
This fragment is available on index.html
This publication includes IP covered under the following statements.
| Type | Reference | Content |
|---|---|---|
| web | example.org | value : https://example.org/DRUG-X/smart-application |
| web | github.com | US Medication Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategies (REMS) FHIR IG, published by HL7 International / Pharmacy. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2.0.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/fhir-medication-rems-ig/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions |
| web | cds-hooks.org |
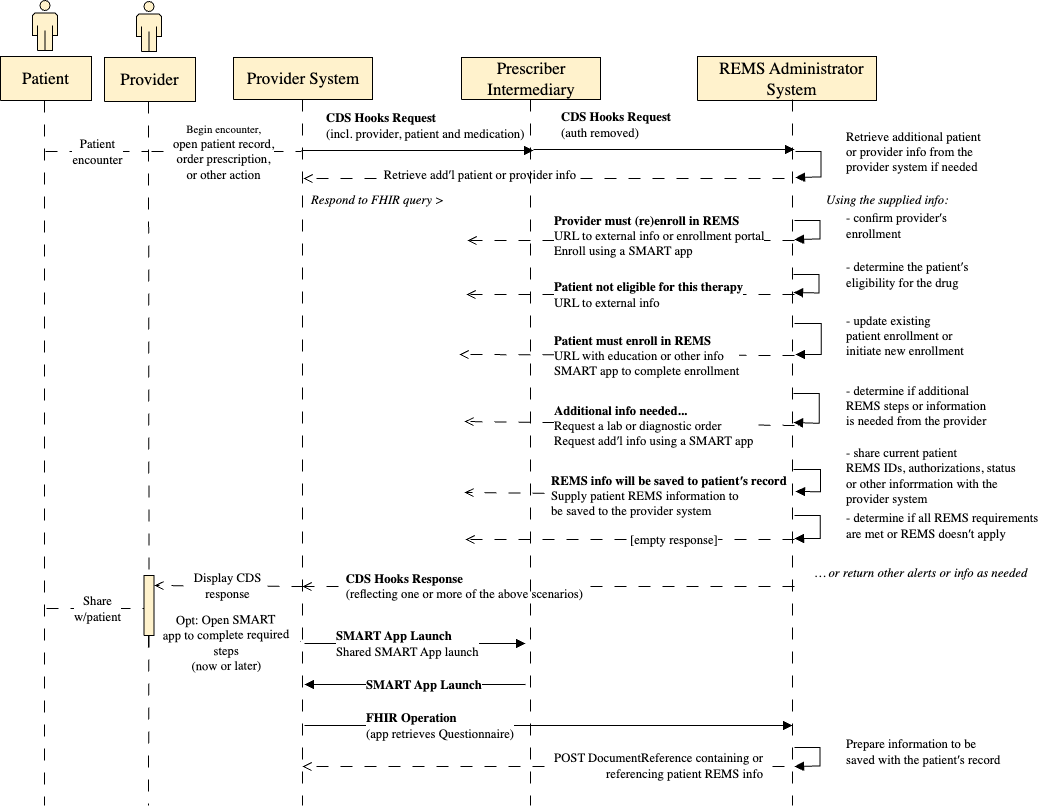
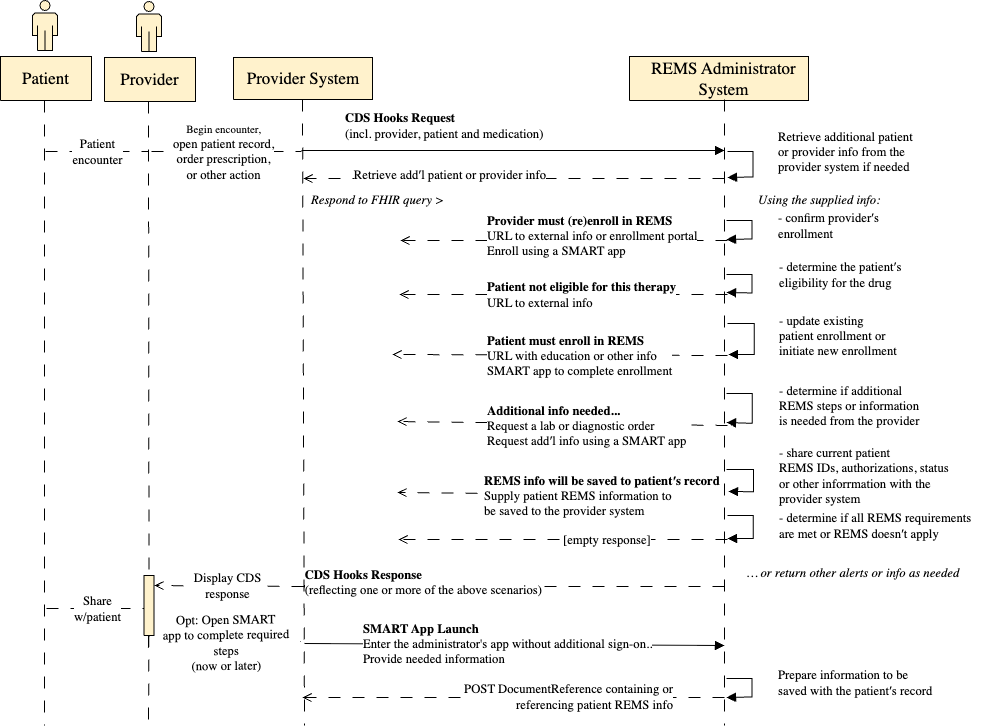
Indicates that this input holds app context information to be used by the SMART application. This content will be included as appContext
in the token response as is specified here in the CDS Hooks specification
|
| web | cds-hooks.org |
order-sign
which occurs at the point in the ordering process when the prescriber finalizes the prescription
|
| web | cds-hooks.org |
order-select
which occurs after the clinician selects the medication at the start of the ordering process
|
| web | cds-hooks.org |
patient-view
which occurs when the user opens a patient's record; typically called only once at the beginning of a user's interaction with a specific patient's record
|
| web | cds-hooks.org |
encounter-start
which is invoked when the user is initiating a new encounter. In an inpatient setting, this would be the time of admission. In an outpatient/community environment, this would be the time of patient-check-in for a face-to-face or equivalent for a virtual/telephone encounter
|
| web | www.iso.org |
ISO maintains the copyright on the country codes, and controls its use carefully. For further details see the ISO 3166 web page: https://www.iso.org/iso-3166-country-codes.html
Show Usage
|
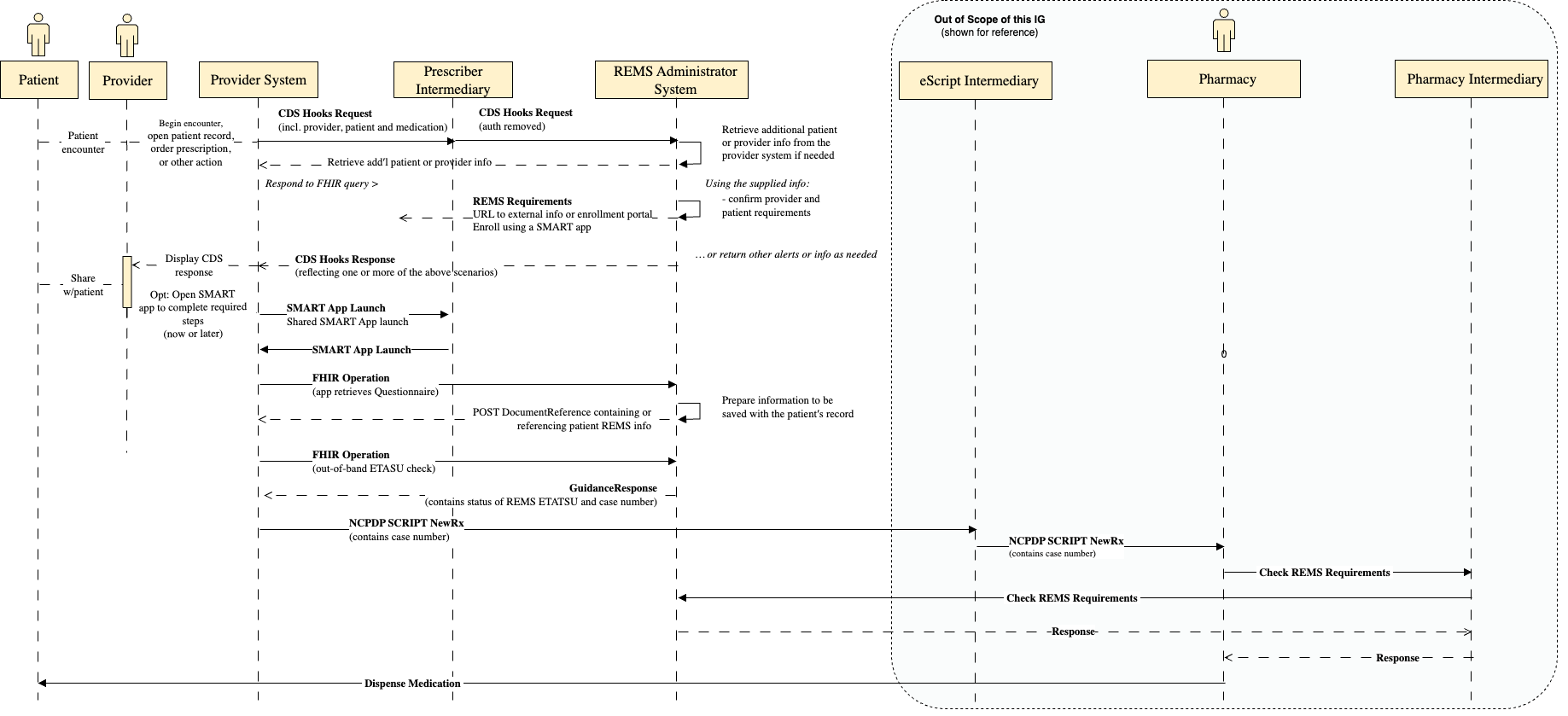
| web | standards.ncpdp.org | The Pharmacy interactions are out of scope of this IG but are detailed in the NCPDP Implementation Guides (see the NCPDP standards page for more information). These interactions detail the use of the REMS specific messages within the NCPDP SCRIPT standard. Using the standard, the Pharmacy system is able to use standard messages to query the REMS Administrator though a REMS Pharmacy Intermediary. This intermediary forwards the messages to the correct REMS Administrator and returns reject codes if the medication cannot be dispensed. A successful message will provide dispense authorization for the Pharmacy to finally dispense the medication to the Patient. |
| web | standards.ncpdp.org | The EHR SHALL send the medication to the Pharmacy using the standard NCPDP SCRIPT NewRx message. This message contains information about the Patient and the Medication being prescribed. For more details on the message please see the NCPDP SCRIPT specification . Under current prescribing processes, the NCPDP SCRIPT NewRx message is sent from the EHR to an eScript intermediary and then is routed to the correct pharmacy as depicted in the figure above. |
| web | standards.ncpdp.org | Prescription drug electronic prescribing and electronic prior authorization is completed using the NCPDP (National Council for Prescription Drug Programs) SCRIPT standards . These standards are also used for completing the pharmacy workflow within the REMS programs. This guide describes sending NCPDP SCRIPT messages including NewRx for electronic prescribing. For more details, please reference the NCPDP SCRIPT standards. |
ehr-launch-sequence-with-intermediary.png 
|
ehr-launch-sequence-with-pharmacy.png 
|
ehr-launch-sequence.png 
|
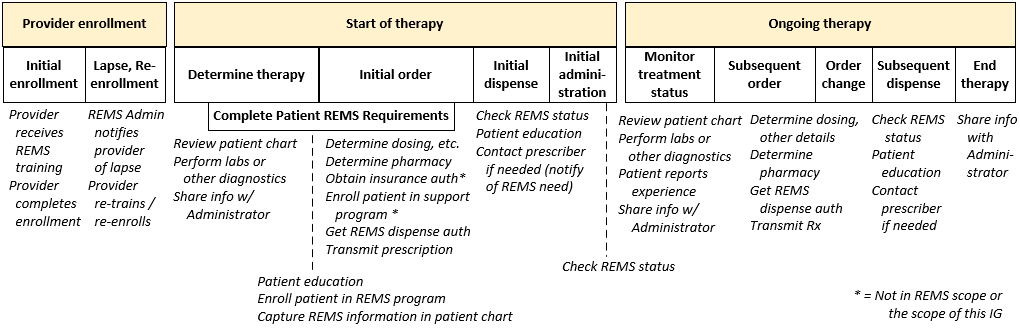
flow.png 
|
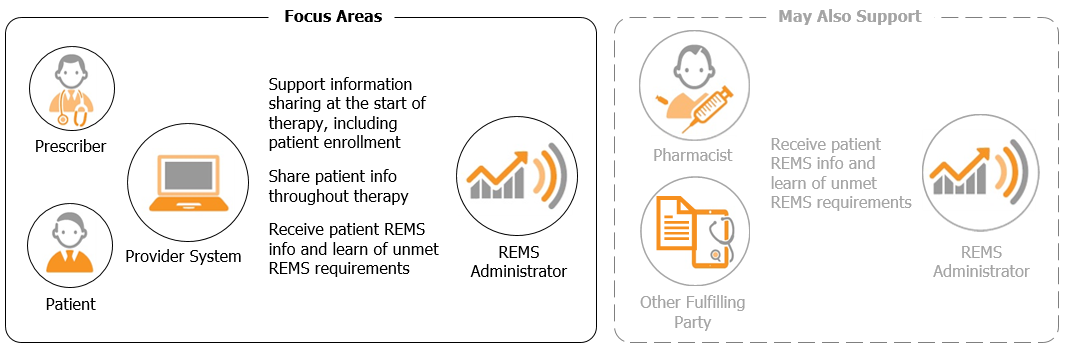
focus-areas.png 
|
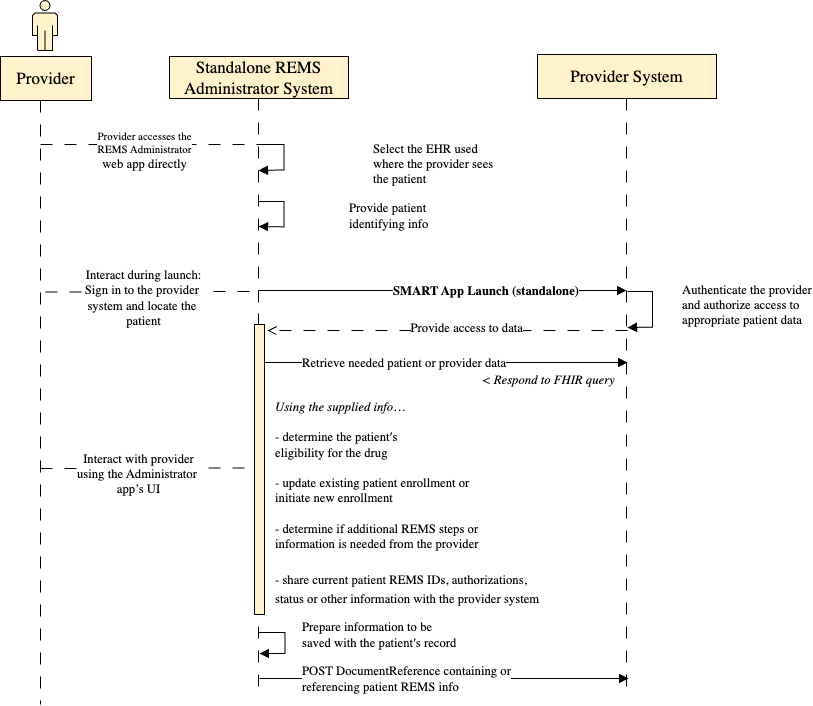
standalone-launch-sequence.png 
|
steps.png 
|
tree-filter.png 
|