NPHCDA Immunization FHIR IG
1.0.0 - ci-build
NPHCDA Immunization FHIR IG
1.0.0 - ci-build
NPHCDA Immunization FHIR IG, published by https://nphcda.gov.ng. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 1.0.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/Nigeria-FHIR-Community/ImmunizationIG/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
| Official URL: http://nphcda.gov.ng/ig/immunization/ImplementationGuide/ng.gov.nphcda.immunization | Version: 1.0.0 | |||
| Draft as of 2025-08-04 | Computable Name: NigeriaimmunizationFHIRIG | |||
| Name | Date | Reason for Changes | Version |
|---|---|---|---|
| NPHCDA Immunization IG development GitHub pages build after stakeholder validation | 4th July 2025 | Fifth Draft | 0.5.0 |
| NPHCDA Immunization FHIR IG upload to build.fhir.org | 4th August 2025 | 1st ci-build Draft | 1.0.0 |
This Nigeria Immunization FHIR Implementation Guide (IG) is designed to support the country’s adoption of the WHO SMART Guidelines approach by presenting the Digital Adaptation Kit (Business Requirments) for Immunization developed from National Primary Health Care Development Agency (NPHCDA) immunization guidelines. In addition, this IG presents the minimal Client/Server Capability for software-agnostic immunization systems in Nigeria. It presents the workflow in form of logical models, profiles and extensions, terminology structures (ValueSets and CodeSystems), and examples. Also, key operations necessary for conformance of the priority profiles where also presented. This initiative aims to strengthen immunization data management, enhance interoperability, and improve data-driven decision-making by developing standardized, contextually relevant digital solutions.
Immunization is one of the most cost-effective public health interventions, yet many countries, including Nigeria, face challenges in achieving full vaccine coverage. Digital tools and data management systems are being integrated into immunization programs to improve efficiency, accuracy, and accessibility. However, the successful adoption and scaling of these systems require solutions that are country-driven, user-friendly, reliable, and contextually relevant.
The WHO SMART Guidelines provide a standardized framework for developing and implementing interoperable, evidence-based, and scalable digital health solutions. This is particularly crucial for immunization, where timely and accurate data supports vaccine coverage tracking, identification of zero-dose children, and equitable service delivery. A key component of this approach is the Digital Adaptation Kit (DAK), which includes health interventions, workflows, core data elements, decision support logic, and other technical components necessary for effective immunization service management.
Nigeria has faced challenges such as data quality issues, fragmented systems, and disparities in access to immunization services. To address these, the country is aligning with the SMART Guidelines methodology and national health strategies like the National Immunization Strategy (NIS) and Immunization Agenda 2030 (IA2030). This initiative aims to enhance data interoperability, decision-making, and service delivery through the adoption of FHIR-based digital systems.
A User Requirement Gathering (URG) process is critical in developing Nigeria’s Immunization DAK. This process ensures that the digital immunization system is effective, adaptable, and user-friendly by engaging key stakeholders (health workers, program managers, and data specialists) to define essential system functionalities. This FHIR Implementation Guide (IG) serves as a blueprint for Nigeria’s interoperable, scalable, and standardized immunization data system, ensuring seamless integration with national and global health initiatives.
This Implementation Guide (IG) defines the core FHIR profiles, extensions, value sets, and terminology bindings required to support routine immunization workflows in Nigeria, using HL7® FHIR® standards using the WHO SMART Guidelines framework. Developed under the leadership of the National Primary Health Care Development Agency (NPHCDA), this IG provides structured guidance for digitizing, exchanging, and interpreting immunization-related data in an interoperable and scalable way.
The scope of this guide focuses on the following core components:
The IG covers the following key immunization use cases (which will continue to expand in subsequent iterations) prioritized by NPHCDA and stakeholders:
This guide does not prescribe a specific software platform or vendor product. Instead, it defines a set of national interoperability standards that can be adopted by EMR vendors, immunization registries, mobile app developers, and data exchange platforms to ensure consistency, data quality, and alignment with Nigeria’s digital health strategy.
The overview of the business processes in this DAK captures all business processes at a high level.
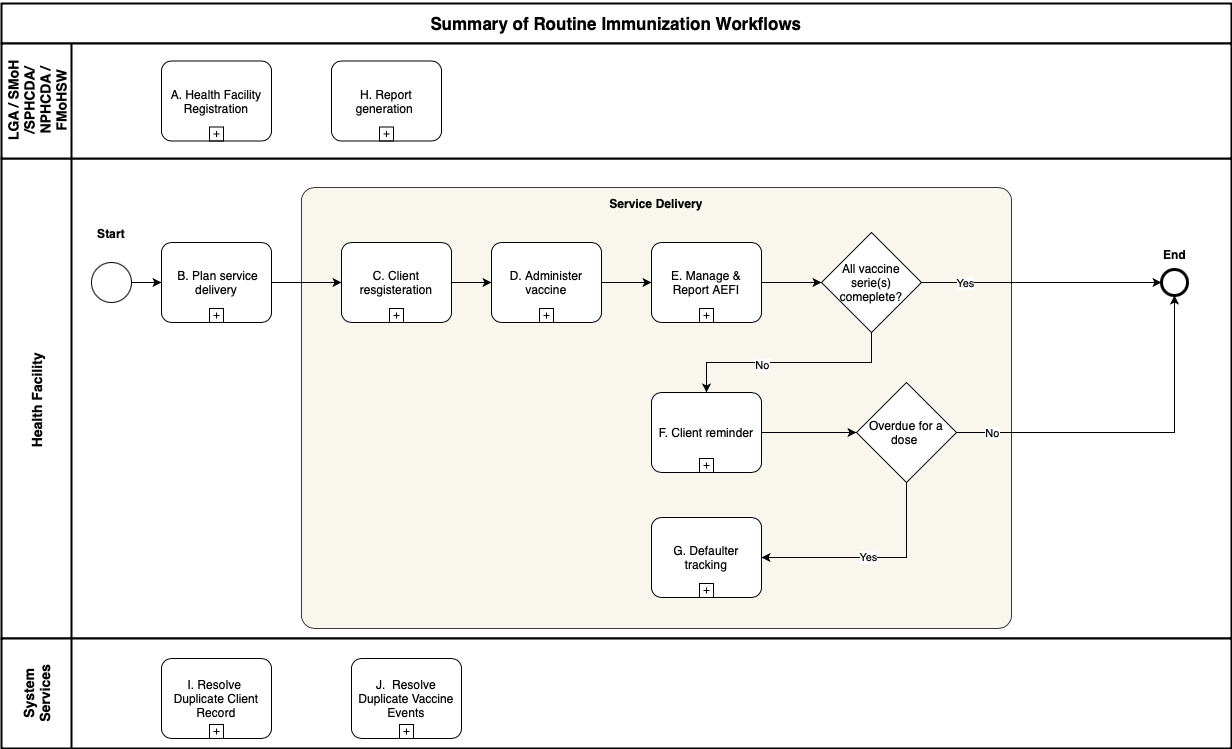
This FHIR IG is designed to promote system interoperability across the Nigerian digital health ecosystem. The artifacts defined in this guide (such as profiles, extensions, and value sets) are intended to work in conjunction with external health and administrative data systems to enable seamless integration and real-time information sharing. Specifically, this IG enables integration with the following external platforms:
These integrations are essential to achieving the goals of a nationally scalable, data-driven immunization system, and reflect Nigeria’s commitment to advancing digital public infrastructure (DPIs) and universal health coverage (UHC).
| SN | Acronym | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | AEFI | Adverse Event Following Immunization |
| 2. | BCG | Bacille Calmette-Guérin |
| 3. | BPMN | Business Process Modelling Notation |
| 4. | CHEW | Community Health Extension Worker |
| 5. | CRVS | Civil Registration and Vital Statistics |
| 6. | DAK | Digital Adaptation Kit |
| 7. | DHI | Digital Health Information |
| 8. | DHIS2 | District Health Information System 2 |
| 9. | DPI | Digital Public Infrastructure |
| 10. | DPT | Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus |
| 11. | eCHIS | electronic Community Health Information System |
| 12. | EIR | Electronic Immunization Registry |
| 13. | EMR | Electronic Medical Record |
| 14. | EPI | Expanded Program on Immunization |
| 15. | FHIR | Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resource |
| 16. | FMoHSW | Federal Ministry of Health and Social Welfare |
| 17. | Hep B | Hepatitis B Vaccine |
| 18. | HFR | Health Facility Registry |
| 19. | HL7 | Health Level-7 |
| 20. | HMIS | Health Management Information System |
| 21. | HPVV | Human Papilloma Virus Vaccine |
| 22. | HWR | Health Workforce Registry |
| 23. | IA2030 | Immunization Agenda 2030 |
| 24. | IG | Implementation Guide |
| 25. | IPV | Inactivated Polio Vaccine |
| 26. | LGA | Local Government Authority |
| 27. | LIO | Logistics Immunization officer |
| 28. | MDCN | Medical and Dental Council of Nigeria |
| 29. | NIS | National Immunization Strategy |
| 30. | NPHCDA | National Primary Health Care Development Agency |
| 31. | OIC | Officer In Charge |
| 32. | OPV | Oral Polio Vaccine |
| 33. | PHC | Primary Health Care |
| 34. | SIO | State Immunization Officer |
| 35. | SMART | Standards-based, Machine-readable, Adaptive, Requirements-based, Testable |
| 36. | SMoH | State Ministry of Health |
| 37. | SPHCDB | State Primary Health Care Development Board |
| 38. | SRS | Software Requirements Specification |
| 39. | UHC | Universal Health Coverage |
| 40. | URG | User Requirement Gathering |
| 41. | WHO | World Health Organization |