WADA List, published by adamzk. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 0.1.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/adamzkover/wada-list-fhir/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
Implementation
The implementation is limited to a subset of the List, and medicinal products on the Norwegian market. Substances that are not active ingredients in any approved medicinal product in Norway are out of scope. Statements like "og andre stoffer med lignende kjemisk struktur eller lignende biologisk(e) effekt(er)" are only evaluated in the scope of medicinal products approved in Norway.
Groups in scope for the implementation:
- S1. Anabole stoffer
- S2. Peptidhormoner, vekstfaktorer, relaterte stoffer og mimetika
- S3. Beta-2-agonister
The implementation uses medicinal product core data and substance codes from the Norwegian Electronic Prescription Support System (FEST) from the Norwegian Medical Products Agency (NOMA). For a discussion of the role of terminology and using different code systems, see the terminology page.
Architecture
The figure below illustrates the components of the implementation guide, and its role in a larger decision support system. The organizational roles represented in the figure build on a model of cooperative authoring, between Anti-Doping Norway (ADNO), the Norwegian WADA affiliate, and Felleskatalogen (FK), the Norwegian Pharmaceutical Product Compendium.
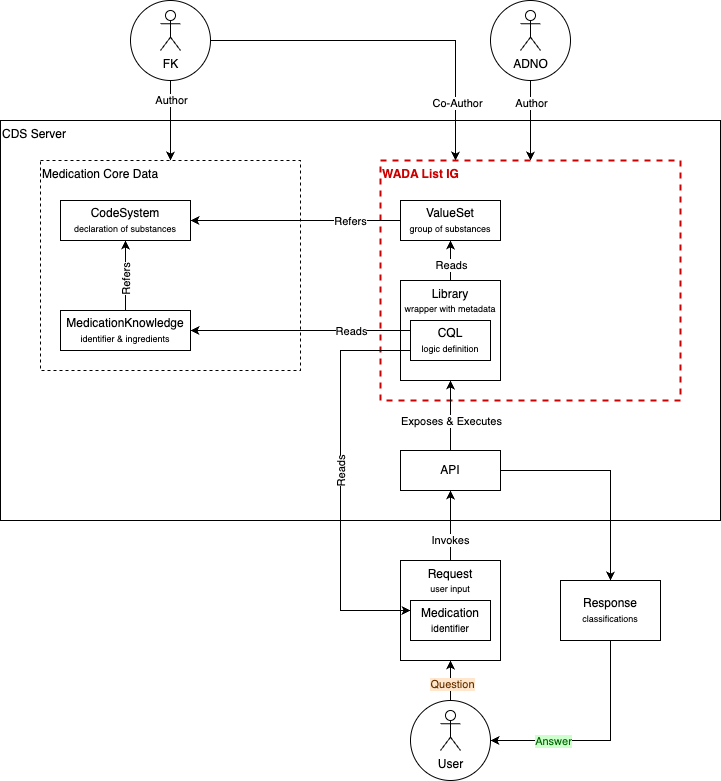
Components
The knowledge base of the implementation guide consists of Library and ValueSet resources.
- Library: contains the clinical logic of the guidelines (CQL), processes the user input and reads ValueSets and external MedicationKnowledge resources
- ValueSet: defines a selection of substances to wich particular guidelines apply
The ValueSets and the guideline logic Libraries make use of resources not contained in the implementation guide:
- MedicationKnowledge: representation of a medicinal product, registers the product identifiers and the coded ingredients
- CodeSystem: declares the existence of substances and assigns identifiers to them; ValueSets select codes from a CodeSystem
See the profiles and examples in the Artifacts Summary for more details on these resources.
API
The resources of the implementation guide and supporting core data can be uploaded to a compatible FHIR server (e.g., a CQF Ruler successor, HAPI FHIR) to provide a clinical decision support API.
Example configuration for running a HAPI FHIR server is in the hapi directory of the implementation guide's repository on GitHub. Scripts for uploading resources from the implementation guide and querying the service are provided in the same directory.
Sample knowledge base resources are available as part of the test cases in the input/tests directory.
Client systems interact with the guidelines through the Library/$evaluate operation. See the example resources for examples of input and output parameters.
Input
The operation input is a Parameters resource with the Bundle of Medication resources in the data parameter:
<Parameters xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir">
<parameter>
<name value="data" />
<resource>
<Bundle>
<type value="collection" />
<entry>
<fullUrl value="urn:uuid:2dcb5f4b-7f62-46d6-84ca-5e6c78d2e599" />
<resource>
<Medication>
<id value="2dcb5f4b-7f62-46d6-84ca-5e6c78d2e599" />
<code>
<coding>
<system value="http://legemiddelverket.no/FEST/LegemiddelMerkevareID" />
<code value="ID_1127913B-48A9-4E32-994D-173BC4DF752C" />
<display value="Retacrit inj, oppl 30 000 IE/sprøyte" />
</coding>
<text value="Retacrit inj, oppl 30 000 IE/sprøyte" />
</code>
</Medication>
</resource>
</entry>
</Bundle>
</resource>
</parameter>
</Parameters>
The Medication resources sent by the user contain the medication identifiers only. Ingredients are extracted by the clinical logic from the MedicationKnowledge resources that are matched by the input identifiers.
Extension: Allow the input to contain MedicationAdministration (MA), MedicationRequest (MR), and MedicationStatement (MS) resources. These resources can refer to a Medication, and in addition contain information about dose form, route of administration, dose, and a timestamp.
Output
The operation returns a Parameters resource with the medications from the input and any issues implicated by the WADA guidelines. As both parameters are lists of resources, parameters with the names medications and issues can repeat.
<Parameters xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir">
<parameter>
<name value="issues"/>
<resource>
<DetectedIssue xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir">
<status value="final"/>
<implicated>
<reference value="Medication/2dcb5f4b-7f62-46d6-84ca-5e6c78d2e599"/>
</implicated>
<detail value="Retacrit inj, oppl 30 000 IE/sprøyte: Epoetin zeta: forbudt iht. WADAs dopingliste (S2)"/>
<reference value="https://www.antidoping.no/medisinsk/dopinglisten/dopinggruppe-s2"/>
</DetectedIssue>
</resource>
</parameter>
<parameter>
<name value="medications"/>
<resource>
<Medication xmlns="http://hl7.org/fhir">
<id value="2dcb5f4b-7f62-46d6-84ca-5e6c78d2e599"/>
<code>
<coding>
<system value="http://legemiddelverket.no/FEST/LegemiddelMerkevareID"/>
<code value="ID_1127913B-48A9-4E32-994D-173BC4DF752C"/>
<display value="Retacrit inj, oppl 30 000 IE/sprøyte"/>
</coding>
<text value="Retacrit inj, oppl 30 000 IE/sprøyte"/>
</code>
</Medication>
</resource>
</parameter>
</Parameters>