HL7 Czech Imaging Report IG
0.1.0-ballot - ci-build
HL7 Czech Imaging Report IG
0.1.0-ballot - ci-build
HL7 Czech Imaging Report IG, published by HL7 Czech Republic. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 0.1.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7-cz/img/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
The purpose of the document is to create a national, functional and technical specification for the exchange of imaging examination results. At the same time, the proposed standard must guarantee basic compatibility with similar standards that are being developed within the framework of the European X-eHealth project and other similar projects. The concept of the functional specification is therefore based on the European specification for imaging examination results adopted by the European eHealth Network (eHN) and within the objectives of this project, its adaptation to the conditions of the Czech healthcare system is carried out so that its practical use in the Czech Republic is possible.
The document focuses mainly on the area of semantic interoperability, but also addresses some legal, regulatory and organizational aspects that are important for the exchange of data within the domain of diagnostic imaging methods.
This document focuses on aspects of interoperability of imaging examination results, typically radiological examinations or nuclear medicine examinations, but also examinations performed by clinicians, such as gynecological ultrasound. Typical for imaging examination methods is the acquisition of an image record, currently mainly in digital form, which is assessed by healthcare professionals specializing in these examination methods. The report from imaging methods contains information about the examination itself and its result in written form and is part of the medical documentation. The report is stored as part of the patient's medical documentation kept by the provider and is also transmitted or made available to the physician who indicated the procedure and to the patient, unless the procedure is performed as part of hospitalization.
The document focuses on:
The functional specification is applicable to cases of hospital care, specialized outpatient care and general practice as well as emergency care.
The document focuses on standardizing the content of structured electronic records of imaging methods (radiological methods, nuclear medicine methods, ultrasound methods, etc.) and metadata, on interoperability and machine processing aspects, but also on data extensions, e.g. references to related records, selected DICOM data from imaging studies, additional annexes, etc. The document also focuses on aspects related to the exchange and sharing of these messages using information technology.
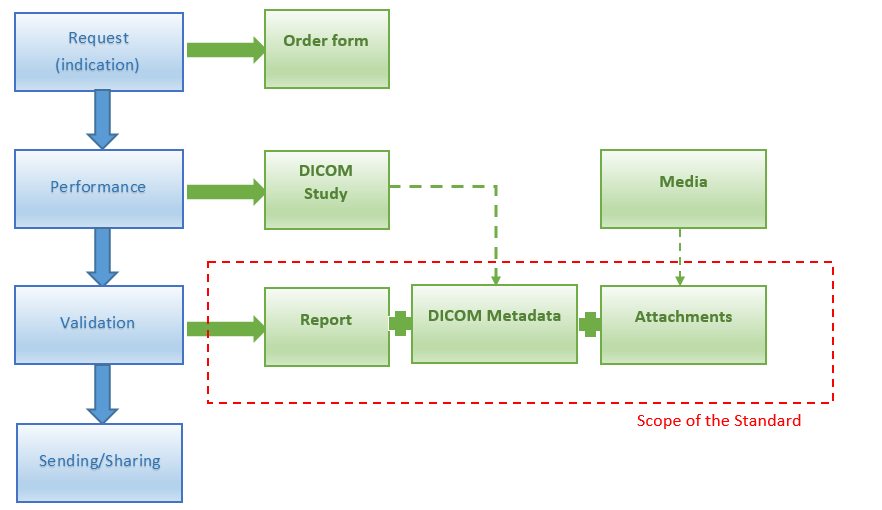
Fig. 1: CONTENT OF THE STANDARD
The document does not cover the area of image documentation in the form of digital image records (studies) from devices. These image studies are created, processed, stored and transmitted in standardized formats and using communication protocols of the international DICOM standard. For transmission or sharing between healthcare providers, two exchange networks (ePACS and ReDiMed) based on the DICOM standard are currently available in the Czech Republic.
Imaging result report could be divided into several parts: document header, body, presented form in PDF and optionally it could also have various attachments.
Imaging methods are performed upon request (usually) by the referring physician. The request should also contain the justification for the examination. Requests (orders) are sent in paper form or electronically. They are always registered in the information system (RIS/HIS/AIS). Individual work requirements for modalities (devices) are then created from the request. Data from the request is usually automatically transferred to the REPORTS.
Reason for requesting health services. The report can respond to more than one of the reasons listed. The reason for the request should have been included in the request (order).
Information about the sample, if the material is the subject of testing. Biological species refers to samples taken from subjects other than human subjects. Material of the sample taken, time of collection, anatomical location, morphological abnormalities of the anatomical location from which the material is taken, for example "wound" or "ulcer", etc. The SNOMED CT code system is proposed for most data.
Type of procedure
Classification of the examination. Currently, the ERTN classification is used, for which the ÚZIS maintains a mapping to the codes of procedures of the VZP codebook.
It is also proposed to use LOINC "Imaging Document Codes" or to also ensure mapping of the Czech Radiological Classification (ČRK) to LOINC.
Body part
Description of the part of the body, or laterality ("side"), on which the procedure is performed. Structured or at least free text.
Modality
Imaging modality (abbreviation) that performed the image recording. DICOM Standards PS 3.3-2011, section C.7.3.1.1.1
Reason for performance
Reason for performance of the procedure given by the healthcare professional responsible for performing the procedure. It may be different from that given in the request by the referring physician, or it supplements it.
Technique for performance of the procedure
Description of the technical implementation of the imaging method (e.g. used MR sequence, image projection, etc.). It also contains coded items. The description of the technical implementation can also be made in a formalized notation, i.e. structured, but at least (mandatory) in free text.
The description of the technical implementation also contains information on the administration of substances, e.g. a substance or other medicinal contrast agent administered in connection with the procedure (e.g. contrast agent or sedative, etc.). At least the name of the medicinal product, dose and date and time of administration must be provided. If an adverse reaction occurs after administration, information on the adverse reaction must also be recorded.
Results
The description of the results of the performed procedures (examinations) must be at least free text and an observation code (SNOMED CT).
Conclusion
The conclusion summarizes the most important findings and/or diagnoses that were made based on the results of the imaging methods (possibly taking into account other clinical information). This section may contain a free text description of the clinical conclusion and/or a coded assessment, for example, a BI-RADS category or equivalent.
Recommendations
The recommendations may include, for example, recommendations for subsequent examinations or procedures that resulted from the results and/or conclusions. The structured part of this item is identical to the item of the same name in the discharge report.
A reference to related previously performed imaging methods, e.g. for comparing results or trends, or to an older version of the Report changed by this report. The relevant report must belong to the same patient. The proposal does not prescribe the implementation method, how user information about previous examinations will be attached. A free text note is also possible.
Key images related to this report. There may be multiple attachments. In addition to metadata describing individual attached media, the attachment may contain the actual media content (inline) or a direct link to the source media. In addition to metadata, free text may be entered for the attachment. The proposal does not prescribe the implementation method, in which way the media will be attached by the user. The media, attachments, may also include outputs from devices in the form of images (e.g. ECG curves, microscope images, etc.) and also a trusted form of the document ("fingerprint" of the PDF/A document with a qualified signature).
Selected relevant data from the DICOM study without image data. The goal is to make the data available to all users without transferring entire DICOM image studies and without software enabling reading of DICOM data from image studies. Data that is part of DICOM is not overwritten, but is attached to the Report (into the Report) automatically. The "consumer" of the News receives information about the image study and can only get previews of some series, some images by "clicking through" from the news, etc.