Clinical Practice Guidelines, published by HL7 International / Clinical Decision Support. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 2.0.0 built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/cqf-recommendations/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
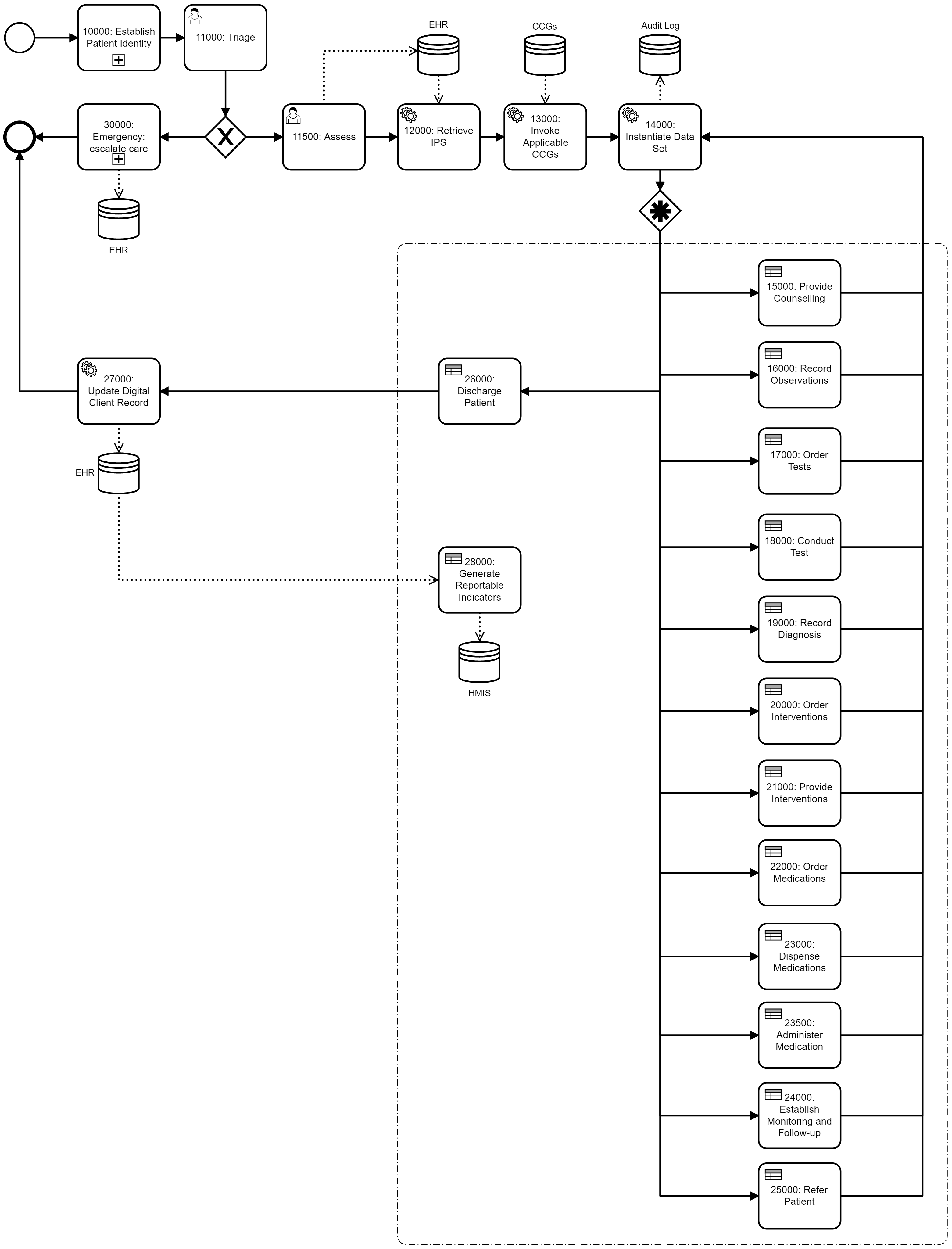
NOTE: This is a proposed common pathway for ambulatory care processes. —
Establish Patient Identity
Identifying and recording the subject of care.
Retrieve Patient Health Summary
Retrieving a summary of the patient's health.
Triage
Performing basic triage to identify any signs that emergency care is required
Emergency: Escalate Care
Providing emergency care in trauma cases or as part of guideline-based care escalation.
Invoke Applicable CCGs
Invoking the CCGs (Clinical Commissioning Groups) that are applicable to the situation.
Provide Counseling
Informing the subject of care about their treatment options and about how their ongoing care should be managed between visits. This is also where treatment consents are obtained and where health education is provided.
Record Observations
Gathering clinical history and performing and recording observations regarding the patient's health (e.g. blood pressure, temperature, etc.).
Order Tests
Ordering and conducting diagnostic tests, including lab tests, collection of samples, and other diagnostic tests. Lab testing may be done locally (e.g. HIV quick test) or the samples may require lab order fulfillment workflow.
Evaluate Test Results
Using available information from the patient's history, current examinations, tests, and assessments to assist in developing a diagnosis.
Record Diagnosis
Recording the diagnosis that was reached in the evaluation process.
Order Interventions
Ordering the necessary interventions.
Provide Interventions
Providing the interventions to the patient.
Order Medications
Clinicians ordering medications to be dispensed by a pharmacy. Pharmacies may be local to the care facility or community-based, and involves supply chain transactions to support medication management.
Dispense Medications
Administering medications to the patient.
Establish Monitoring and Follow-up
Monitoring and tracking progress for each patient based on guideline recommendations.
Discharge/Refer Patient
Discharging or referring a patient, including the movement of patients through levels of care delivery (e.g. acute to primary, primary to community, etc.) or the enrollment of patients in guideline-based care programs (e.g. HIV, maternal, diabetes, injury rehabilitation, etc.).
Update Digital Client Record
Updating the Digital Client Record with the appropriate information
Generate Reportable Indicators
Recording and reporting patient-specific care management information which may be aggregated to develop reportable system management indicators at the provider, facility, district, national, and international levels.