HL7 FHIR Implementation Guide: Profiles for Transfusion and Vaccination Adverse Event Detection and Reporting, published by Biomedical Research & Regulation WG. This is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 1.0.1). This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/fhir-icsr-ae-reporting/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
A computable phenotype is a clinical condition or characteristic that can be ascertained by means of a computerized query to an electronic health record (EHR) system or clinical data repository using a defined set of data elements and logical expressions1.
This implementation guide contains FHIR CQL queries for phenotypes that can be used to identify cases for review and reporting using data available in FHIR formats. In addition, it includes code lists that are used by each algorithm to identify different pieces of evidence (conditions, immunizations, etc.) of adverse event or biologic product in the EHR’s structured data.
Currently, the algorithms below focus on identification of adverse events temporally associated with COVID-19 or influenza vaccine exposure, however future versions will include algorithms for identification of adverse events related to other biologics. Additionally future versions may include other algorithm components, such as unstructured data, along with other mediums for expressing the algorithm logic, such as FHIR search.
Reference:
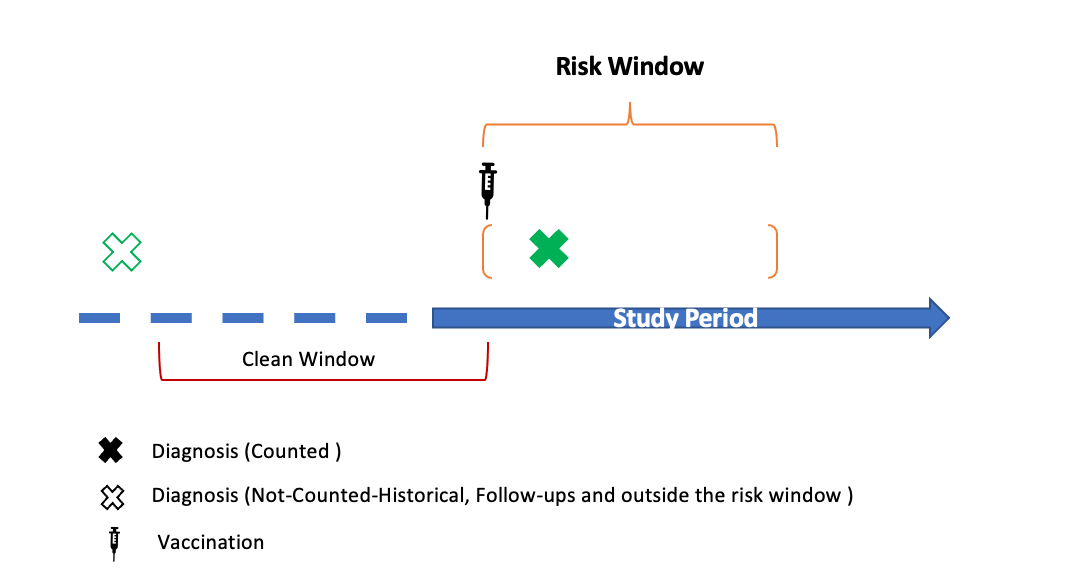
These algorithms are named “claims comparable” because they are designed to mimic phenotypes built by epidemiologists on medical claim data sources. These phenotypes are limited to using data that would be available in those sources including condition diagnoses (ICD-10), immunizations (NDC, CPT, RxNorm), and encounter data. The algorithm consists of codelists to identify the adverse event and vaccine exposure combined with additional logic requiring the adverse event to occur during a post vaccination risk window and not have the adverse event diagnosis initially be made during a clean window prior to the vaccine exposure.
The claims comparable algorithms utilize interoperable codes and condition, encounter, and immunization data elements to identify potential adverse events following immunizations (AEFIs). In a FHIR Server, these algorithms query the following resources: Condition, Immunization, Procedure, and Encounter.
These algorithms apply rules-based claims-comparable algorithm logic. These phenotypes are built using interoperable condition diagnoses (ICD-10, SNOMED-CT), immunization (CVX, NDC, CPT, RxNorm) data, and encounter type (Inpatient, Outpatient, etc.) data. These phenotypes can be used to find incident cases of adverse events or a case observed in the risk window of a vaccine exposure.
The components of the phenotype algorithms include:
Clinical Quality Language (CQL) is an HL7 language standard that is meant to be human readable and structured enough to run the logic specified in the file. For more information on CQL, you can visit the HL7 CQL site.
There are many projects being developed for CQL implementation.
The following tables list the available phenotypes for each algorithm type. The tables include links to the relevant CQL file for that algorithm, as well as the location of codelists or termsets (if applicable) used to develop the algorithm. NOTE: all of the code lists are found in the US National Library of Medicine Value Set Authority Center (VSAC) and require a VSAC login to view.
| Adverse Event | Care Setting* | Clean Window | Risk Window | Vaccine Relevance | FHIR CQL File | Codelists |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Guillain-Barre Syndrome | IP | 365 days | 1-42 days | Influenza and Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-42 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Bell’s Palsy | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 183 days | 1-42 days | Influenza and Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Anaphylaxis | IP,OP-ED | 30 days | 0-2 days | Influenza and Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Appendicitis | IP, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-42 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Encephalomyelitis | IP | 183 days | 1-42 days | Influenza and Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Narcolepsy | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-42 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC) | IP, OP-ED, OP/PB | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Transverse Myelitis | IP, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-90 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS) | IP, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-42 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Febrile Seizures | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 42 days | 0-1 days | Influenza and Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Kawasaki Disease | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Non-hemorrhagic Stroke | IP | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Hemorrhagic Stroke | IP | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Acute Myocardial Infarction | IP | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Myocarditis/Pericarditis | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-42 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Deep Vein Thrombosis | IP, OP/PB, OP-ED | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
| Pulmonary Embolism | IP, OP/PB,OP-ED | 365 days | 1-28 days | Covid-19 | CQL | Diagnosis Codes |
*IP - inpatient stays, OP/PB - all outpatient visits and professional/provider services including clinics, OP-ED - subset of outpatient visits occurring in the emergency department