provide status information for the artifact. NOTE: This is a modifier extension. |
| artifact-title | Allows resources that do not define a title element to provide title information for the artifact. |
| artifact-uriReference | Allows resources to define a reference to a resource that is not canonical, but is being used as a knowledge artifact (e.g., a Substance or Medication resource that is modeling the definition of a substance or medication, rather than a specific instance). The resource referenced must be using the artifact-url and artifact-version extensions to provide a canonical reference for the resource. |
| artifact-url | Allows resources that do not define a url element to provide a canonical url for the artifact. |
| artifact-usage | Allows resources that do not define a usage element to provide usage information for the artifact. |
| artifact-useContext | Allows resources that do not define a useContext element to provide useContext information for the artifact. |
| artifact-version | Allows resources that do not define a version element to provide version information for the artifact. |
| artifact-versionAlgorithm | Allows resources that do not define a versionAlgorithm element to provide version algorithm information for the artifact. |
| artifact-versionPolicy | Allows versioning policy information to be provided for an artifact (e.g., strict, loose, metadata, and package). |
| codeOptions | This extension supports specifying the focus of an activity as a set of possible codes when there is no specific code available that captures the candidate activities. |
| cqf-alternativeExpression | An extension applied to an Expression to indicate an alternative, equivalent expression in a different language. |
| cqf-artifactComment | Allows comments such as review notes or additional documentation to be added to any artifact. |
| cqf-cdsHooksEndpoint | An extension applied to a PlanDefinition to indicate that it provides the behavior for a CDS Hooks service endpoint. |
| cqf-certainty | An extension that can be applied to a knowledge resource to indicate the certainty of some aspect of the resource such as confidence, strength, or quality. |
| cqf-contactAddress | An extension that can be applied to a ContactDetail to indicate the address of a contributor. |
| cqf-contactReference | An extension that can be applied to a ContactDetail to provide a reference to a resource that is the contact. |
| cqf-contributionTime | An extension that can be applied to a ContactDetail to indicate the time when a contributor made their contribution. |
| cqf-cqlAccessModifier | An extension that can be applied to a ParameterDefinition to indicate whether the declaration it represents is public or private. |
| cqf-cqlOptions | An extension that can be applied to an artifact to refer to a Parameters resource that provides translation options for a CQL-to-ELM translator. |
| cqf-cqlType | An extension that can be applied to parameters and parameter definitions to provide the actual FHIRPath or CQL type of the parameter. |
| cqf-criteriaReference | An extension that can be applied to populations and references to identify a specific measure criteria that is the source for the element on which it appears. |
| cqf-defaultValue | An extension that can be applied to a ParameterDefinition to indicate the default value for the parameter when none is supplied as part of an evaluation request. |
| cqf-definitionTerm | An extension that can be applied to any artifact to provide definitions that clarify usage and intent of the artifact. |
| cqf-directReferenceCode | An extension that can be applied to any artifact to indicate that a specific code is reference by logic within the artifact. |
| cqf-expansionParameters | An extension that can be applied to a Library or ImplementationGuide resource to indicate what parameters should be used for expansion for artifacts in the library or implementation guide. Also called Manifest Parameters. |
| cqf-expression | A general purpose extension that supports the use of languages such as FHIRPath and Clinical Quality Language within FHIR. |
| cqf-fhirQueryPattern | An extension that can be applied to a DataRequirement to provide a parameterizable RESTful FHIR API Query that can satisfy the data requirement. |
| cqf-improvementNotationGuidance | An extension that can be applied to a Measure and MeasureReport to provide additional guidance for the interpretation of a measure score. |
| cqf-initialValue | An extension that can be applied to any element to define an expression that can be evaluated to determine the initial value for the element when it appears in a creation context, such as when filling out a questionnaire or creating a new instance of a resource. |
| cqf-inputParameters | An extension that can be applied to any resource to indicate the parameters that were input to the operation that resulted in the creation of the resource. For example, a MeasureReport can use this extension to indicate what parameters were passed to the $evaluate operation that produced the MeasureReport. This extension is also used to capture the input expansion parameters as part of the CRMI $release operation. |
| cqf-isEmptyList | An extension that is applied to any parameter value to indicate that the value represents an empty list. This is necessary because the FHIR Parameters parameter element does not allow a parameter element to be represented without a value or resource present. |
| cqf-isEmptyTuple | An extension that is applied to any parameter value to indicate that the value represents an empty tuple. This is necessary because the FHIR Parameters parameter element does not allow a parameter element to be represented without a value or resource present. |
| cqf-isPrefetchToken | An extension that can be applied to a ParameterDefinition to indicate whether the parameter may be used to parameterize prefetch queries. |
| cqf-isPrimaryCitation | An extension that can be applied to any citation related artifact to indicate that it is considered a primary citation for the artifact. |
| cqf-isSelective | An extension that can be applied to a DataRequirement to indicate that it is a selective criteria for the artifact, meaning that it is a criteria that has a high selectivity with respect to the artifact (i.e., it has a high likelihood of significantly reducing the number of results that will satisfy the artifact overall). For example, a DataRequirement that indicates Condition of Diabetes, would have a high selectivity for a diabetes recommendation. |
| cqf-knowledgeCapability | Allows resources that do not define a knowledgeCapability element to provide knowledge capability information for the artifact. |
| cqf-knowledgeRepresentationLevel | Allows resources that do not define a knowledgeRepresentationLevel element to provide knowledge representation level information for the artifact. |
| cqf-library | A general purpose extension that supports the declaration of dependencies that can be accessed by expression logic. |
| cqf-library | An extension that can be applied to any library reference to indicate an alias that should be used for that library within expression logic used in the artifact. |
| cqf-logicDefinition | An extension that can be applied to any artifact to allow specific logic definitions used by the artifact to be identified. This extension is not intended to be used to define normatively referenced expression logic, that is done via libraries and expression-valued elements. This extension is only used to facilitate narrative rendering of knowledge artifact logic, and is always generated from other content. |
| cqf-measureInfo | An extension that can be applied to resources to indicate the measure criteria they satisfy. Used in evaluated resource bundles as part of reporting measure results for a patient to identify resources that contributed to the patient's membership in a particular population criteria. |
| cqf-messages | An extension that can be applied to resources to provide any messages that were produced in the evaluation process that produced the resource on which it appears. For example, a MeasureReport may use this extension to provide warnings that were produced during the creation of the MeasureReport. |
| cqf-modelInfo-isIncluded | An extension that can be applied to conformance resources to indicate whether or not they should be included in the resulting model information. |
| cqf-modelInfo-isRetrievable | An extension that can be applied to conformance resources to indicate whether or not they result in retrievable classes in the resulting model information. |
| cqf-modelInfo-label | An extension that can be applied to conformance resources to indicate an author-friendly label for the resulting class in the resulting model information. |
| cqf-modelInfo-primaryCodePath | An extension that can be applied to conformance resources to indicate what the primary code path is for the structure on which it appears. |
| cqf-modelInfoSettings | An extension that can be applied to library or implementation guide resources to provide the model information settings for the conformance resources included in the library or implementation guide. |
| cqf-parameterDefinition | An extension that can be applied to a TriggerDefinition to indicate a parameter that is supplied to the event handler for the trigger. |
| cqf-qualityOfEvidence | An extension that can be applied to indicate the quality of evidence in support of a particular artifact or recommendation. |
| cqf-relatedRequirement | An extension that can be used on any DataRequirement to define a relationship between data requirements (i.e., to indicate that the data requirement on which it appears is related to another data requirement, and cannot be evaluated without reference to the related data requirement). |
| cqf-relativeDateTime | [DEPRECATED] An extension that can be applied to define a date/time value relative to another event. This extension is deprecated, use the relative-date extension instead |
| cqf-resourceType | An extension that can be used on any canonical reference to indicate the type of the resource that is referenced by the canonical. This is the canonical equivalent of the type element of the Reference type. |
| cqf-shouldTraceDependency | An extension that can be applied to any structure or element to indicate whether or not the element should be included in a dependency trace. |
| cqf-strengthOfRecommendation | An extension that can be applied to indicate the strength of a recommendation. |
| cqf-supportedCqlVersion | An extension that can be applied to a CapabilityStatement to indicate what versions of CQL a server supports processing. |
| cqf-testArtifact | An extension that can be applied to a Group or Library to identify the artifact under test. |
| cqf-valueFilter | An extension that can be applied to any data requirement to define a value-based filter as part of the data requirement. This extension is only used in R4 to provide the capability of the valueFilter element. |
| data-absent-reason | An extension that is applied to any parameter value to indicate that the parameter it represents does not have a value. This is necessary because the FHIR Parameters parameter element does not allow a parameter element to be represented without a value or resource present. |
| display | An extension that can be used on any canonical reference to indicate the display for the resource that is referenced by the canonical. This is the canonical equivalent of the display element of the Reference type. |
| targetConstraint | An extension that can be applied to a definitional resource to define a constraint that should be applied to instances created from the definition. For example, a Measure could use this extension to define a constraint on MeasureReports created from that Measure. |
The following list of services are minimum capability statements defining some basic functionality. More detailed treatment is available in the Canonical Resource Management Infrastructure implementation guide, as well as the Quality Measure implementation guide.
| Service | Description |
|---|---|
| Knowledge Repository | Defines minimum service capabilities for a knowledge repository. |
| Measure Processor | Defines minimum service capabilities for a measure processor. |
Because Knowledge Artifacts are typically patient-independent, many of the resources in the clinical reasoning module have no patient security and privacy concerns beyond the normal sensitivity that should be paid in any electronic healthcare system environment. However, the evaluation use case, including decision support guidance request/response, as well as quality measure evaluation have significant patient security and privacy concerns.
For the clinical decision support evaluation use case, as with any patient-specific information, care should be taken to ensure that the request and response are properly secured both at rest and in-motion, and that all access to the patient's information is done via a properly authenticated and authorized mechanism. This is particularly true of decision support artifacts where the logic is ingested as part of the definition of the artifact. In this scenario, the evaluation engine must ensure that data access within the ingested logic is subject to the same authentication and authorization requirements as any other access.
For guidance services that receive patient information, ensure that logging and auditing trails do not inadvertently compromise patient privacy and security by logging potentially sensitive information in an unencrypted way. In addition, guidance and recommendations returned from the service must ensure that content that contains patient information is clearly indicated so that consuming clients can take the appropriate care in integrating and displaying the resulting guidance.
For quality measure evaluation, individual and patient-list reports have the potential to contain large amounts of patient information. As with the decision support guidance responses, care must be taken to ensure the patient information is only accessible to properly authenticated and authorized agents, and that inadvertent breaches are minimized by following appropriate logging and auditing protocols.
In particular, because expression languages, depending on their power and scope, can provide the ability to access large amounts of data, as well as the potential for infinite recursion or looping, care should be taken to ensure that implementations adequately safeguard against Denial-of-Service-style attacks that leverage these capabilities to compromise systems by overloading capacity.
For more general considerations, see the Security and Privacy module, and in particular the Implementer's Safety Checklist.
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Providing a dynamic value for a resource element | Using expressions to define the value for an element of a FHIR resource. |
| Defining a CQL library | Using the Library resource to incorporate a Clinical Quality Language library for use in FHIR resources. |
| Defining a Model Definition artifact | Using the Library resource to incorporate the definition of an information model for use with expressions in FHIR. |
| Defining an Event Condition Action rule | Using the PlanDefinition resource to represent an event-condition-action rule in FHIR. |
| Defining a Referral Request activity | Using the ActivityDefinition resource to define a referral request activity that can be used as part of a knowledge artifact. |
| Defining a Medication Request activity | Using the ActivityDefinition resource to define a medication request activity that can be used as part of a knowledge artifact. |
| Defining an Order Set | Using the PlanDefinition resource to represent an order set. |
| Defining a Protocol | Using the PlanDefinition resource to represent a protocol. |
| Representing Computable Guidelines | Using the clinical reasoning module and FHIR implementation guides to represent computable clinical practice guidelines. |
| Obtaining guidance from a Decision Support Service | Using services such as CDS Hooks to request and process guidance from a decision support service. |
| Defining a Measure | Using the Measure resource to represent a clinical quality measure. |
| Evaluating a Measure | Using the $evaluate-measure operation to request calculation of a clinical quality measure. |
| Applying an ActivityDefinition | Using the $apply operation to realize the intent resource defined by an ActivityDefinition. |
| Applying a PlanDefinition | Using the $apply operation to realize a plan definition for a specific context. |
| Representing Quality of Evidence/Strength of Recommendation | Using the qualityOfEvidence and strengthOfRecommendation extensions to indicate ratings associated with evidence for a particular artifact or recommendation. |
The resources defined for the Clinical Reasoning module are the result of the combined efforts of multiple communities working on the shared goal of harmonized standards and specifications for clinical decision support, quality measurement, public health reporting, evidence sharing, and other clinical reasoning use cases. The current state of the module reflects changes incorporated both from previous ballots on the FHIR-specific material, as well as content derived from several other balloted specifications in decision support, quality measurement, public health, and computable practice guideline domains. The content at this point is capable of supporting the two primary use cases of sharing and evaluation in multiple domains and for a broad variety of artifacts.
In particular, the use of Clinical Quality Language (CQL) as a foundational mechanism for representing clinical quality logic enables knowledge artifacts across this spectrum of use cases to share common definitions. For example, a Chlamydia Screening measure and related decision support artifacts focused on improving the measure can share a common library that describes the criteria for detecting when Chlamydia Screening is required in a patient. The decision support rule applies these criteria to determine when and how to impact a workflow, while the quality measure uses these same criteria to determine whether the screening goal has been met for a patient or population. In addition, the resources defined in this module use common patterns for describing the structure of artifacts and their associated metadata, enabling a consistent approach to the sharing and distribution of clinical knowledge artifacts.
Since the initial trial use publication as part of FHIR STU 3 in 2017, the Clinical Reasoning module has been used in a broad range of clinical use cases, including quality measurement and decision support, to represent, exchange, and evaluate knowledge artifacts. These use cases have been described in multiple implementation guides built on the Clinical Reasoning Module, and this usage has generated substantial feedback resulting in the addition of new elements, as well as guidance for using the Clinical Reasoning module. Although this feedback has resulted in some substantive changes, there have been comparatively few, and the goals of the module for the next several years are to sustain this stability for the core use cases of representation and evaluation of clinical knowledge.
Some of these implementation guides include:
 : This implementation guides provides universally applicable guidance for the use of Clinical Quality Language with FHIR resources for a variety of use cases.
: This implementation guides provides universally applicable guidance for the use of Clinical Quality Language with FHIR resources for a variety of use cases. : This implementation guide provides universally applicable guidance related to the content development lifecycle, including authoring, packaging, publishing, distributing, and consuming conformance resources and knowledge artifacts.
: This implementation guide provides universally applicable guidance related to the content development lifecycle, including authoring, packaging, publishing, distributing, and consuming conformance resources and knowledge artifacts. : This implementation guide provides an approach and methodology for the representation and implementation of computable clinical guidelines using the resources and capabilities provided by the Clinical Reasoning module.
: This implementation guide provides an approach and methodology for the representation and implementation of computable clinical guidelines using the resources and capabilities provided by the Clinical Reasoning module. : This implementation guide provides conformance criteria and guidance for using CDS Hooks with FHIR. The IG describes logical models for representing CDS Hooks constructs, mappings from those constructs to FHIR resources, as well as how CDS Hooks can be used to surface FHIR Clinical Reasoning services.
: This implementation guide provides conformance criteria and guidance for using CDS Hooks with FHIR. The IG describes logical models for representing CDS Hooks constructs, mappings from those constructs to FHIR resources, as well as how CDS Hooks can be used to surface FHIR Clinical Reasoning services. : This implementation guide provides detailed conformance requirements and guidance for the use of the Measure and Library resources to support the specification of quality measures.
: This implementation guide provides detailed conformance requirements and guidance for the use of the Measure and Library resources to support the specification of quality measures. : This implementation guide provides detailed guidance to support reporting quality measures specified by the Quality Measures IG.
: This implementation guide provides detailed guidance to support reporting quality measures specified by the Quality Measures IG.Note that the Canonical Resource Management Infrastructure implementation guide in particular includes the Shareable, Publishable, Computable, and Executable content patterns, profiles, and guidance provided in previously published versions of several of the above implementation guides as well as previous versions of this specification. All of the Shareable, Publishable, Computable, and Executable profiles in the base specification are now defined in and evolving as part of the CRMI implementation guide. Applications making use of these patterns should use the profiles defined in CRMI.
The FHIR Clinical Reasoning module is sponsored by the Clinical Decision Support (CDS) and Clinical Quality Information (CQI) HL7 Work Groups, with input and coordination from the FHIR Infrastructure, Terminology Infrastructure, Service Oriented Architecture, Patient Care, Patient Administration, and Public Health HL7 Work Groups.
The guidance in this module was prepared as a Universal Realm Specification with support from the Clinical Quality Framework (CQF) initiative  , which was a public-private partnership sponsored by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) to identify, develop, and harmonize standards for clinical decision support and electronic clinical quality measurement. The Clinical Quality Framework
, which was a public-private partnership sponsored by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) and the U.S. Office of the National Coordinator for Health Information Technology (ONC) to identify, develop, and harmonize standards for clinical decision support and electronic clinical quality measurement. The Clinical Quality Framework  effort transitioned to HL7's Clinical Quality Information (CQI) and Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Work Groups in 2016.
effort transitioned to HL7's Clinical Quality Information (CQI) and Clinical Decision Support (CDS) Work Groups in 2016.
The Clinical Quality Framework is focused on harmonizing the historically disjoint specifications used by the Clinical Quality Measurement and Clinical Decision Support communities. Specifically, the initiative has focused on the specifications used to represent knowledge artifacts within the two communities. The strategy employed has been to break the conceptual content of knowledge artifacts into three core components, to define common standards for these core components, and to re-use these common standards for both clinical decision support and clinical quality measurement:
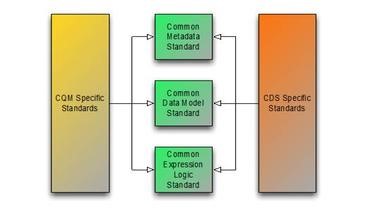
The first component has resulted in the Clinical Quality Common Metadata Conceptual Model  , an informative document harmonizing metadata requirements between Quality Measurement and Decision Support artifacts.
, an informative document harmonizing metadata requirements between Quality Measurement and Decision Support artifacts.
The second component has resulted in the QUICK Conceptual and Logical  Models, a harmonization of the Virtual Medical Record (vMR)
Models, a harmonization of the Virtual Medical Record (vMR)  used in Decision Support and the Quality Data Model (QDM)
used in Decision Support and the Quality Data Model (QDM)  used in Quality Measurement, and with its core requirements realized in FHIR as the Quality Improvement Core (QICore) profiles
used in Quality Measurement, and with its core requirements realized in FHIR as the Quality Improvement Core (QICore) profiles  . Ongoing work in this area is focusing on coordination with the Clinical Information Modeling Initiative (CIMI) and a methodology for producing FHIR profiles from CIMI models. Currently, the QICore FHIR profiles (which are in turn derived from the US-Core profiles) can be used to model clinical quality data, and to present a consistent model for use in authoring and evaluating clinical quality artifacts.
. Ongoing work in this area is focusing on coordination with the Clinical Information Modeling Initiative (CIMI) and a methodology for producing FHIR profiles from CIMI models. Currently, the QICore FHIR profiles (which are in turn derived from the US-Core profiles) can be used to model clinical quality data, and to present a consistent model for use in authoring and evaluating clinical quality artifacts.
Finally, the third component has resulted in the Clinical Quality Language specification  , a harmonization of the expressive capabilities of the Clinical Decision Support Knowledge Artifact Specification (CDS KAS)
, a harmonization of the expressive capabilities of the Clinical Decision Support Knowledge Artifact Specification (CDS KAS)  (produced by the Health eDecisions
(produced by the Health eDecisions  (HeD) Standards and Interoperability (S&I) initiative), and the Health Quality Measures Format (HQMF)
(HeD) Standards and Interoperability (S&I) initiative), and the Health Quality Measures Format (HQMF)  .
.
As part of the ongoing CQF initiative pilot efforts, these developing specifications are being used to support knowledge artifact sharing, as well as evaluation of knowledge artifacts as part of decision support request/response and measure evaluation.
This module continues the harmonization of quality domain specifications by defining an approach to using a FHIR server as a component of a knowledge system in both the Knowledge Repository and Knowledge Evaluation Service roles.
More broadly, the FHIR Clinical Reasoning module provides a foundation for a Quality Improvement Ecosystem, depicted in the following diagram:
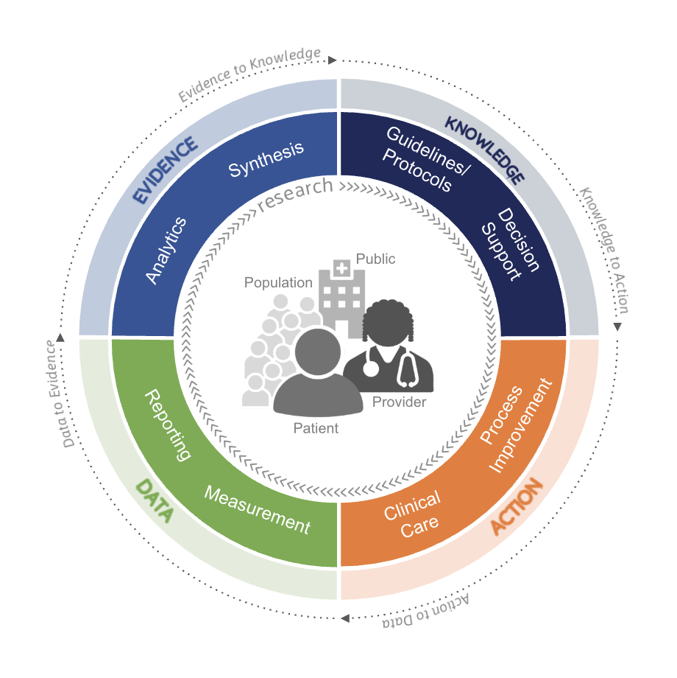
Also referred to as a "Learning Health System", the diagram highlights the ideal iterative flow of data from clinical care, measurement, and reporting, becoming evidence through analytics and synthesis into knowledge in the form of guidelines and protocols, operationalized as decision support, process improvement, and integration with clinical care, ultimately producing data that feeds back into the cycle. This process can be seen at work throughout the healthcare industry, from the microcosm of direct patient-provider interactions to determine and understand the best course of treatment for a patient, through quality improvement initiatives enacted within institutions to drive better patient outcomes and provider experience, up to industry-wide efforts including payer-provider collaboration and quality programs. The FHIR Clinical Reasoning module and the implementation guides based on it, build on the semantic interoperability enabled by FHIR to reduce friction throughout this cycle and across the settings in which it manifests to enable not only exchange of semantically interoperable data, but of knowledge.
The approach and representations within this guide are derived from and intended to be consistent with the following specifications:





This material includes SNOMED Clinical Terms ® (SNOMED CT®), which are used by permission of the International Health Terminology Standards Development Organisation (IHTSDO). All rights reserved. SNOMED CT was originally created by the College of American Pathologists. "SNOMED ®" and "SNOMED CT ®" are registered trademarks of the IHTSDO.
This material contains content from Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC®) (http://loinc.org  ). The LOINC table, LOINC codes, and LOINC panels and forms file are copyright © 1995-2017, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and the LOINC Committee and available at no cost under the license at http://loinc.org/terms-of-use
). The LOINC table, LOINC codes, and LOINC panels and forms file are copyright © 1995-2017, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and the LOINC Committee and available at no cost under the license at http://loinc.org/terms-of-use  .
.
This material contains content from the Unified Code for Units of Measure (UCUM) (http://unitsofmeasure.org  ). The UCUM specification is copyright © 1999-2017, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and available at no cost under the license at http://unitsofmeasure.org/trac/wiki/TermsOfUse
). The UCUM specification is copyright © 1999-2017, Regenstrief Institute, Inc. and available at no cost under the license at http://unitsofmeasure.org/trac/wiki/TermsOfUse  .
.
This material contains quality measure content developed by the National Committee for Quality Assurance (NCQA). The measure content is copyright (c) 2008-2017 National Committee for Quality Assurance and used in accordance with the NCQA license terms for non-commercial use.
The resources and guidance provided in this module are the combined work of a joint project between the HL7 Clinical Quality Information and Clinical Decision Support Work Groups with the co-sponsorship of the FHIR Infrastructure, Implementable Technology Specifications, and Service Oriented Architecture Work Groups.