OHSU Hypertension Implementation Guide
0.1.0 - CI Build
Unknown region code '840'
OHSU Hypertension Implementation Guide
0.1.0 - CI Build
Unknown region code '840'
OHSU Hypertension Implementation Guide, published by Oregon Health and Science University. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 0.1.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/OHSUCMP/htnu18ig/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
Contents:
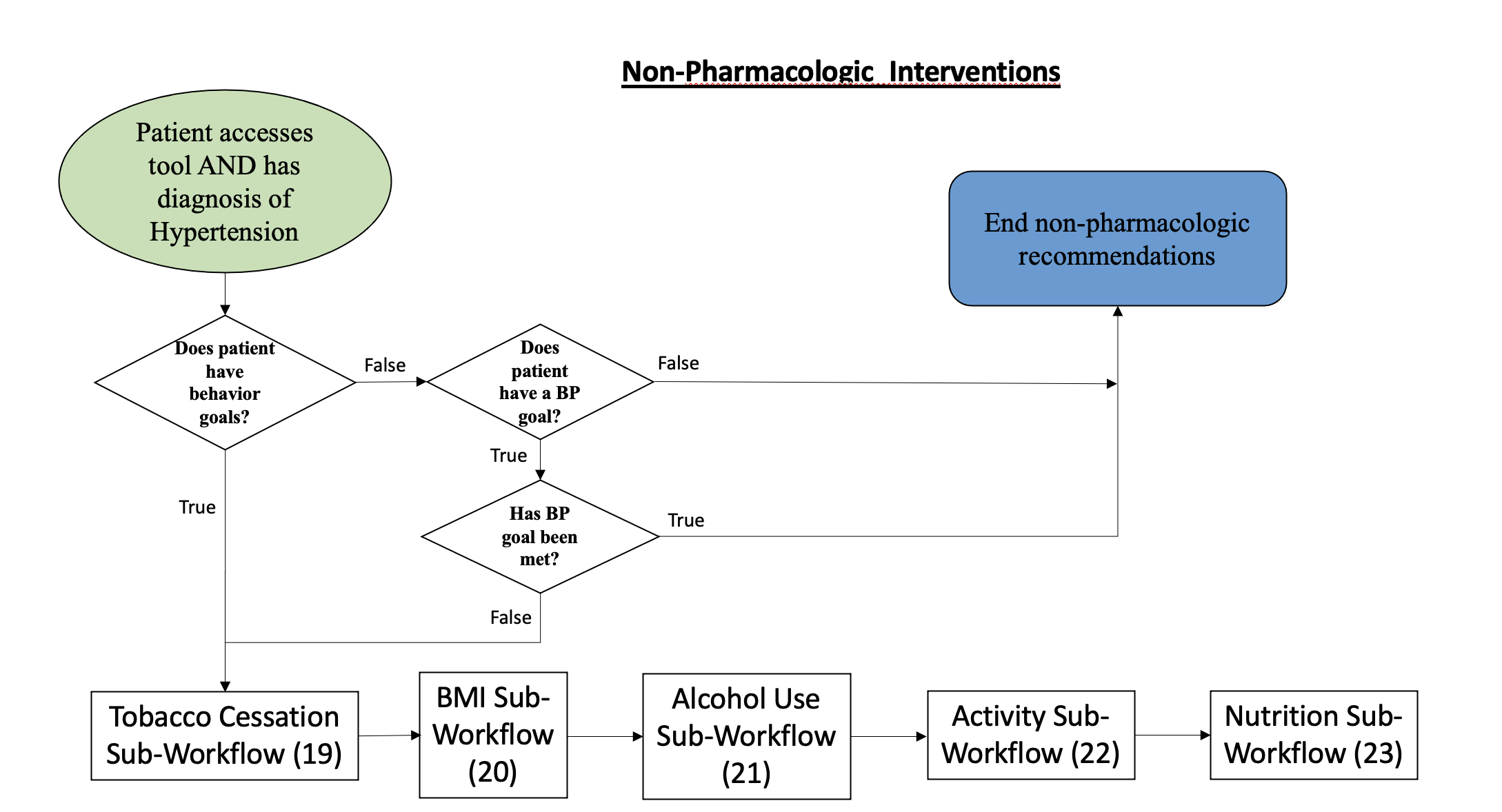
Non-pharmacologic intervention, including lifestyle and behavior modification goals, are an important part of blood pressure management. This is a prime area for patient engagement in care, as patients are encouraged to set and regularly update goals that suit their lifestyle that they can reasonably achieve and which can help in lowering their blood pressure.
For each time the patient logs into the tool and has progressed to this workflow, the tool will check to see if patient has current non-pharmacologic goals. If they do, a sub-workflow to set, check-in on, and update goals will activate for each type of goal.
If the patient does not have any current non-pharmacologic goals, the tool will check if the patient has reached their blood pressure goal, whether the default of 140/90 or a custom goal set by the patient. If that goal has been met, no further action is taken. If the goal has not been met, the workflow proceeds through the goalsetting sub-workflows.
Sub-workflows include:
These categories of lifestyle change goals have been shown to substantially influence blood pressure in hypertensive patients. All are supported by clinical literature. This tool allows patients to prioritize types of goals suitable to their own preferences for care when setting goals.
For all sub-workflows, the tool first checks to see if the patient has a current goal in this category. If the patient does not, the tool then queries the EHR to see if that category of goal is appropriate for the patient. If it is not relevant to the patient, it is not displayed as an option. For example, non-smokers should never receive a recommendation to set a goal that will help them stop smoking.
If the patient does not currently have an active goal relating to a sub-workflow, but that workflow is relevant to the patient, the tool will check to see if the patient has received counseling from their care team about that category of lifestyle change. If the patient has not received counseling, the tool will provide information about the potential health benefits to taking action and will ask the patient to set a goal. If the patient has received counseling, including previously being asked to set a goal, the tool will provide a reminder of the recommendations relating to this category of lifestyle change.
Patients are able to set goals using a mad-libs interface with dropdown options. This allows implementers to define goals according to their clinical practice guidelines and policies. A free text option is also available to patients for goalsetting. All goals require the patient to identify a date when they would like to have achieved this goal. It is recommended that patients focus on short-term, achievable goals that can be accomplished within two weeks and to iterate upon those goals as the patient sees fit. This is in accordance with SMART goal setting practices (Link to Mayo Clinic SMART goals page), which have been shown to assist with achieving personal goals in healthcare.
If the patient has an active goal within a sub-workflow, the tool will check to see if the completion date of the goal has arrived or passed. If it has, the tool will request that the patient update the goal by marking it as complete or incomplete. They may also set a new goal in this category. If the completion date has not yet arrived, the tool will display the current goal to the patient. The patient may choose to update a goal prior to the completion date selected.
Once a sub-workflow has completed, the next will run.
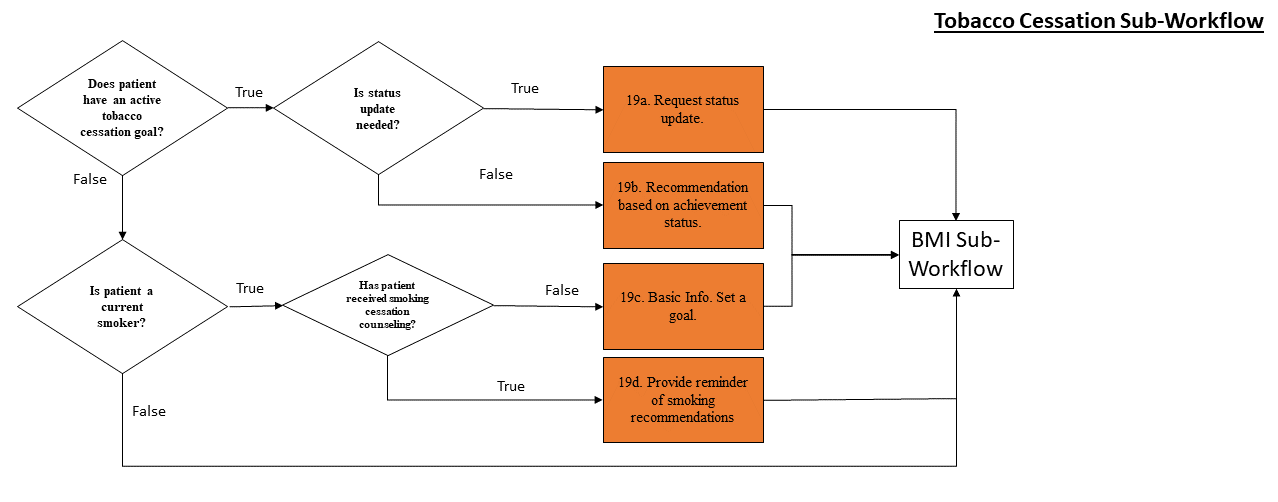
The tool checks to see if the patient has an active smoking goal or is considered a current smoker (most recent smoking observation was within the last 5 years). If the patient does not smoke or has quit smoking and has no active goal, this workflow will not activate.
Links:
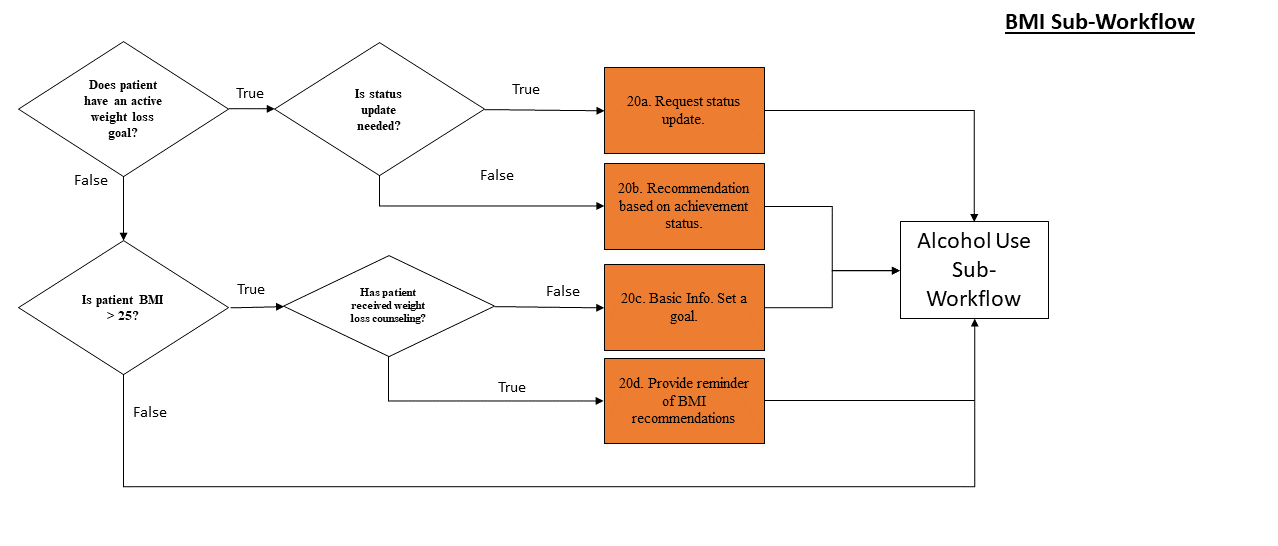
If the patient has any weight loss goals or their most recent BMI in the previous 2 years is above 25, this workflow will activate.
Links:
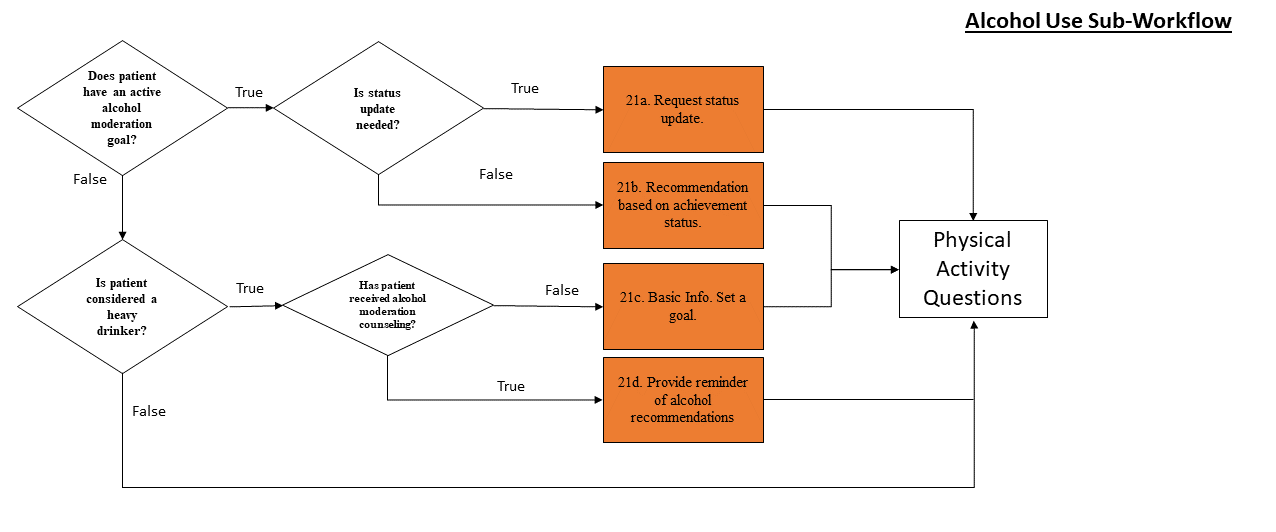
This workflow is activated if the patient has a current goal to reduce drinking or the patient is classified as a heavy drinker. Heavy drinking is defined as consuming 2+ drinks/day for women and 3+ drinks/day for men or having an alcohol abuse disorder. Observations of drink frequency older than 5 years are disregarded.
Links:
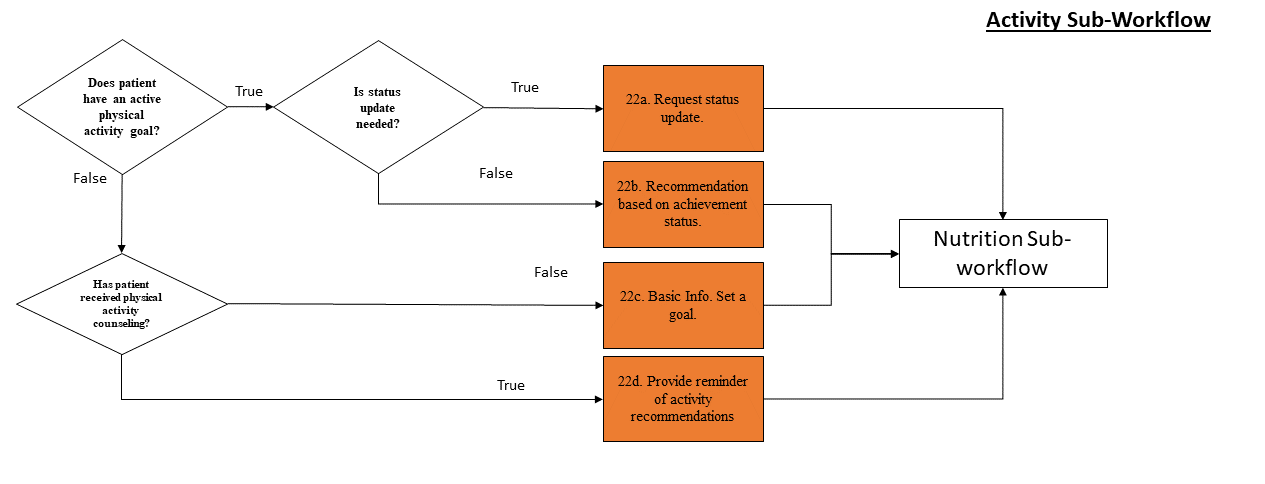
The tool does not check to see if the patient needs to engage in physical activity. Instead, it presents physical activity as a potential goal to all users. This allows patients and care teams to implement physical activity goals if and as appropriate to patient lifestyle and priorities for care.
Links:
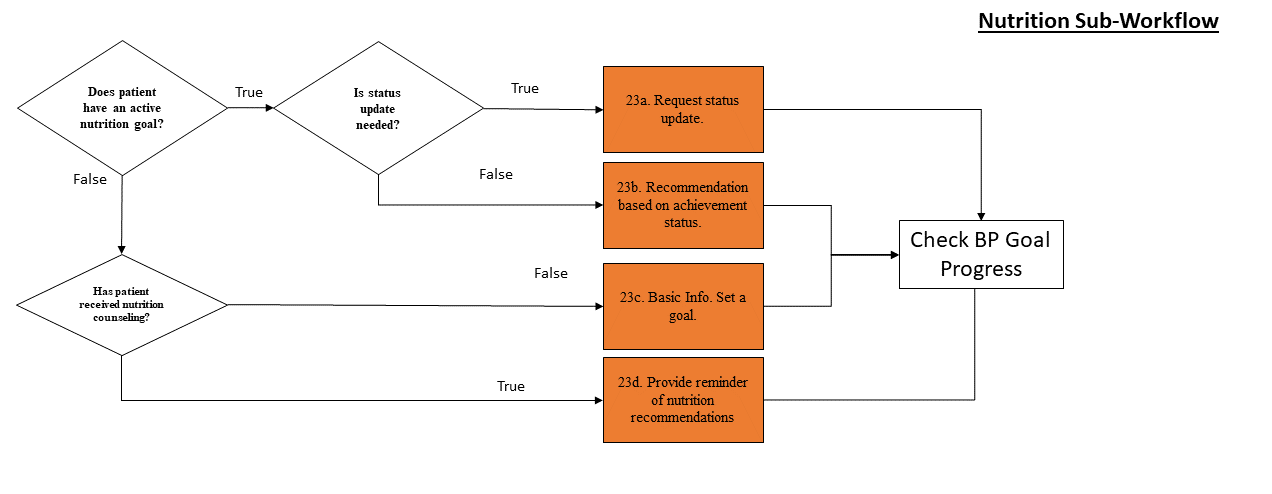
The tool does not check to see if the patient needs to adjust their diet. Instead, it presents dietary change recommendations as potential goals to all users. This allows patients and care teams to implement dietary change goals if and as appropriate to patient lifestyle and priorities for care.