Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange, published by HL7 International / Financial Management. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2.1.1 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/davinci-epdx/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
| Official URL: http://hl7.org/fhir/us/davinci-pdex/ImplementationGuide/hl7.fhir.us.davinci-pdex | Version: 2.1.1 | |||
| IG Standards status: Trial-use | Maturity Level: 2 | Computable Name: DaVinciPayerDataExchange | ||
Copyright/Legal: Used by permission of HL7 International, all rights reserved Creative Commons License |
||||
The PDex work group has made changes to the original version of the IG following the publication of the final CMS Interoperability and Patient Access Rule (CMS-9115) and the subsequent Advancing Interoperability and Improving Prior Authorization Rule (CMS-0057).
The STU 2.1 version of the IG incorporates changes to support the sharing of Prior Authorization information with members, providers and other payers. This is done through the profiling of the ExplanationOfBenefit resource. This version of the Implementation guide also introduces two Bulk APIs that enable the data available through the Patient Access API to also be made available to In-Network/Contracted Providers and other Health Plans through the Provider Access API and the Payer-to-Payer Bulk API.
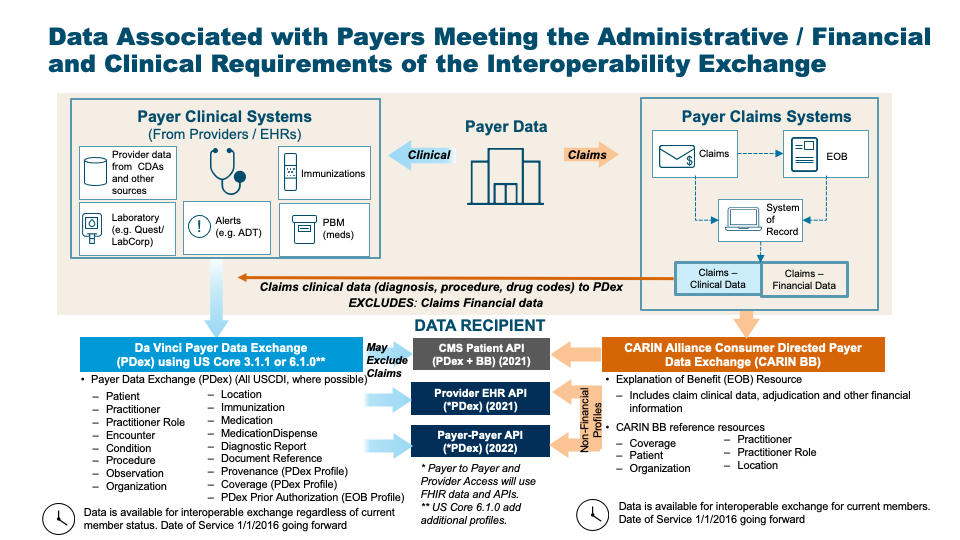
CMS Guidance defines two sets of data to be made available by payers in the Patient Access API: Claims and Encounter Data and Clinical data. They provide links to specific implementations guides for the Patient Access API to provide guidance. Use of these implementation guides is not required but is recommended. If used these guides will provide information payers can employ to meet the requirements of the policies being finalized. The CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange IG (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) defines how Claims and Encounter Data are to be provided; This Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange IG (PDex) and the US Core 3.1.1 IG, US Core 6.1.0 IG or US Core 7.0.0 IG define how Clinical Data is to be provided.
This version of the Implementation Guide introduces support for US Core 7.0.0 IG. Since the IG embraces US Core the support for US Core 7.0.0 is similar to the support for US Core 6.1.0 which required minimal changes to the PDex IG. Throughout this IG references to US Core 6.1.0 can also be interpreted as supporting US Core 7.0.0 which is expected to supercede US Core 6.1.0 in 2028.
This IG recognizes that the healthcare industry is rapidly evolving methods, such as TEFCA, to enable the secure exchange of information between Providers and Payers and between payers. Incorporating prescriptive definitions for connecting, registering and authorizing access to the Provider Access or Payer-to-Payer API risks complicating the adoption of solutions that will enable secure exchange of data, at scale. Health Plans implementing the Da Vinci guides that address the CMS Prior Authorization Rule (Payer Data Exchange, Coverage Requirements Discovery, Documents templates and Rules and Prior Authorization Support) are urged to continue to engage with their respective work groups in order to be aware of ongoing developments and emergent implementation approaches, as the industry works to evolve methods that will enable adoption of these Interoperability Standards at scale. Developments are to be expected in the area of automated registration and access to the secure APIs documented in these IGs.
There are two parallel paths pursued by the CARIN Alliance (Creating Access to Real-time Information) and the Da Vinci Project related to providing health plan data to various stakeholders. CARIN Alliance approaches the issue primarily from a financial (claims) perspective, with some limited associated clinical data. The Da Vinci Project approaches the issue primarily from a clinical perspective and leaves financial data out of scope.
The CARIN Alliance focused on replicating the CMS Blue Button 2.0 solution directed at providing beneficiaries access to claims information for Medicare Fee For Service (FFS) in the form of a FHIR based ExplanationOfBenefit (EOB). The CARIN Alliance Consumer-Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) solution was intended to provide the same information based on commercial payer databases, at least for Medicare Advantage products. The CMS Interoperability and Patient Access Final Rule expanded the scope of a Blue Button 2.0 equivalent to include not just Medicare Advantage but also Medicaid HMO, CHIP HMO and QHP's in the federal marketplace.
The Da Vinci Payer Data Exchange (PDex) solution started with the goal of providing payer sourced information to providers in the form of FHIR resources consistent with US Core profiles for FHIR Release 4 (R4). The CMS Interoperability Final Rule directs covered payers (as noted above) to make Encounter and Clinical data available to members through an API (defined by the ONC 21st Century Cures Act Final Rule) for, at a minimum, information defined in USCDI release 1.1. Since PDex was already focused on making the same information available through a compliant API, Da Vinci expanded the scope of PDex to include not only payer to provider exchange at the request of the provider but also payer to third party application exchange at the request of the member.
In addition, the CMS Interoperability Final Rule requires a covered plan, at the member’s request, to make their information (as defined by USCDI release 1.1), at a minimum available to any other plan as directed by the member. This ability must exist for up to 5 years after the member leaves the plan. Da Vinci expanded the scope of the PDex Implementation Guide to support this exchange. This aspect of the CMS-9115 Interoperability and Patient Access Rule was never enforced. However, in the following Prior Authorization Rule (CMS-0057) CMS requires Payers to enable Payers to perform a Payer-to-Payer exchange of data for opted-in and matched members that have moved to a new plan from a regulated health plan.
At this point we have two solutions that provide an overlapping but different set of information for the members of a health plan. The first is the CARIN IG for Blue Button® which is focused on providing claims information, including the adjudication information, in the form of a FHIR ExplanationOfBenefit (EOB). The second solution is to provide all payer information related to the clinical condition and care of the patient using US Core profiles on FHIR R4 resources. In the latter case, USCDI information coming from claims is represented as US Core resources and includes, at a minimum: encounters, providers, organizations, locations, dates of service, diagnoses (conditions), procedures and observations. This information would also include clinical information from sources other than claims maintained by the payer, such as:
Unlike the US Core 3.1.1 IG or US Core 6.1.0 IG, PDex provides guidance to payers on how to make the following information available via the Patient Access API:
|
This IG uses the same Member Health History "payload" for member-authorized exchange of information with other Health Plans, in network providers and with Third-Party Applications. It describes the interaction patterns that, when followed, allow the various parties involved in managing healthcare and payer data to more easily integrate and exchange data securely and effectively.
This IG covers the exchange of:
In support of the Prior Authorization Rule (CMS-0057) This IG adds support for Prior Authorizations and the supporting clinical information used in reaching a decision. This information iis added to the Patient Access API and is also available to In-Network Providers and other Payers through the Provider Access and Payer-to-Payer Bulk APIs.
This IG covers the exchange of this information using US Core and Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HRex) Profiles. This superset of clinical profiles forms the Health Plan Member's Health History.
This IG covers the exchange of a Member's Health History in the following scenarios:
The latter two scenarios are provided to meet the requirements identified in the CMS Interoperability Notice for Proposed Rule Making issued on February 11, 2019. To meet the requirements of the CMS Prior Authorization Rule this IG adds two new APIs:
There are items in this guide that are subject to update. This includes:
See the Table of Contents for more information.
The Data Mapping section addresses the mapping of Claims and Encounter data to Clinical profiles. Some US Core profiles correlate with data provided in the Consumer-Directed Payer Data Exchange (Blue Button 2.0) IG. The Data Mapping section provides tables to assist implementers in mapping between these IGs.
With the CMS Prior Authorization Rule (CMS-0057) recommending the series of Da Vinci Burden Reduction Implementation Guides (Coverage Requirements Discovery, Documents Templates and Rules and Prior Authorization Support) it is expected that Payers will receive more clinical data from Providers. Much of that data will be in structured form, as defined by the US Core Implementation Guide. The Payer-to-Payer Bulk API also requires the exchange of unstructured data that supports a Prior Authorization decision. Such data would be embedded in a DocumentReference resource for exchange. This is likely to result in Payers having far more clinical data to exchange wih Members, Providers and other Payers.
The IG will continue to be tested at connectathons and will continue to utilize commonly adopted standards (e.g., US Core profiles) that have been tested by other groups (e.g., Argonaut). USCDI concepts are encapsulated in US Core Profiles on FHIR Resources. The Code Systems, Value Sets and codings used in this IG are based on US Core Profiles. Regardless of the way in which payers store their administrative and clinical information they will need to map it appropriately to these profiles.
In addition, we are creating a supplemental guide to provide more examples of how to populate the resources that are being exchanged based on the nature of the source information (e.g., lab results via V2 transactions, CDA, or claims).
Implementers of this IG SHOULD support the endpoint discovery mechanism defined in the HRex specification to allow discovery of the endpoints used in this IG - specifically the following: §pdex-81
This HL7 specification contains and references intellectual property owned by third parties ("Third Party IP"). Implementers and testers of this specification SHALL abide by the license requirements for each terminology content artifact utilized within a functioning implementation. §pdex-82 Terminology licenses SHALL be obtained from the Third-Party IP owner for each code system and/or other specified artifact used. §pdex-83 It is the sole responsibility of each organization deploying or testing this specification to ensure their implementations comply with licensing requirements of each Third-Party IP.
This publication includes IP covered under the following statements.
This implementation guide (IG) uses specific terminology to flag statements that have relevance for the evaluation of conformance with the guide:
SHALL indicates requirements that must be met to be conformant with the specification. §pdex-84
SHOULD indicates behaviors that are strongly recommended (and which may result in interoperability issues or sub-optimal behavior if not adhered to) but which do not, for this version of the specification, affect the determination of specification conformance. §pdex-85
MAY describes optional behaviors that are free to consider but where there is no recommendation for, or against, adoption. §pdex-86
For profiles defined in other IGs, the meaning of Must Support is established in the defining IG. Note that the Must Support requirements for this IG are modeled after the US Core Implementation Guide. For further information see the Must Support section in the Introduction page.
Security and Privacy are critically important when exchanging information. Please refer to the Security and Privacy page in this IG and the guidance it references in the Health Record Exchange (HRex) IG.
It is important to differentiate in the Implementation Guide between identifiers used by the Provider/EMR and those used by the Payer/Health Plan to identify the patient/subject/member.
For the purposes of this IG we will use the following terms:
patient or subject id will be used to express the identifier used by the provider to identify a patient/subject.
member id will be used to express the identifier used by the payer/health plan to identify an individual member. Health Plans may historically have referred to these individual members as:
| Implementation Guide | Version(s) | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Data Access IG | 2.0.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Member Attribution (ATR) List (and potentially others) |
| CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) | 2.1.0 | |
| 2.0.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Prior Authorization Support (PAS) FHIR IG (and potentially others) | |
| Da Vinci - Coverage Requirements Discovery | 2.1.0 | |
| 2.0.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Prior Authorization Support (PAS) FHIR IG (and potentially others) | |
| Da Vinci - Documentation Templates and Rules | 2.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Clinical Data Exchange (CDex) (and potentially others) |
| Da Vinci - Member Attribution (ATR) List | 2.1.0 | |
| Da Vinci Clinical Data Exchange (CDex) | 2.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Member Attribution (ATR) List (and potentially others) |
| Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HRex) | 1.1.0 | Defines common conformance rules across all Da Vinci IGs, as well as additional constraints and profiles beyond U.S. Core |
| 1.0.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Coverage Requirements Discovery (and potentially others) | |
| Da Vinci PDex Plan Net | 1.2.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Member Attribution (ATR) List (and potentially others) |
| Da Vinci Prior Authorization Support (PAS) FHIR IG | 2.1.0 | |
| FHIR Extensions Pack | 5.2.0 | Imported by CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) (and potentially others) |
| 5.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HRex) (and potentially others) | |
| 1.0.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Coverage Requirements Discovery (and potentially others) | |
| FHIR R4 package : Core | 4.0.1 | Imported by US Core (and potentially others) |
| HL7 Terminology (THO) | 6.3.0 | Defines terminologies and coddesystems used in HIR IGs |
| 6.2.0 | Imported by CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) (and potentially others) | |
| 6.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HRex) (and potentially others) | |
| 5.5.0 | Imported by US Core (and potentially others) | |
| 5.3.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Coverage Requirements Discovery (and potentially others) | |
| 5.0.0 | Imported by Subscriptions R5 Backport (and potentially others) | |
| 4.0.0 | Imported by Security for Scalable Registration, Authentication, and Authorization (and potentially others) | |
| National Directory of Healthcare Providers & Services (NDH) | 1.0.0 | |
| Public Health Information Network Vocabulary Access and Distribution System (PHIN VADS) | 0.12.0 | Imported by US Core (and potentially others) |
| SMART App Launch | 2.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Member Attribution (ATR) List (and potentially others) |
| 2.0.0 | Imported by US Core (and potentially others) | |
| Security for Scalable Registration, Authentication, and Authorization | 1.0.0 | Imported by National Directory of Healthcare Providers & Services (NDH) (and potentially others) |
| 0.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HRex) (and potentially others) | |
| Structured Data Capture | 3.0.0 | Imported by US Core (and potentially others) |
| Subscriptions R5 Backport | 1.1.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Prior Authorization Support (PAS) FHIR IG (and potentially others) |
| US Core | 7.0.0 | Defines USCDI v4 EHR expectations on a range of resources that will be passed to and/or queried by CRD servers. |
| 6.1.0 | Defines USCDI v3 EHR expectations on a range of resources that will be passed to and/or queried by CRD servers | |
| 3.1.1 | Defines USCDI v1 EHR expectations on a range of resources that will be passed to and/or queried by CRD servers. | |
| Value Set Authority Center (VSAC) | 0.7.0 | Imported by CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) (and potentially others) |
| 0.21.0 | Imported by CARIN Consumer Directed Payer Data Exchange (CARIN IG for Blue Button®) (and potentially others) | |
| 0.19.0 | Imported by Da Vinci Health Record Exchange (HRex) (and potentially others) | |
| 0.18.0 | Imported by US Core (and potentially others) | |
| 0.11.0 | Imported by Da Vinci - Coverage Requirements Discovery (and potentially others) |
A history of changes made since the publication of the STU1 version of the PDex IG is maintained in ChangeHistory.
See the Credits page for a list of contributors to the creation and maintenance of this Implementation Guide.
This IG was built with Sushi and the FHIR Publisher (v1.6.5 or greater).