This is the Continuous Integration Build of FHIR (will be incorrect/inconsistent at times). Directory of published versions
12.1 Resource Task - Content
A task to be performed as a part of a workflow and the related informations like inputs, outputs and execution progress. While very simple workflows can be implemented with Request alone, most workflows would require a Task (explicit or contained) as a means to track the execution progress (i.e. inputs, outputs, status). Please refer to Fulfillment/Execution .
12.1.1 Scope and Usage
A Task resource describes an activity that can be performed and tracks the state of
completion of that activity. It is a representation that an activity should be or has been
initiated, and eventually, represents the successful or unsuccessful completion of that
activity.
Concretely the Task resource could be used in FHIR to serve different purposes like:
Note that there are a variety of processes associated with making and processing orders.
Some orders may be handled immediately by automated systems but most require real-world
actions by one or more humans. Some orders can only be processed when other real-world actions
happen, such as a patient presenting themselves so that the action to be performed
can actually be performed. Often these real-world dependencies are only implicit in the order
details.
12.1.2 Background and Context 12.1.2.1 Using Tasks in a RESTful context In a RESTful context, a server functions as a repository of tasks. The server itself, or
other agents are expected to monitor task activity and initiate appropriate actions to ensure
task completion, updating the status of the task as it proceeds through its various stages of
completion. These agents can be coordinated, following well choreographed business logic to
ensure that tasks are completed. Task management may also be centrally controlled using some
form of a workflow engine, in which case, the workflow engine itself may update and maintain the
Task resources in the server, and through its orchestration activities ensure that tasks are
completed. The Task resource enables either model of task management yet provides a
consistent view of the status of tasks being executed in support of healthcare workflows.
The assignment of tasks into categories by type of task, type of performer and task status
enable the server to function as a queue of work items. This queue can be polled or subscribed
to by various agents, enabling automation of workflows in FHIR using existing search and subscription
mechanisms. Owners, requesters, other agents (e.g. workflow managers) can thus be ready to
initiate the next steps in a complex workflow.
Note to Implementers:
Currently, task pre-requisites can be represented using Task's `description` element or the RequestOrchestration resource. We are seeking input from the implementer community in evaluating whether there is need for adding another mechanism to this resource for this purpose.
Feedback here .
12.1.3 Boundaries and Relationships Task spans both intent and event and tracks the execution through to
completion. A Task is a workflow step such as cancelling an order,
fulfilling an order, signing an order, merging a set of records, admitting a
patient. In contrast, Procedures are actions
that are intended to result in a physical or mental change to or for the
subject (for example, surgery, physiotherapy, training, counseling). A Task resource
often exists in parallel with clinical resources. For example, a Task could
request fulfillment of a ServiceRequest
ordering a procedure that would result in a Procedure, Observation , DiagnosticReport , ImagingStudy or similar resource. Another
example would be a Task that requests fulfillment of a CommunicationRequest to be performed
between various actors. The task resource tracks the state of a task, enabling
systems to ensure that tasks are completed. This information is kept separate
from the operational details necessary to complete the task, as those details
vary across and even within workflows. That detail is expected to be carried
in the referenced .focus of the task.
The Task resource can represent an authorization for a service to be provided
or the fulfillment of an authorization (by another Task or resource type that
implements the Request pattern). For further information about the separation of
responsibilities, refer to the Fulfillment/Execution
section of the Request pattern. Information about the details of the fulfillment
of an authorization may be handled by additional Task resource instances.
Tasks may have named inputs and outputs. Inputs represent
information that may or must be present in order for a task to
complete. Outputs represent intermediate or final results produced by a
task. For example, in a task supporting reading of radiology image, the
inputs might include both the imaging study to be read, as well as
relevant prior images. Outputs could represent radiology measurements
as well as the Radiologist's diagnostic report.
Inputs and outputs are tracked by the task because workflow
management activity may automate the transfer of outputs from one task
to inputs to a subsequent task.
To facilitate the integration of off the shelf workflow applications
with FHIR, the Task resource may reference a definition. This
definition can represent a description of the workflow activity to be
performed, using a standard workflow description language such as BPEL,
BPMN, or XPDL, a workflow definition such as those defined in IHE
profiles, or even simple written instructions explaining a process to be
performed.
12.1.4 References to this Resource 12.1.5
Resource Content
UML Diagram (Legend )
Task (DomainResource ) The business identifier for this task identifierIdentifier [0..*]The URL pointing to a *FHIR*-defined protocol, guideline, orderset or other definition that is adhered to in whole or in part by this Task instantiatesCanonicalcanonical [0..1] « ActivityDefinition »The URL pointing to an *externally* maintained protocol, guideline, orderset or other definition that is adhered to in whole or in part by this Task instantiatesUriuri [0..1]BasedOn refers to a higher-level authorization that triggered the creation of the task. It references a "request" resource such as a ServiceRequest, MedicationRequest, CarePlan, etc. which is distinct from the "request" resource the task is seeking to fulfill. This latter resource is referenced by focus. For example, based on a CarePlan (= basedOn), a task is created to fulfill a ServiceRequest ( = focus ) to collect a specimen from a patient basedOnReference [0..*] « Any »A shared identifier common to multiple independent Task and Request instances that were activated/authorized more or less simultaneously by a single author. The presence of the same identifier on each request ties those requests together and may have business ramifications in terms of reporting of results, billing, etc. E.g. a requisition number shared by a set of lab tests ordered together, or a prescription number shared by all meds ordered at one time groupIdentifierIdentifier [0..1]Task that this particular task is part of partOfReference [0..*] « Task »The current status of the task (this element modifies the meaning of other elements) statuscode [1..1] « null (Strength=Required) TaskStatusAn explanation as to why this task is held, failed, was refused, etc statusReasonCodeableReference [0..1] « ; null (Strength=Example) TaskStatusReasonContains business-specific nuances of the business state businessStatusCodeableConcept [0..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskBusinessStatusIndicates the "level" of actionability associated with the Task, i.e. this a proposed task, a planned task, an actionable task, etc intentcode [1..1] « null (Strength=Required) TaskIntentIndicates how quickly the Task should be addressed with respect to other requests prioritycode [0..1] « The task's priority. (Strength=Required) RequestPriorityIf true indicates that the Task is asking for the specified action to *not* occur (this element modifies the meaning of other elements) doNotPerformboolean [0..1]A name or code (or both) briefly describing what the task involves codeCodeableConcept [0..1] « null (Strength=Extensible) TaskCodeThis element has or is affected by some invariants CA free-text description of what is to be performed descriptionmarkdown [0..1]The request being fulfilled or the resource being manipulated (changed, suspended, etc.) by this task focusReference [0..1] « Any » « This element has or is affected by some invariants CThe entity who benefits from the performance of the service specified in the task (e.g., the patient) forReference [0..1] « Any »The healthcare event (e.g. a patient and healthcare provider interaction) during which this task was created encounterReference [0..1] « Encounter »Indicates the start and/or end of the period of time when completion of the task is desired to take place requestedPeriodPeriod [0..1]Identifies the time action was first taken against the task (start) and/or the time final action was taken against the task prior to marking it as completed (end) executionPeriodPeriod [0..1]The date and time this task was created authoredOndateTime [0..1]The date and time of last modification to this task lastModifieddateTime [0..1]The creator of the task requesterReference [0..1] « Device |Organization |Patient | Practitioner |PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson » The kind of participant or specific participant that should perform the task requestedPerformerCodeableReference [0..*] « Practitioner | PractitionerRole |Organization |CareTeam |HealthcareService | Patient |Device |RelatedPerson ; null (Strength=Preferred) ProcedurePerformerRoleCodes Party responsible for managing task execution ownerReference [0..1] « Practitioner |PractitionerRole | Organization |CareTeam |Patient |RelatedPerson » Principal physical location where this task is performed locationReference [0..1] « Location »A description, code, or reference indicating why this task needs to be performed reasonCodeableReference [0..*] « Any ; null (Strength=Example) TaskReasonInsurance plans, coverage extensions, pre-authorizations and/or pre-determinations that may be relevant to the Task insuranceReference [0..*] « Coverage |ClaimResponse »Free-text information about the task during its lifecycle noteAnnotation [0..*]Links to Provenance records for past versions of this Task that identify key state transitions or updates that are likely to be relevant to a user looking at the current version of the task relevantHistoryReference [0..*] « Provenance »Performer A code or description of the performer of the task functionCodeableConcept [0..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskPerformerFunctionCodeThe actor or entity who performed the task actorReference [1..1] « Practitioner |Device |Organization | PractitionerRole |Organization |CareTeam |Patient |RelatedPerson » Restriction Indicates the number of times the requested action should occur repetitionspositiveInt [0..1]The time-period for which fulfillment is sought. This must fall within the overall time period authorized in the referenced request. E.g. ServiceRequest.occurance[x] periodPeriod [0..1]For requests that are targeted to more than one potential recipient/target, to identify who is fulfillment is sought for recipientReference [0..*] « Patient |Practitioner |PractitionerRole | RelatedPerson |Group |Organization » Input A code or description to distinguish between inputs typeCodeableConcept [1..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskInputOutputParameterTypeThe value of the input parameter as a basic type value[x]* [1..1]Output A code or description to distinguish between outputs typeCodeableConcept [1..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskInputOutputParameterTypeThe value of the Output parameter as a basic type value[x]* [1..1]The entity who performed the requested task performer[0..*] If the Task.focus is a request resource and the task is seeking fulfillment (i.e. is asking for the request to be actioned), this element identifies any limitations on what parts of the referenced request should be actioned restriction[0..1] Additional information that may be needed in the execution of the task input[0..*] Outputs produced by the Task output[0..*]
JSON Template
{Task Resource : id , meta , implicitRules , and language
// from DomainResource : text , contained , extension , and modifierExtension
"identifier " : [{ Identifier // Task Instance Identifier instantiatesCanonical " : "<canonical ActivityDefinition )>", // Formal definition of task instantiatesUri " : "<uri // Formal definition of task basedOn " : [{ Reference (Any )// Request fulfilled by this task groupIdentifier " : { Identifier // Requisition or grouper id partOf " : [{ Reference (Task )// Composite task status code // R! draft | requested | received | accepted | + statusReason " : { CodeableReference // Reason for current status businessStatus " : { CodeableConcept // E.g. "Specimen collected", "IV prepped" intent " : "<code // R! unknown | proposal | plan | order | original-order | reflex-order | filler-order | instance-order | option priority " : "<code // routine | urgent | asap | stat doNotPerform boolean // True if Task is prohibiting action code " : { CodeableConcept // I Task Type description " : "<markdown // Human-readable explanation of task focus " : { Reference (Any )// I What task is acting on for " : { Reference (Any )// Beneficiary of the Task encounter " : { Reference (Encounter )// Healthcare event during which this task originated requestedPeriod " : { Period // When the task should be performed executionPeriod " : { Period // Start and end time of execution authoredOn " : "<dateTime // Task Creation Date lastModified " : "<dateTime // Task Last Modified Date requester " : { Reference (Device |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |
PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// Who is asking for task to be done requestedPerformer " : [{ CodeableReference (CareTeam |Device |
HealthcareService |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |PractitionerRole |
RelatedPerson )// Who should perform the Task owner " : { Reference (CareTeam |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |
PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// Responsible individual performer " : [{ // Who or what performed the task function " : { CodeableConcept // Type of performance actor " : { Reference (CareTeam |Device |Organization |Organization |Patient |
Practitioner |PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// R! Who performed the task location " : { Reference (Location )// Where task occurs reason " : [{ CodeableReference (Any )// Why task is needed insurance " : [{ Reference (ClaimResponse |Coverage )// Associated insurance coverage note " : [{ Annotation // Comments made about the task relevantHistory " : [{ Reference (Provenance )// Key events in history of the Task restriction " : { // I Constraints on fulfillment tasks repetitions " : "<positiveInt // How many times to repeat period " : { Period // When fulfillment is sought recipient " : [{ Reference (Group |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |
PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// For whom is fulfillment sought? input " : [{ // Information used to perform task type " : { CodeableConcept // R! Label for the input // value[x]: Content to use in performing the task . One of these 54:
"valueBase64Binary " : "<base64Binary valueBoolean " : <boolean valueCanonical " : "<canonical valueCode " : "<code valueDate " : "<date valueDateTime " : "<dateTime valueDecimal " : <decimal valueId " : "<id valueInstant " : "<instant valueInteger " : <integer valueInteger64 " : "<integer64 valueMarkdown " : "<markdown valueOid " : "<oid valuePositiveInt " : "<positiveInt valueString " : "<string valueTime " : "<time valueUnsignedInt " : "<unsignedInt valueUri " : "<uri valueUrl " : "<url valueUuid " : "<uuid valueAddress " : { Address valueAge " : { Age valueAnnotation " : { Annotation valueAttachment " : { Attachment valueCodeableConcept " : { CodeableConcept valueCodeableReference " : { CodeableReference valueCoding " : { Coding valueContactPoint " : { ContactPoint valueCount " : { Count valueDistance " : { Distance valueDuration " : { Duration valueHumanName " : { HumanName valueIdentifier " : { Identifier valueMoney " : { Money valuePeriod " : { Period valueQuantity " : { Quantity valueRange " : { Range valueRatio " : { Ratio valueRatioRange " : { RatioRange valueReference " : { Reference valueSampledData " : { SampledData valueSignature " : { Signature valueTiming " : { Timing valueContactDetail " : { ContactDetail valueDataRequirement " : { DataRequirement valueExpression " : { Expression valueParameterDefinition " : { ParameterDefinition valueRelatedArtifact " : { RelatedArtifact valueTriggerDefinition " : { TriggerDefinition valueUsageContext " : { UsageContext valueAvailability " : { Availability valueExtendedContactDetail " : { ExtendedContactDetail valueDosage " : { Dosage valueMeta " : { Meta output " : [{ // Information produced as part of task type " : { CodeableConcept // R! Label for output // value[x]: Result of output . One of these 54:
"valueBase64Binary " : "<base64Binary valueBoolean " : <boolean valueCanonical " : "<canonical valueCode " : "<code valueDate " : "<date valueDateTime " : "<dateTime valueDecimal " : <decimal valueId " : "<id valueInstant " : "<instant valueInteger " : <integer valueInteger64 " : "<integer64 valueMarkdown " : "<markdown valueOid " : "<oid valuePositiveInt " : "<positiveInt valueString " : "<string valueTime " : "<time valueUnsignedInt " : "<unsignedInt valueUri " : "<uri valueUrl " : "<url valueUuid " : "<uuid valueAddress " : { Address valueAge " : { Age valueAnnotation " : { Annotation valueAttachment " : { Attachment valueCodeableConcept " : { CodeableConcept valueCodeableReference " : { CodeableReference valueCoding " : { Coding valueContactPoint " : { ContactPoint valueCount " : { Count valueDistance " : { Distance valueDuration " : { Duration valueHumanName " : { HumanName valueIdentifier " : { Identifier valueMoney " : { Money valuePeriod " : { Period valueQuantity " : { Quantity valueRange " : { Range valueRatio " : { Ratio valueRatioRange " : { RatioRange valueReference " : { Reference valueSampledData " : { SampledData valueSignature " : { Signature valueTiming " : { Timing valueContactDetail " : { ContactDetail valueDataRequirement " : { DataRequirement valueExpression " : { Expression valueParameterDefinition " : { ParameterDefinition valueRelatedArtifact " : { RelatedArtifact valueTriggerDefinition " : { TriggerDefinition valueUsageContext " : { UsageContext valueAvailability " : { Availability valueExtendedContactDetail " : { ExtendedContactDetail valueDosage " : { Dosage valueMeta " : { Meta
Changes from both R4 and R4B
Task Task.statusReason
Type changed from CodeableConcept to CodeableReference Task.doNotPerform
Task.code
Add Binding `http://hl7.org/fhir/ValueSet/task-code` (extensible) Task.description
Type changed from string to markdown Task.requestedPeriod
Task.requestedPerformer
Task.owner
Type Reference: Removed Target Types HealthcareService, Device Task.performer
Task.performer.function
Task.performer.actor
Task.reason
Task.input.value[x]
Add Types integer64, CodeableReference, RatioRange, Availability, ExtendedContactDetail, Meta Remove Type Contributor Task.output.value[x]
Add Types integer64, CodeableReference, RatioRange, Availability, ExtendedContactDetail, Meta Remove Type Contributor Task.performerType
Deleted (->Task.requestedPerformer) Task.reasonCode
Task.reasonReference
See the Full Difference for further information
This analysis is available for R4 as XML or JSON
and for R4B as XML or JSON .
UML Diagram (Legend )
Task (DomainResource ) The business identifier for this task identifierIdentifier [0..*]The URL pointing to a *FHIR*-defined protocol, guideline, orderset or other definition that is adhered to in whole or in part by this Task instantiatesCanonicalcanonical [0..1] « ActivityDefinition »The URL pointing to an *externally* maintained protocol, guideline, orderset or other definition that is adhered to in whole or in part by this Task instantiatesUriuri [0..1]BasedOn refers to a higher-level authorization that triggered the creation of the task. It references a "request" resource such as a ServiceRequest, MedicationRequest, CarePlan, etc. which is distinct from the "request" resource the task is seeking to fulfill. This latter resource is referenced by focus. For example, based on a CarePlan (= basedOn), a task is created to fulfill a ServiceRequest ( = focus ) to collect a specimen from a patient basedOnReference [0..*] « Any »A shared identifier common to multiple independent Task and Request instances that were activated/authorized more or less simultaneously by a single author. The presence of the same identifier on each request ties those requests together and may have business ramifications in terms of reporting of results, billing, etc. E.g. a requisition number shared by a set of lab tests ordered together, or a prescription number shared by all meds ordered at one time groupIdentifierIdentifier [0..1]Task that this particular task is part of partOfReference [0..*] « Task »The current status of the task (this element modifies the meaning of other elements) statuscode [1..1] « null (Strength=Required) TaskStatusAn explanation as to why this task is held, failed, was refused, etc statusReasonCodeableReference [0..1] « ; null (Strength=Example) TaskStatusReasonContains business-specific nuances of the business state businessStatusCodeableConcept [0..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskBusinessStatusIndicates the "level" of actionability associated with the Task, i.e. this a proposed task, a planned task, an actionable task, etc intentcode [1..1] « null (Strength=Required) TaskIntentIndicates how quickly the Task should be addressed with respect to other requests prioritycode [0..1] « The task's priority. (Strength=Required) RequestPriorityIf true indicates that the Task is asking for the specified action to *not* occur (this element modifies the meaning of other elements) doNotPerformboolean [0..1]A name or code (or both) briefly describing what the task involves codeCodeableConcept [0..1] « null (Strength=Extensible) TaskCodeThis element has or is affected by some invariants CA free-text description of what is to be performed descriptionmarkdown [0..1]The request being fulfilled or the resource being manipulated (changed, suspended, etc.) by this task focusReference [0..1] « Any » « This element has or is affected by some invariants CThe entity who benefits from the performance of the service specified in the task (e.g., the patient) forReference [0..1] « Any »The healthcare event (e.g. a patient and healthcare provider interaction) during which this task was created encounterReference [0..1] « Encounter »Indicates the start and/or end of the period of time when completion of the task is desired to take place requestedPeriodPeriod [0..1]Identifies the time action was first taken against the task (start) and/or the time final action was taken against the task prior to marking it as completed (end) executionPeriodPeriod [0..1]The date and time this task was created authoredOndateTime [0..1]The date and time of last modification to this task lastModifieddateTime [0..1]The creator of the task requesterReference [0..1] « Device |Organization |Patient | Practitioner |PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson » The kind of participant or specific participant that should perform the task requestedPerformerCodeableReference [0..*] « Practitioner | PractitionerRole |Organization |CareTeam |HealthcareService | Patient |Device |RelatedPerson ; null (Strength=Preferred) ProcedurePerformerRoleCodes Party responsible for managing task execution ownerReference [0..1] « Practitioner |PractitionerRole | Organization |CareTeam |Patient |RelatedPerson » Principal physical location where this task is performed locationReference [0..1] « Location »A description, code, or reference indicating why this task needs to be performed reasonCodeableReference [0..*] « Any ; null (Strength=Example) TaskReasonInsurance plans, coverage extensions, pre-authorizations and/or pre-determinations that may be relevant to the Task insuranceReference [0..*] « Coverage |ClaimResponse »Free-text information about the task during its lifecycle noteAnnotation [0..*]Links to Provenance records for past versions of this Task that identify key state transitions or updates that are likely to be relevant to a user looking at the current version of the task relevantHistoryReference [0..*] « Provenance »Performer A code or description of the performer of the task functionCodeableConcept [0..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskPerformerFunctionCodeThe actor or entity who performed the task actorReference [1..1] « Practitioner |Device |Organization | PractitionerRole |Organization |CareTeam |Patient |RelatedPerson » Restriction Indicates the number of times the requested action should occur repetitionspositiveInt [0..1]The time-period for which fulfillment is sought. This must fall within the overall time period authorized in the referenced request. E.g. ServiceRequest.occurance[x] periodPeriod [0..1]For requests that are targeted to more than one potential recipient/target, to identify who is fulfillment is sought for recipientReference [0..*] « Patient |Practitioner |PractitionerRole | RelatedPerson |Group |Organization » Input A code or description to distinguish between inputs typeCodeableConcept [1..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskInputOutputParameterTypeThe value of the input parameter as a basic type value[x]* [1..1]Output A code or description to distinguish between outputs typeCodeableConcept [1..1] « null (Strength=Example) TaskInputOutputParameterTypeThe value of the Output parameter as a basic type value[x]* [1..1]The entity who performed the requested task performer[0..*] If the Task.focus is a request resource and the task is seeking fulfillment (i.e. is asking for the request to be actioned), this element identifies any limitations on what parts of the referenced request should be actioned restriction[0..1] Additional information that may be needed in the execution of the task input[0..*] Outputs produced by the Task output[0..*]
JSON Template
{Task Resource : id , meta , implicitRules , and language
// from DomainResource : text , contained , extension , and modifierExtension
"identifier " : [{ Identifier // Task Instance Identifier instantiatesCanonical " : "<canonical ActivityDefinition )>", // Formal definition of task instantiatesUri " : "<uri // Formal definition of task basedOn " : [{ Reference (Any )// Request fulfilled by this task groupIdentifier " : { Identifier // Requisition or grouper id partOf " : [{ Reference (Task )// Composite task status code // R! draft | requested | received | accepted | + statusReason " : { CodeableReference // Reason for current status businessStatus " : { CodeableConcept // E.g. "Specimen collected", "IV prepped" intent " : "<code // R! unknown | proposal | plan | order | original-order | reflex-order | filler-order | instance-order | option priority " : "<code // routine | urgent | asap | stat doNotPerform boolean // True if Task is prohibiting action code " : { CodeableConcept // I Task Type description " : "<markdown // Human-readable explanation of task focus " : { Reference (Any )// I What task is acting on for " : { Reference (Any )// Beneficiary of the Task encounter " : { Reference (Encounter )// Healthcare event during which this task originated requestedPeriod " : { Period // When the task should be performed executionPeriod " : { Period // Start and end time of execution authoredOn " : "<dateTime // Task Creation Date lastModified " : "<dateTime // Task Last Modified Date requester " : { Reference (Device |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |
PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// Who is asking for task to be done requestedPerformer " : [{ CodeableReference (CareTeam |Device |
HealthcareService |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |PractitionerRole |
RelatedPerson )// Who should perform the Task owner " : { Reference (CareTeam |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |
PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// Responsible individual performer " : [{ // Who or what performed the task function " : { CodeableConcept // Type of performance actor " : { Reference (CareTeam |Device |Organization |Organization |Patient |
Practitioner |PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// R! Who performed the task location " : { Reference (Location )// Where task occurs reason " : [{ CodeableReference (Any )// Why task is needed insurance " : [{ Reference (ClaimResponse |Coverage )// Associated insurance coverage note " : [{ Annotation // Comments made about the task relevantHistory " : [{ Reference (Provenance )// Key events in history of the Task restriction " : { // I Constraints on fulfillment tasks repetitions " : "<positiveInt // How many times to repeat period " : { Period // When fulfillment is sought recipient " : [{ Reference (Group |Organization |Patient |Practitioner |
PractitionerRole |RelatedPerson )// For whom is fulfillment sought? input " : [{ // Information used to perform task type " : { CodeableConcept // R! Label for the input // value[x]: Content to use in performing the task . One of these 54:
"valueBase64Binary " : "<base64Binary valueBoolean " : <boolean valueCanonical " : "<canonical valueCode " : "<code valueDate " : "<date valueDateTime " : "<dateTime valueDecimal " : <decimal valueId " : "<id valueInstant " : "<instant valueInteger " : <integer valueInteger64 " : "<integer64 valueMarkdown " : "<markdown valueOid " : "<oid valuePositiveInt " : "<positiveInt valueString " : "<string valueTime " : "<time valueUnsignedInt " : "<unsignedInt valueUri " : "<uri valueUrl " : "<url valueUuid " : "<uuid valueAddress " : { Address valueAge " : { Age valueAnnotation " : { Annotation valueAttachment " : { Attachment valueCodeableConcept " : { CodeableConcept valueCodeableReference " : { CodeableReference valueCoding " : { Coding valueContactPoint " : { ContactPoint valueCount " : { Count valueDistance " : { Distance valueDuration " : { Duration valueHumanName " : { HumanName valueIdentifier " : { Identifier valueMoney " : { Money valuePeriod " : { Period valueQuantity " : { Quantity valueRange " : { Range valueRatio " : { Ratio valueRatioRange " : { RatioRange valueReference " : { Reference valueSampledData " : { SampledData valueSignature " : { Signature valueTiming " : { Timing valueContactDetail " : { ContactDetail valueDataRequirement " : { DataRequirement valueExpression " : { Expression valueParameterDefinition " : { ParameterDefinition valueRelatedArtifact " : { RelatedArtifact valueTriggerDefinition " : { TriggerDefinition valueUsageContext " : { UsageContext valueAvailability " : { Availability valueExtendedContactDetail " : { ExtendedContactDetail valueDosage " : { Dosage valueMeta " : { Meta output " : [{ // Information produced as part of task type " : { CodeableConcept // R! Label for output // value[x]: Result of output . One of these 54:
"valueBase64Binary " : "<base64Binary valueBoolean " : <boolean valueCanonical " : "<canonical valueCode " : "<code valueDate " : "<date valueDateTime " : "<dateTime valueDecimal " : <decimal valueId " : "<id valueInstant " : "<instant valueInteger " : <integer valueInteger64 " : "<integer64 valueMarkdown " : "<markdown valueOid " : "<oid valuePositiveInt " : "<positiveInt valueString " : "<string valueTime " : "<time valueUnsignedInt " : "<unsignedInt valueUri " : "<uri valueUrl " : "<url valueUuid " : "<uuid valueAddress " : { Address valueAge " : { Age valueAnnotation " : { Annotation valueAttachment " : { Attachment valueCodeableConcept " : { CodeableConcept valueCodeableReference " : { CodeableReference valueCoding " : { Coding valueContactPoint " : { ContactPoint valueCount " : { Count valueDistance " : { Distance valueDuration " : { Duration valueHumanName " : { HumanName valueIdentifier " : { Identifier valueMoney " : { Money valuePeriod " : { Period valueQuantity " : { Quantity valueRange " : { Range valueRatio " : { Ratio valueRatioRange " : { RatioRange valueReference " : { Reference valueSampledData " : { SampledData valueSignature " : { Signature valueTiming " : { Timing valueContactDetail " : { ContactDetail valueDataRequirement " : { DataRequirement valueExpression " : { Expression valueParameterDefinition " : { ParameterDefinition valueRelatedArtifact " : { RelatedArtifact valueTriggerDefinition " : { TriggerDefinition valueUsageContext " : { UsageContext valueAvailability " : { Availability valueExtendedContactDetail " : { ExtendedContactDetail valueDosage " : { Dosage valueMeta " : { Meta
Changes from both R4 and R4B
Task Task.statusReason
Type changed from CodeableConcept to CodeableReference Task.doNotPerform
Task.code
Add Binding `http://hl7.org/fhir/ValueSet/task-code` (extensible) Task.description
Type changed from string to markdown Task.requestedPeriod
Task.requestedPerformer
Task.owner
Type Reference: Removed Target Types HealthcareService, Device Task.performer
Task.performer.function
Task.performer.actor
Task.reason
Task.input.value[x]
Add Types integer64, CodeableReference, RatioRange, Availability, ExtendedContactDetail, Meta Remove Type Contributor Task.output.value[x]
Add Types integer64, CodeableReference, RatioRange, Availability, ExtendedContactDetail, Meta Remove Type Contributor Task.performerType
Deleted (->Task.requestedPerformer) Task.reasonCode
Task.reasonReference
See the Full Difference for further information
This analysis is available for R4 as XML or JSON
and for R4B as XML or JSON .
Additional definitions: Master Definition XML + JSON ,
XML Schema /Schematron + JSON
Schema , ShEx (for Turtle ) + see the extensions , the spreadsheet version & the dependency analysis
12.1.5.1
Terminology Bindings
12.1.5.2 Constraints UniqueKey Level Location Description Expression Rule (base) Last modified date must be greater than or equal to authored-on date. lastModified.exists().not() or authoredOn.exists().not() or lastModified >= authoredOn Rule (base) Task.restriction is only allowed if the Task is seeking fulfillment and a focus is specified. restriction.exists() implies code.coding.where(code='fulfill' and system='http://hl7.org/fhir/CodeSystem/task-code').exists() and focus.exists()
12.1.6 Tasks vs. other Requests
While Task can be used to seek fulfillment of other authorizations such as ServiceRequests ,
MedicationRequests , etc., Task can also be used on its own to solicit action without any
prior authorization. However, such requests for action should be tightly time-bound and be satisfied with a single 'event'.
I.e. they should ask as a task-list checkbox that can easily be marked as complete. Any action that requires ongoing repeated
performance should be captured using a different type of resource, not Task.
12.1.7 Task Titles
Tasks often have titles (eg "My Tasks", "Outstanding Tasks for Patient X") which can be presented in a list. The task title should go into the Task.code as a coded concept and/or text.
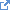
12.1.8 Task state machine Tasks start in a Draft state. Once they have been assigned to an owner they transition to
the Ready state, indicating that they are ready to be performed. Once the owner initiates
activity on the task, the task transitions to the In Progress state, indicating that work is
being performed. Upon normal completion, the task enters the Completed state. If there is a
failure during the task execution that prevents the task from being completed, it can also
enter a Failed state, indicating an abnormal termination of the task. A task in any
non-terminal state may also be Cancelled, representing an abnormal termination of the task due
to external forces, rather than an error condition.
Tasks in any non-terminal state (Draft, Ready, In Progress) can be suspended and resumed.
When a task is suspended, it is typically resumed in the state it was in when it was
originally suspended. Suspending a task suspends all of its children as well. Resuming a task
resumes all of its children.
An In-progress task can also be stopped, returning it to a Ready state. This may be in
preparation for delegation or reassignment (e.g., because it cannot be completed by the
current owner), to restart a task due to a temporary failure (e.g., to reattempt completion of
the activity), or in preparation to allow others to claim the task.
The task history allows applications monitoring the state of a workflow to identify tasks
that are long running, perhaps stuck in some queue, to enable management activities that could
ensure completion. It also enables tracking of task statistics such as wait time, or time in
progress, or time to completion, enabling capture of important task metrics in support of
optimization and quality improvement.
The following diagram reflects the "typical" state machine for Task. Note that not all states will be supported by all workflows
and that some workflows may support additional transitions, including transitions from terminal states (e.g. back to "in-progress"
from "failed" or "completed").
Note to Implementers:
Currently, task pre-requisites can be represented using Task's `description` element or the RequestOrchestration resource. We are seeking input from the implementer community in evaluating whether there is need for adding another mechanism to this resource for this purpose.
Feedback here .
12.1.9 The Cancelled state
While the intention of a "cancelled" task is that all work authorized by the task should cease, this
might not always be possible practice. It is possible that the originally requested action could still
be completed and still attached to the Task but this would not change the status of the task. If the
placer cancels a task, it signals they no longer care about the outcome of the task.
12.1.10 Search Parameters
Search parameters for this resource. See also the full list of search parameters for this resource ,
and check the Extensions registry for search parameters on extensions related to this resource.
The common parameters also apply. See Searching for more
information about searching in REST, messaging, and services.
Name Type Description Expression In Common actor reference Search by specific performer.
Task.performer.actorPractitioner , Organization , CareTeam , Device , Patient , PractitionerRole , RelatedPerson )
authored-on date Search by creation date
Task.authoredOn
based-on reference Search by requests this task is based on
Task.basedOn
business-status token Search by business status
Task.businessStatus
code token Search by task code
Task.code
21 Resources encounter reference Search by encounter
Task.encounterEncounter )
29 Resources focus reference Search by task focus
Task.focus
group-identifier token Search by group identifier
Task.groupIdentifier
identifier token Search for a task instance by its business identifier
Task.identifier
65 Resources input reference Search by task input
Task.input.value.ofType(Reference)
intent token Search by task intent
Task.intent
modified date Search by last modification date
Task.lastModified
output reference Search by task output
Task.output.value.ofType(Reference)
owner reference Search by task owner
Task.ownerPractitioner , Organization , CareTeam , Patient , PractitionerRole , RelatedPerson )
part-of reference Search by task this task is part of
Task.partOfTask )
patient reference Search by patient
Task.for.where(resolve() is Patient)Patient )
65 Resources performer token Search by recommended type of performer (e.g., Requester, Performer, Scheduler).
Task.requestedPerformer.concept
period date Search by period Task is/was underway
Task.executionPeriod
priority token Search by task priority
Task.priority
requestedperformer-reference reference Search by specific requested performer.
Task.requestedPerformer.reference
requester reference Search by task requester
Task.requesterPractitioner , Organization , Device , Patient , PractitionerRole , RelatedPerson )
status token Search by task status
Task.status
subject reference Search by subject
Task.for
 Work Group
Work Group ),
), ).
)..
 tsk-0
tsk-0 tsk-1
tsk-1.