Canonical Resource Management Infrastructure Implementation Guide, published by HL7 International / Clinical Decision Support. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2.0.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/crmi-ig/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
| Official URL: http://hl7.org/fhir/uv/crmi/ImplementationGuide/hl7.fhir.uv.crmi | Version: 2.0.0-ballot | |||
| IG Standards status: Trial-use | Maturity Level: 4 | Computable Name: CRMI | ||
| Other Identifiers: OID:2.16.840.1.113883.4.642.40.38 | ||||
The Canonical Resource Management Infrastructure implementation guide defines profiles, operations, capability statements and guidance to facilitate the content management lifecycle for authoring, publishing, distribution, and implementation of FHIR knowledge artifacts such as value sets, profiles, libraries, rules, and measures. The guide is intended to be used by specification and content implementation guide authors as both a dependency for validation of published artifacts, and a guide for construction and publication of content.
This implementation guide is based upon work in multiple quality improvement and reporting domains. Various implementation guides have developed similar infrastructure-level profiles for conformance and knowledge artifacts. These profiles are being refactored into universal-realm, domain-independent profiles that can then be re-used in future versions of those specifications, as well as included in future versions of the base FHIR specification.
This implementation guide is focused on facilitating consistent exchange of knowledge artifacts throughout the artifact management lifecycle, from authoring, through publishing and distribution, to implementation. At the highest level, this is done through the definition of capability categories that roughly correspond to these lifecycle phases:
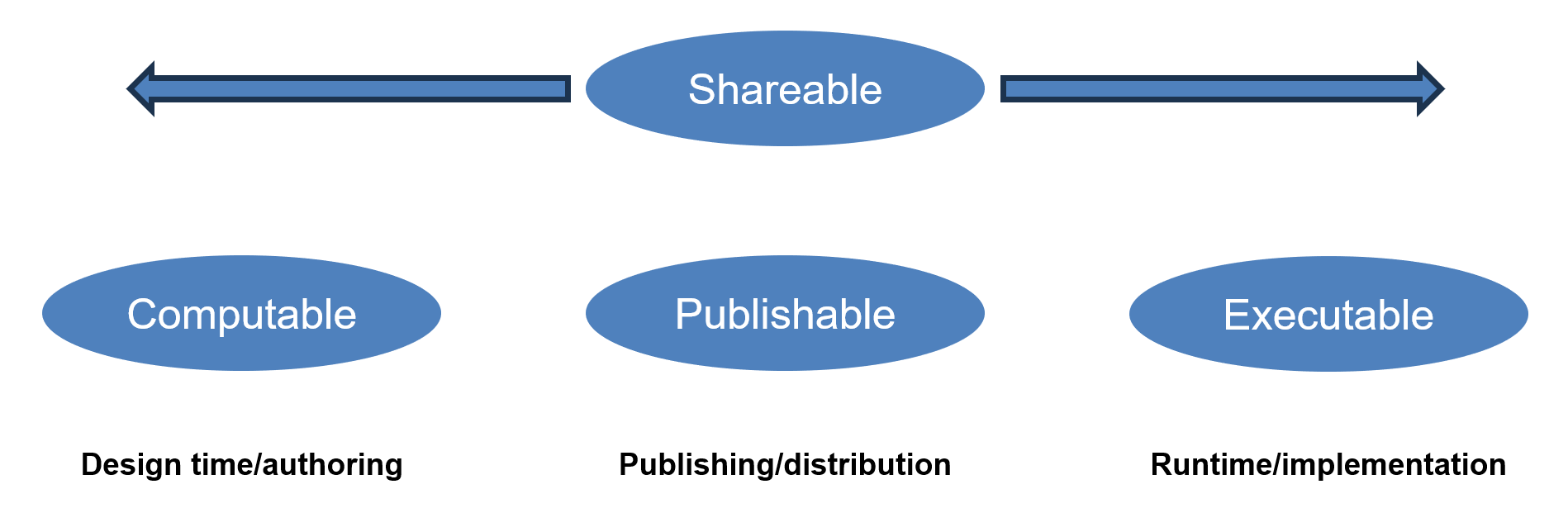
These categories are proposed as a way to help facilitate management of expectations in the artifact development lifecycle, as well as address common challenges that have been encountered in the development of knowledge artifacts across the quality improvement spectrum, including guideline development, public health reporting specifications, clinical decision support rules, and quality measures. The expectation is that these same challenges will arise in any knowledge artifact development effort, and that the profiles and solutions proposed here will be useful in addressing those challenges.
The implementation guide defines:
In particular, this implementation guide enables a consistent approach to developing knowledge artifacts as FHIR resources so that they can be seamlessly integrated with the existing FHIR publishing ecosystem, and can be easily deployed and implemented as part of existing FHIR infrastructures. At the same time, the additional capabilities for packaging and distribution enable use cases that cannot be easily achieved with current FHIR packages, such as:
An artifact in this implementation guide is a FHIR resource whose primary focus is the representation of context-independent knowledge such as a profile, a value set, a decision support rule, or a quality measure specification, as opposed to FHIR resources such as Patient, Organization, or Observation, that are typically focused on the representation of instance data for patients and other healthcare related entities. Most of the resource types for representing artifacts in FHIR are also canonical resources, and often metadata resources. However, some FHIR resources are not defined by FHIR as canonical resources, but may still be used to represent context-independent knowledge (e.g. Medication, or Substance). The use of the term artifact in this IG applies to both canonical resources as defined by the base specification, as well as these non-canonical artifact resources.
The following table lists the resource types that are considered artifacts, along with a categorization of those artifacts.
| Artifact Category | Description | Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Knowledge Artifacts | Representing decision support rules, quality measures, logic libraries, and activity definitions | ActivityDefinition Library Measure PlanDefinition Questionnaire |
| Terminology Artifacts | Code systems, value sets, naming systems, and concept maps | ValueSet CodeSystem ConceptMap NamingSystem |
| Conformance Artifacts | Profiles, extensions, structure maps, and artifacts related to defining and testing conformance | GraphDefinition ImplementationGuide StructureDefinition StructureMap |
| Domain Artifacts | Medications, substances, groups, and other domain-related artifacts | CareTeam (profiled) Group (non-canonical artifact) Location (profiled) Medication (non-canonical artifact) MedicationKnowledge (non-canonical artifact) Practitioner (profiled) PractitionerRole (profiled) Organization (profiled) Substance (non-canonical artifact) |
| Evidence-based Medicine (EBM) Artifacts (Roadmap) | Artifacts related to supporting evidence-based medicine | Evidence EvidenceVariable |
(profiled) For entity-related Domain Artifacts (i.e. Organization, Location, Practitioner, Patient, and CareTeam), this implementation guide uses profiling to address references to these types of resources in the artifact space (i.e. when a PlanDefinition references a particular type of CareTeam for example, the canonical reference is to a profile of the CareTeam resource.
The audience for this IG includes modelers (authors of FHIR profiles); terminologists; knowledge developers (authors of measures, guidelines, order catalogs, clinical logic/rules, assessments); and healthcare system and software developers using FHIR-based knowledge artifacts.
This Guide is divided into several pages which are listed at the top of each page in the menu bar:
This Implementation Guide was made possible by the thoughtful contributions of the following people and organizations:
Health level seven. Clinical Quality Framework - HL7 Clinical Decision Support Work Group Confluence Page. [Online]. Available from: https://confluence.hl7.org/display/CQIWC/Clinical Quality Framework [Accessed 11 October 2019].
Health level seven. Publishing terminology to the FHIR Ecosystem - FHIR Product Family Confluence Page. [Online]. Available from: https://confluence.hl7.org/display/FHIR/Publishing+terminology+to+the+FHIR+Ecosystem [Accessed 17 May 2022]
Health Level Seven. FHIR Clinical Guidelines. [Online]. Available from: http://hl7.org/fhir/uv/cpg [Accessed October 2023].
Health Level Sevent. Electronic Case Reporting. [Online]. Available from: http://hl7.org/fhir/us/ecr [Accessed October 2023].
Health Level Seven. Quality Measure Implementation Guide. [Online]. Available from: http://hl7.org/fhir/us/cqfmeasures [Accessed October 2023].
Health Level Seven. FHIR Quality Profile. [Online]. Available from: http://hl7.org/fhir/us/qicore [Accessed March 2024].
Health Level Seven. US Core. [Online]. Available from: http://hl7.org/fhir/us/core [Accessed March 2024].
| IG | Package | FHIR |
|---|---|---|
| hl7.fhir.uv.crmi#2.0.0-ballot | R4 | |
| hl7.terminology.r4#6.5.0 | R4 | |
| hl7.fhir.uv.extensions.r4#5.2.0 | R4 | |
| hl7.fhir.uv.tools.r4#0.9.0 | R4 |
This is an R4 IG. None of the features it uses are changed in R4B, so it can be used as is with R4B systems. Packages for both R4 (hl7.fhir.uv.crmi.r4) and R4B (hl7.fhir.uv.crmi.r4b) are available.
There are no Global profiles defined
This publication includes IP covered under the following statements.