FHIRcast, published by HL7 International / Infrastructure And Messaging. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 3.0.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/fhircast-docs/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
FHIRcast also defines content exchange between clients subscribed to the same topic using FHIRcast messages. Content is exchanged using FHIR resources contained in the most recently opened context which serves as the anchor context of exchanged information (see anchor context).
FHIR resources are used to carry the information being shared. These resources are entries in the Bundle resource inside the updates key. One and only one Bundle SHALL be present in a [FHIR resource]-update request (see FHIRcast Content Update Bundle). No resource SHALL appear multiple times in the update Bundle.
The FHIR transaction interaction defines how multiple actions can be grouped together and performed as one, such that all information being created or updated is contained in an entry’s resource (i.e., information is passed by value). For example, an Observation resource usually contains all relevant information regarding that observation. While it is possible to communicate content by reference even within a transaction bundle, implementer experimentation is needed for increased use of references to resources not contained in the Bundle.
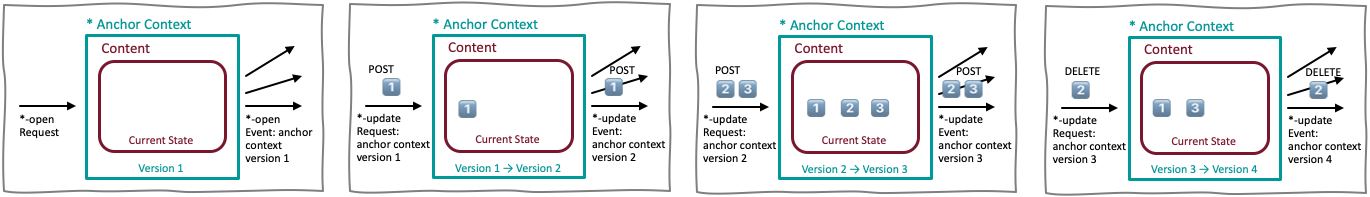
A key concept of the content sharing events is that the content is shared in a transactional manner. The diagram below shows a series of operations beginning with a [FHIR resource]-open request followed by three [FHIR resource]-update requests. The content in an anchor context is built up by the successive [FHIR resource]-update requests which contain only changes to the current state. These changes are propagated by the Hub to all Subscribers using [FHIR resource]-update events containing only the changes to be made.
At any time a Subscriber MAY issue a GET Context request to the Hub in order to retrieve the current context along with all attributes provided in the current context’s resources and any content in the anchor context.
In order to avoid lost updates and other out of sync conditions, the Hub serves as the transaction coordinator. It fulfills this responsibility by creating a version of the content’s state with each update operation. If an operation is requested by a Subscriber which provides an incorrect version, this request is rejected. This approach is similar to the version concurrency approach used by FHIR versions and managing resource contention. Additionally, many of the FHIRcast content sharing concepts have similarities to the FHIR messaging mechanisms and where possible the approaches and structures are aligned.
FHIR resources are used to convey the structured information being exchanged in [FHIR resource]-update operations. However, it is possible that these resources are never persisted in a FHIR server. During the exchange of information, the content (FHIR resource instances) is often very dynamic in nature with a user creating, modifying, and even removing information which is being exchanged. For example, a measurement made in an imaging application could be altered many times before it is finalized and it could be removed.
Support of content sharing by a Hub is optional. If supporting content sharing, a FHIRcast Hub SHALL fulfill additional responsibilities:
context.versionId when processing a [FHIR resource]-open request - the context.versionId does not need to follow any convention but SHALL be unique in the scope of a topic[FHIR resource]-update request if the version does not match the current context.versionId. A request can be rejected by returning a 4xx/5xx HTTP Status Code or a 202 HTTP status code followed by a SyncError.context.versionId for the anchor context’s content and provide the new context.versionId along with the context.priorVersionId in the event corresponding to the validated update request[FHIR resource]-update request in an atomic fashion and maintain a list of current FHIR resource content in the anchor context so that it may provide the anchor context’s content in response to a GET Current Context request[FHIR resource]-close request is received, the Hub should dispose of the content for the current anchor context (i.e., the context being closed by this request) since the Hub has no responsibility to persist the content[FHIR resource]-select event to all SubscribersA Hub is not responsible for structurally validating FHIR resources. While a Hub must be able to successfully parse FHIR resources sufficiently to perform its required capabilities (e.g., find the id of a resource), a Hub is not responsible for additional structural checking. If the Hub does reject an update request, for any reason, it SHALL reject the entire request - it SHALL NOT accept some changes specified in the bundle and reject others.
A Hub is not responsible for any long-term persistence of shared information and should purge the content when a [FHIR resource]-close request is received.
Additionally, a Hub is not responsible to prevent applications participating in exchanging structured information from causing inconsistencies in the information exchanged. For example, an inconsistency could arise if an application removes from the anchor context’s content a resource which is referenced by another resource. The Hub may check [FHIR resource]-update requests for such inconsistencies and MAY reject the request with an appropriate error message; however, it is not required to do so. Additionally, a Hub MAY check for inconsistencies which it deems to be critical but not perform exhaustive validation. For example, a Hub could validate that the content in a DiagnosticReport anchor context always includes at least one primary imaging study.
Clients wishing to exchange structured information SHALL:
[FHIR resource]-open request to open a new resource which becomes the anchor context[FHIR resource]-update request when appropriate. The [FHIR resource]-update request contains a Bundle resource which is a collection of resources that are atomically processed by the Hub with the anchor context’s content being adjusted appropriatelycontext.versionId of the anchor context provided by the Hub so that a subsequent [FHIR resource]-update request may provide the current context.versionId which will be validated by the Hub[FHIR resource]-update event but should still track the context.versionId for subsequent use[FHIR resource]-update request fails with the Hub, the Subscriber may issue a GET Context request to the Hub in order to retrieve the current content in the anchor context and its current context.versionIdExchange of information is made transactionally using change sets in the [FHIR resource]-update event (i.e., the complete current state of the content is not provided in the Bundle resource in the updates key). Therefore, it is essential that applications interested in the current state of exchanged information process all events and process the events in the order in which they were successfully received by the Hub. Each [FHIR resource]-update event posted to the Hub SHALL be processed atomically by the Hub (i.e., all entries in the request’s Bundle should be processed prior to the Hub accepting another request).
The Hub plays a critical role in helping Subscribers stay synchronized with the current state of exchanged information and, as described in Request For Context Change, responds to a FHIRcast event with either a synchronous HTTP status or an HTTP 202 [Accepted] followed by either a SyncError or a broadcast of the FHIRcast event. On receiving a [FHIR resource]-update request the Hub SHALL examine the context.versionId of the anchor context. The Hub SHALL compare the context.versionId of the incoming request with the context.versionId the Hub previously assigned to the anchor context (i.e, the context.versionId assigned by the Hub when the previous [FHIR resource]-open or [FHIR resource]-update request was processed). If the incoming context.versionId and last assigned context.versionId do not match, the Hub SHALL reject the request and SHOULD do so by returning a 4xx HTTP Status Code. Note that if the Hub rejects the request for any reason, the entire request is rejected - the Hub SHALL NOT accept some updates requested in the Bundle resource while reject other updates requested in the Bundle.
If the context.versionId values match, the Hub proceeds with processing each of the FHIR resources in the Bundle and SHALL process all Bundle entries in an atomic manner. After updating its copy of the current state of exchanged information, the Hub SHALL assign a new context.versionId to the anchor context and use this new context.versionId in the [FHIR resource]-update event it forwards to subscribed applications. The Hub SHALL also include the context.priorVersionId in the distributed event which receiving applications MAY use to ensure they are apply the updates to the proper context version. The distributed update event SHALL contain a Bundle resource with the same Bundle id which was contained in the request.
[FHIR resource]-update events MAY also update attributes of the anchor context or associated context resources. For example, a Subscriber might wish to update the status attribute of the anchor context resource.
When a [FHIR resource]-update event is received by a Subscriber, the application should respond as is appropriate for its clinical use. For example, an image reading application may choose to ignore an observation describing a patient’s blood pressure. Since transactional change sets are used during information exchange, no problems are caused by applications deciding to ignore exchanged information not relevant to their function. However, they should read and retain the context.versionId of the anchor context provided in the event for later use.
A FHIRcast Hub SHALL process a [FHIR resource]-update event even if the anchor context referenced differs from the current context (the anchor context is present in the context attribute in [FHIR resource]-update events). The proposed [FHIR resource]-update event SHALL be processed in scope of the referenced context (not the current context) following the same rules as if the referenced context were the current context. The current context is not changed by a [FHIR resource]-update event that references an anchor context that is not the current context.
|
|
Implementer feedback on the generation and general handling of a resource's identifiers, including its logical `id` is requested. Should the logical id of a FHIR resource created during a content sharing session persist when the resource is persisted? How should id conflicts be resolved? Additionally, the ability of Subscribers who participated in a content sharing session to [reopen](2-10-1-ContentSharingFHIRcastMessaging.html#content-creation-and-reopen-scenario) a content sharing session including the state of content at the time of the prior close of the session |
When a Subscriber creates a FHIR resource which it asks be added to the anchor context’s content, it SHALL create an id for the resource (see: Resource.id). Two approaches to populating the resource’s id are possible:
id for the resource this id SHOULD be used for the resource’s id in addition to the resource’s entry in the update bundle’s fullUrl attribute when adding the resource to the anchor context’s content.id such that it will be globally unique (e.g., a UUID).If the same anchor context is reopened and used for a content sharing session, the same Resource.id used during the initial content sharing session should be used by any Subscriber adding the same resource to this reopened content sharing session. Hence, should any Subscriber participating in a content sharing session decide to persist a resource after the content sharing session is closed, it SHOULD ensure that the original Resource.id and the fullUrl attribute of the resource’s entry in the update bundle (if populated) is part of the persisted resource. This enables a Subscriber to add the resource to a reopened content sharing session with the original Resource.id or to identify (match) resources added to a reopened content sharing session with the resource in the original content sharing session.
For further discussion on the reopening of content sharing sessions see Section 4.6 FHIRcast Event-based Content Sharing.