HL7 CZ Laboratory IG
0.5.0 - ci-build
HL7 CZ Laboratory IG
0.5.0 - ci-build
HL7 CZ Laboratory IG, published by HL7 Czech Republic. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 0.5.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7-cz/cz-lab/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
The Laboratory Results Report use case covers the processes involved in performing tests and issuing result reports by the clinical laboratory in response to orders for in-vitro diagnostic tests.
After completing the internal testing workflow—which includes consolidating all test orders or order sets, plus every quality-control and validation step—the laboratory produces a fully finished results report based on the requirements and parameters set by the order placer.
The laboratory marks the report as “Final” (the laboratory-results-report status is changed to “final”) and sends it to the clinical-practice application (called the Order Result Tracker) as well as to every correspondent listed in the laboratory-test order. A copy may also be stored in a connected EHR repository.
Every individual test result contained in the final laboratory results report must itself be in the “final” or “cancelled” state.
In some situations the laboratory may release a results report that is either incomplete (some results are not yet available or not yet flagged as “final”) or un-verified.
Typical cases include:
In such cases the report status must be set to “preliminary” or “partial”. See Table 2 for details.
If the content of a results report—or any referenced resources—changes after the report was marked “final” and signed-off by an authorised person, its status must be updated to “amended”, “corrected” or “appended”, depending on the situation. See Table 2 for definitions.
Occasionally the laboratory cannot perform any of the ordered tests and therefore cannot issue a results report.
Reasons may include lost specimens, broken tubes, analyser failure, and so on. In such cases the report status must be set to “cancelled” and specific details provided—preferably as values of the TestResult.value.codedResult element. Additional information can also be supplied in a results comment.
If a laboratory results report was created or released by mistake, its status must be set to “entered-in-error”. This state indicates that the previously published report is invalid and should be disregarded completely.
As described above, laboratory results reports can exist in several states depending on the exact workflow.
Applications that consume these reports must carefully watch for updates (revisions) and ensure that withdrawn reports are handled appropriately.
Applications that provide diagnostic reports—including laboratory results reports—should not mark a report as final until all its data items are complete or attached.
If a report is withdrawn after it was previously released in the final state, the report and all associated observations should be withdrawn by changing their status codes to “entered-in-error” and adding a conclusion or comment such as “This report has been withdrawn.”
A free-text reason for withdrawal may be supplied. The state machine documents possible transitions between statuses.
Figure 1: State diagram of the laboratory results report
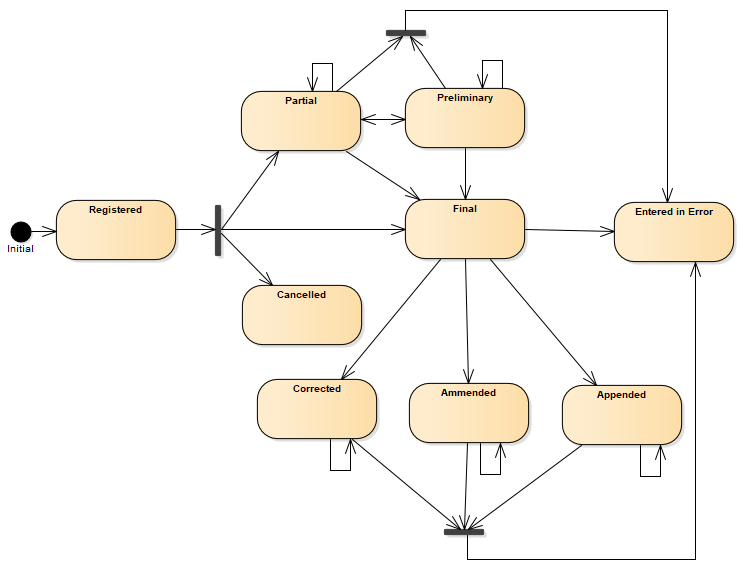
Table 2: Possible statuses of a laboratory results report
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Registered (registered) | The report is recorded, but nothing is yet available. |
| Incomplete (partial) | An incomplete (e.g. provisional) report: data may be missing or unverified. |
| Preliminary (preliminary) | Early verified results are available, but not all results are final. |
| Final (final) | The report is complete and verified by an authorised person. |
| Amended (amended) | After the report was marked final, its content was changed (results, diagnosis, narrative text, or other report elements). |
| Corrected (corrected) | After the report was marked final, an error in the report or issued results was corrected. |
| Appended (appended) | After the report was marked final, new content was added; existing content remains unchanged. |
| Cancelled (cancelled) | The report is unavailable because the measurement did not occur, was not finished, or was interrupted. |
| Entered in Error (entered-in-error) | The report was withdrawn after previously being released as final. This electronic record should never have existed, although clinical decisions may have been based on it. (If physical actions were taken, the status should be cancelled rather than entered-in-error.) |
Not only the report itself but also its individual items (i.e. the single test results included in the laboratory report) follow distinct life-cycle phases.
These phases can be expressed by statuses as described in Table 3. Transitions are illustrated in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Overview of states for a laboratory test result
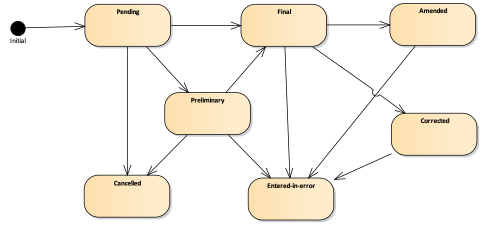
Table 3: Possible statuses of a laboratory test result
| Status | Description |
|---|---|
| Pending (pending) | The measurement has been requested and recorded, but the result is not yet available. |
| Preliminary (preliminary) | A provisional or preliminary measurement: data may be incomplete or unverified. |
| Final (final) | The definitive result. |
| Amended (amended) | After the result was marked final, it was modified (updated, supplemented, or corrected). |
| Corrected (corrected) | After the result was marked final, an error in the test result was corrected. |
| Cancelled (cancelled) | The result is unavailable because the measurement did not occur, was not finished, or was interrupted. |
| Entered in Error (entered-in-error) | The result was withdrawn after previously being released as final. This electronic record should never have existed, although clinical decisions may have been based on it. (If physical actions were taken, the status should be cancelled rather than entered-in-error.) |
Although the document status and the statuses of its items are partly independent, some basic consistency rules can be defined based on their definitions.
Table 4: Relationship between report status and individual result statuses
| Report Status | Description of Report Status | Consistency Rules with Result Statuses (for implementation) |
|---|---|---|
| Registered | The report is recorded, but nothing is yet available. | ALL results registered OR cancelled |
| Incomplete | An incomplete (e.g. provisional) report: data may be missing or unverified. | SOME (registered, preliminary, final, cancelled) OR SOME NOT verified |
| Preliminary | Early verified results are available, but not all results are final. | SOME (registered, preliminary, final) AND ALL (verified OR cancelled) |
| Final | The report is complete and verified by an authorised person. | ALL (final AND verified) OR SOME cancelled |
| Amended | After the report was marked final, its content was changed. | SOME amended OR entered-in-error OR other report content changed |
| Corrected | After the report was marked final, an error was corrected. | SOME corrected OR entered-in-error |
| Appended | After the report was marked final, new content was added; existing content unchanged. | ALL (final AND verified) |
| Cancelled | The report is unavailable because the measurement did not occur, was not finished, or was interrupted. | ALL cancelled |
| Entered in Error | The report was withdrawn after previously being released as final. This electronic record should never have existed, although clinical decisions may have been based on it. (If physical actions were taken, the status should be cancelled rather than entered-in-error.) | ALL entered-in-error |