FHIRPath Specification
3.0.0-ballot - R2 STU1
FHIRPath Specification
3.0.0-ballot - R2 STU1
FHIRPath Specification, published by Implementable Technology Specifications WG. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 3.0.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/FHIRPath/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
| IG | Package | FHIR | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| hl7.fhirpath#3.0.0-ballot | R4 | ||
| hl7.terminology.r4#7.0.1 | R4 | Automatically added as a dependency - all IGs depend on HL7 Terminology | |
| hl7.fhir.uv.extensions.r4#5.2.0 | R4 | Automatically added as a dependency - all IGs depend on the HL7 Extension Pack | |
| hl7.fhir.uv.tools.r4#0.9.0 | R4 | for example references |
This publication includes IP covered under the following statements.
FHIRPath can be used against HL7 V2 messages. This UML diagram summarizes the Object Model on which the FHIRPath statements are written:
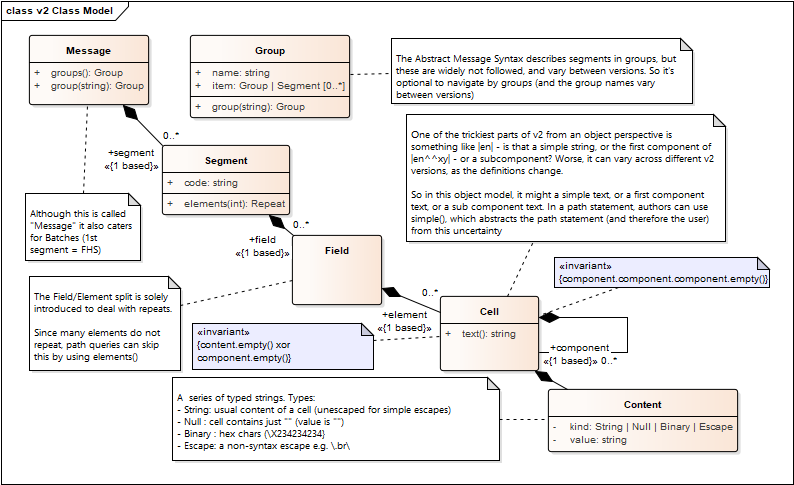
In this Object Model:
\.b\).Some example queries:
Message.segment.where(code = 'PID').field[3].element.first().simple()
Get the value of the first component in the first repeat of PID-3
Message.segment[2].elements(3).simple()
Get a collection with is the string values of all the repeats in the 3rd element of the 2nd segment. Typically, this assumes that there are no repeats, and so this is a simple value.
Message.segment.where(code = 'PID').field[3].element.where(component[4].value = 'MR').simple()
Pick out the MR number from PID-3 (assuming, in this case, that there's only one PID segment in the message. No good for an A17). Note that this returns the whole Cell - e.g. |value^^MR|, though often more components will be present)
Message.segment.where(code = 'PID').elements(3).where(component[4].value = 'MR').component[1].text
Same as the last, but pick out just the MR value
Message.group('PATIENT').group('PATIENT_OBSERVATION').item.ofType(Segment)
.where(code = 'OBX' and elements(2).exists(components(2) = 'LN')))
Return any OBXs from the patient observations (and ignore others e.g. in a R01 message) segments that have LOINC codes. Note that if the parser cannot properly parse the Abstract Message Syntax, group() must fail with an error message.
The list of known tooling and implementation projects for the FHIRPath language has been moved to the HL7 confluence site
This is an R4 IG. None of the features it uses are changed in R4B, so it can be used as is with R4B systems. Packages for both R4 (hl7.fhirpath.r4) and R4B (hl7.fhirpath.r4b) are available.
There are no Global profiles defined