Netherlands - Generic Functions for data exchange Implementation Guide, published by Stichting Nuts. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 0.3.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/nuts-foundation/nl-generic-functions-ig/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
Localization
| Page standards status: Draft |
Introduction
This FHIR Implementation Guide specifies the Generic Function 'Medical Record Localization' (GF Localization), a national initiative led by the Dutch Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sport (VWS). GF-Localization provides a standardized framework that enables healthcare professionals to discover which organizations hold relevant patient data of a specific type, ensuring GDPR compliance through proportionality and subsidiarity principles while facilitating secure and efficient health information exchange.
Patient data is divided over multiple data holders. In today’s healthcare landscape organizations rely on several different types of indices to find data concerning a specific patient and context. However, none of these indices are complete and all of these indices have different requirements for usage, hindering interoperability and timely access to health information. GF-Localization addresses this challenge by providing a unified framework that ensures an index of all data holders concerning a specific patient and type is easily and securely accessible.
This guide outlines the technical requirements and architectural principles underlying GF-Localization, with a focus on trust, authenticity, and data integrity. Key design principles include:
- International standards: The solution should be based on international standards, lowering the bar for international (European) data exchange and adoption by internationally operating software vendors.
- Single Source of Truth: Each localization record originates from exactly one organization: the data holder itself.
- Stakeholder Responsibility: Data holders are accountable for maintaining the accuracy of localization records at the Localization service.
By adhering to these principles, this Implementation Guide supports consistent and secure data holder discovery, fostering improved interoperability within the healthcare ecosystem.
Solution overview
GF-Localization follows the choices made by the MinvWS Localization working group, see GF-Lokalisatie, ADR's. This guide specifies the choices made. Most impactful/striking choice are:
- using one national Medical Record Localization Service: the 'Nationale Verwijs Index' (NVI)
- using a local metadata registry (LMR) per data holder
- reusing the FHIR-interface of the data holder to act as LMR
- using one national service for pseudonymizing and depseudonymizing citizen service numbers (BSN's): the Pseudonymization Service
Here is a brief overview of the processes that are involved:
- Every data holder registers the presence of data concerning a specific patient and data category at the Localization service. This localization record references a document (e.g. Patient, Medication or Imaging-resource) to represent the data category.
- A data user (practitioner and/or system (EHR)) can now use the Localization service to discover data holders for a specific patient and data category.
- The Localization service checks access of the data requester to the referenced document before it exposes the localization record to the data user.
These processes require the use of pseudonyms that are generated and resolved using a national Pseudonymization Service. The Localization service-response provides a list of data holders; the endpoints of these data holders (e.g. FHIR or DICOM-urls) need to be resolved using a Care service (Query) Directory. This process is illustrated in this example.
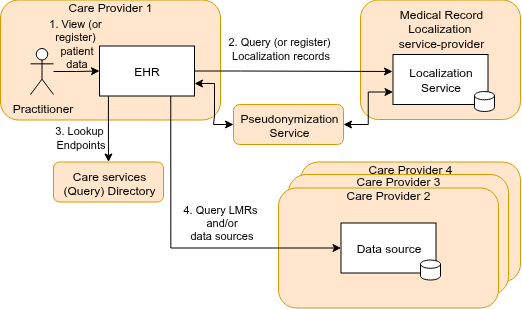
For more detail on the topology of GF-Localization, see GF-Lokalisatie, ADR-2. Each component, data model, and transaction will be discussed in more detail.
Components (actors)
Localization Service
A (Medical Record) Localization Service is responsible for managing the registration, maintenance, and publication of localization records. It should be able to create and update localization records. A Localization Service MUST implement these FHIR capabilities and basically involves creating and searching for FHIR DocumentReferences (see Localization record)
Local Metadata Register
A Local Metadata Register (LMR) is responsible for managing the registration, maintenance, and publication of the metadata of one data holder (the custodian or the healthcare organization). To implement an LMR, existing FHIR-APIs of data sources can be used. Minimum requirements for a LMR are specified in this FHIR capabilitystatement. HTTP-method HEAD SHALL be supported to allow the Localization service to check the access (consent) to the localization-record for the data user at the data holder.
Pseudonymization Service
The Pseudonymization Service is responsible for creating and retrieving Polymorphic Pseudonyms of Patient identifiers. It involves multiple interactions for both a FHIR request and a FHIR response:
- the sender (of the request or response) posts their identifier/pseudonym AND the target organization to the Pseudonymization Service, which returns an opaque value.
- the receiver (of the request or response) exchanges the opaque value for a pseudonym at the Pseudonymization Service. This version of the IG will not go into the details of this Pseudonymization Service and the effect on FHIR transactions. For information on this topic, see the Logius BSNk-pp service.
Data models
Localization record
Within GF-Localization the NL-gf-localization-DocumentReference profile is used to register, search, and validate localization records (NL-GF-IG, ADR#10). This data model basically states "Care provider X has data of type Y for Patient Z". It contains the following elements:
- Organization identifier: The care provider identifier (URA) representing the data holder/custodian.
- Patient identifier: The pseudonymized BSN to identify the patient.
- Type: Represents type of data stored at the data holder/custodian. No ValueSet has been decided upon yet GF-Lokalisatie, ADR#62, so in this IG-version, a fixed LOINC code '55188-7' is used: "Patient data Document"
- Url: A link/url to a document (e.g. FHIR resource) that represents the data type of this localization record. This url used by the Localization service to check authorization (consent) at the data holder for the data user/requester.
A Location record example is in the IG artifacts.
Security and Privacy Considerations
One of things you can do to mitigate privacy risks: Please don't put dates or other privacy-sensitive data into the localization records since it can expose the identity patient
Pseudonymization
Patient identifier BSN (BurgerServiceNummer) is pseudonymized to enhance patient privacy. The pseudonymization service will ensure that patient identities are protected while still allowing organizations to use a joint index.(GF-Lokalisatie, ADR-1)
Authentication and Authorization
Authentication and authorization follows the GF Authorization specification. The required authentication and authorization attributes for Localization Service are:
For POST operations (registering localization records):
- Organization identifier (URA): The organization identifier of the registering organization
For GET operations (querying localization records):
- Organization identifier (URA): The organization identifier of the requesting organization (URA)
- Organization type: The type of healthcare organization making the query
- Practitioner identifier (UZI/DEZI): The unique healthcare professional identifier of the requester
- Role code: The professional role code of the requester
- Patient identifier (pseudoBSN): The Patient identifier, used to check/fetch a Consent
For HEAD operations (checking access for data requester at data holder by localization service):
- Url: Url in the localization record (DocumentReference). Based on the HTTP-status in the response, the relationship between data holder and patient may be exposed to the data requester.
The 'HEAD operation and use of existing (FHIR) APIs' is evaluated in the Proof of concept phase. Other solutions are discussed on this page
These attributes ensure proper access control and auditing while maintaining the security requirements outlined in the GF Authorization specification.
Example Use Cases
Use case: Radiologist registering Imaging Data
Scenario: Dr. Carter, a radiologist at a care provider organization, performs an imaging study for a patient. To enable data discovery by other healthcare professionals, Dr. Carter's organization must register the existence of this imaging data in the national localization index (NVI). This process involves pseudonymizing the patient's identifier, creating a localization record, and submitting it to the NVI with the appropriate authorization attributes.
The following diagram illustrates the registration workflow, including interactions between the radiologist, the PACS system and the NVI. For brevity, interactions to the Pseudonymization Service are left out here.
Use Case: Cardiologist searching for Imaging Data
Scenario: Dr. Smith, a cardiologist at Hospital A, is treating a patient who was recently referred from another hospital. She needs to know what imaging data (X-rays, CT scans, MRIs) might be available from other healthcare providers to avoid unnecessary duplicate examinations and to get a complete picture of the patient's medical history.
For brevity, interactions to the Pseudonymization Service are left out here.
Roadmap for GF Localization
Localization Service
Potential future enhancements to the Localization Service include:
- Audit logging capabilities (MUST HAVE, TODO)
- ValueSet constraint on DocumentReference.type and/or DocumentReference.category
Pseudonymization Service
- Specification of Pseudonymization Service API
- Specification of how to include/combine Pseudonymization transactions in FHIR request/responses