CardX Hypertension Management, published by HL7 International / Clinical Interoperability Council. This guide is not an authorized publication; it is the continuous build for version 1.0.0-ballot built by the FHIR (HL7® FHIR® Standard) CI Build. This version is based on the current content of https://github.com/HL7/CardX-HTN-MNG/ and changes regularly. See the Directory of published versions
| Official URL: http://hl7.org/fhir/uv/cardx-htn-mng/ImplementationGuide/hl7.fhir.uv.cardx-htn-mng | Version: 1.0.0-ballot | |||
| Draft as of 2024-04-05 | Computable Name: HTNMngCardX | |||

Hypertension affects an estimated 1.28 billion adults aged 30-79 years and is the leading cause of premature death and cardiovascular disease internationally. Less than half of adults with hypertension are diagnosed and treated and only 1 in 5 adults with hypertension have it under control 1. A self-measured blood pressure (SMBP) approach, referring to the regular measurement of blood pressure by the patient outside the clinical setting, can help clinicians better diagnose and manage hypertension 2. A standardized approach to hypertension management that emphasizes capturing data once and reusing it for multiple purposes will increase the proportion of patients treated to goal, improve clinical outcomes, reduce clinician burden, and enable more complete and accurate reporting. The objective of the CardX Hypertension Management Implementation Guide (CardX HTN IG) is to improve HTN diagnosis, management, and outcomes by facilitating the collection and exchange of data from widely implemented SMBP programs. Compared to the traditional approach of only measuring blood pressure in the clinical setting, this could help more patients reach their target BPs.
This FHIR Implementation Guide (IG) aligns with and harmonizes existing work to create a vendor-agnostic set of data exchange standards that enable interoperable, scalable, and accessible hypertension management. Due to the global prevalence of hypertension, this IG is adopting a universal realm approach, aiming to provide a comprehensive and consistent framework for healthcare information exchange across diverse geographic regions and healthcare systems. The IG provides FHIR profiles, extensions, and value sets to represent, query for, and exchange data for evidence-based management of hypertension. The CardX Hypertension Management IG includes profiles to represent self-measured blood pressure monitoring data and associated metadata. These profiles support the hypertension management workflow by providing a meaningful exchange of blood pressure data between devices, third-party patient-facing health management platforms (identified here as personal health intermediaries), and clinical Electronic Health Record Systems or patient portals. This will allow self-measured blood pressure readings to be sent directly to the physician at pre-defined intervals. In future iterations, this Implementation Guide will include additional evidence-based elements to support hypertension management, enabling bi-directional data exchange between patients and clinicians to manage hypertension.
In the diagram below, the red arrows between Device Gateway, Personal Health Intermediary, and EHR identify the scope of structured FHIR data exchange within SMBP data management. The standards identified in this IG are primarily supported in the first and second arrow exchange:
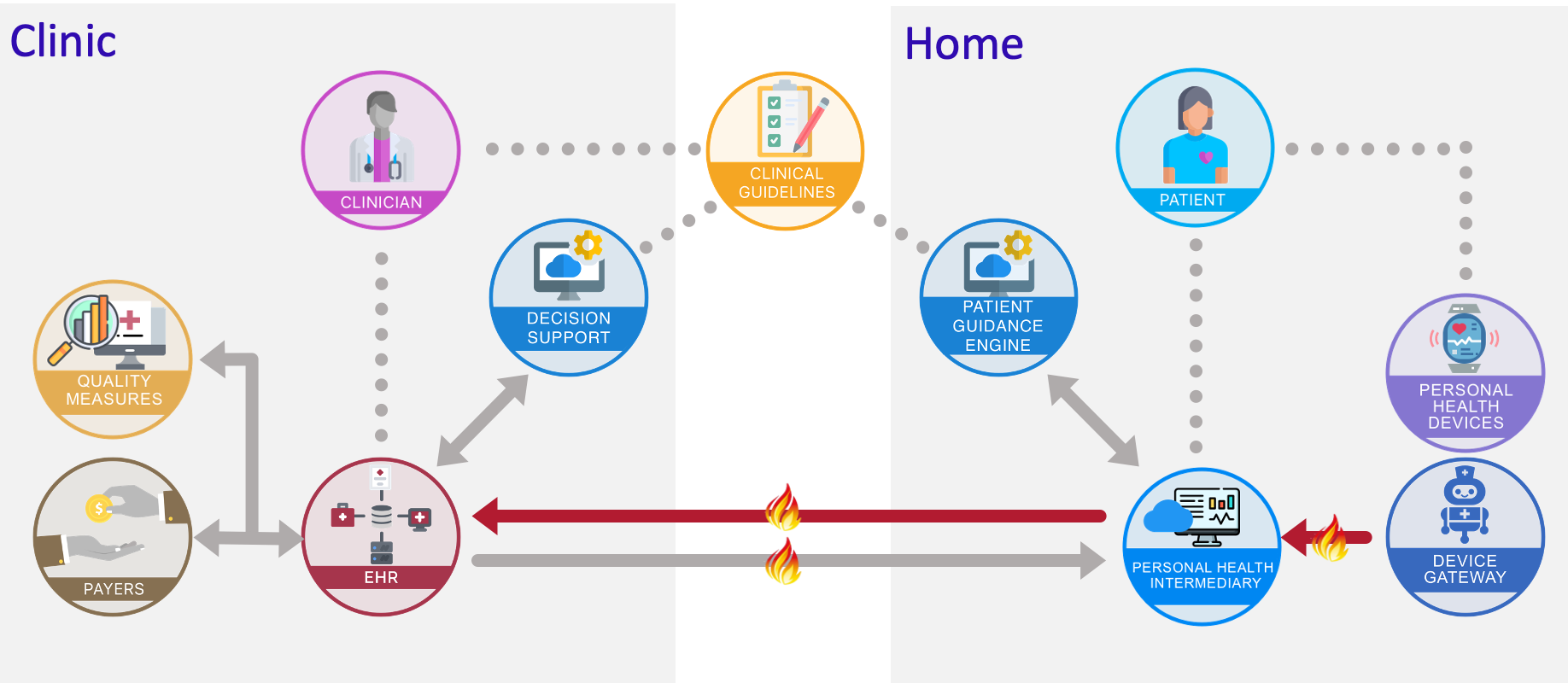
The intended actors include:
| Actor | Description |
|---|---|
| An individual diagnosed with hypertension and enrolled in a self-measure blood pressure monitoring program. | |
| Includes licensed clinicians, nurses, physician assistants, or other medical providers that interact with the patient to diagnosis, refer, monitor, and treat hypertension. | |
| Any device that allows patients or caregivers to capture their own health data such as their blood pressure and then integrate the device provided data with an associated app. These systems will primarily act as FHIR clients. | |
| Any system that allows patients to manage their health information. These may be web-based applications, mobile applications, or device gateways. These systems act as FHIR servers to receive data from a device and act as FHIR clients capable of sending data to other systems. | |
| Any system that allows patients and caregivers to capture and share information about their blood pressure, integrate device provided data. These may be web-based applications, mobile applications, or traditional software. These systems will primarily act as FHIR clients. | |
| An Electronic Health Record system involved in reviewing patient hypertension related data, that may receive SMBP observations from other systems, and that will coordinate all management activities for hypertension patients. These systems could also represent Patient Portals. |
A primary care provider enrolls a patient in a self-measured blood pressure monitoring program to manage the patient’s hypertension. The patient follows the provided instructions and takes their blood pressure as per protocol. The blood pressure data is uploaded via Bluetooth to the Device Gateway. The patient’s blood pressure information is pushed, via a FHIR API, to a receiving Personal Health Intermediary platform where the data is stored, aggregated, and managed. Once the information has been retrieved, the Personal Health Intermediary can store, share, reuse, and display the standardized information in their preferred view.
The Personal Health Intermediary calculates an average blood pressure reading based on the SMBP protocol timeframe. The patient’s average blood pressure and the individual blood pressure’s that comprise the average are pushed, via a FHIR API to an EHR’s FHIR-enabled patient portal. The EHR performs a GET request to retrieve the average blood pressure and associated observations. Once the information has been retrieved, the EHR can store, share, reuse, and display the standardized information in their preferred view.
| Implementation Guide | Version | Dependency |
|---|---|---|
| FHIR Release 4 | 4.0.1 | The CardX Self-Measured Blood Pressure profile is derived from the FHIR R4 Observation Blood Pressure profile. |
| FHIR Release 4 | 4.0.1 | The CardX Average Self-Measured blood pressure profile is derived from the FHIR R4 Observation resource. |
| FHIR Release 4 | 4.0.1 | The CardX SMBP Associated Heart Rate profile is derived from the FHIR R4 Observation Heart Rate profile. |
| Implementation Guide | Relationship |
|---|---|
| US Core | Profiles in this IG align with US Core 3.1.1 as much as possible. Where possible, effort will also be made to align with future U.S. Core releases. U.S. Core also sets expectations for a variety of referenced resources and establishes baseline conformance expectations. |
| Vital Signs with Qualifying Elements | All profiles in this IG align with the profiles in the Vital Signs with Qualifying Elements IG (Universal Realm). |
| FHIR Write | Specifies FHIR write back capabilities for Vital Signs Observations including Blood Pressure. |
The Personal Health Device IG and the mHealthADE were also considered in an initial landscape analysis. These IGs are out of scope for this IG at this time.
| Initiative | Description |
|---|---|
| CDC Million Hearts 2027 Optimizing Care Initiative | Million Hearts® is a national initiative to prevent 1 million heart attacks and strokes within 5 years. It focuses on implementing a small set of evidence-based priorities and targets that can improve cardiovascular health for all. The initiative includes improving blood pressure control through evidence-based strategies like (self-measured blood pressure monitoring (SMBP). |
| AHA’s National Hypertension Council Initiative (NCHI) | Through the NHCI, the American Heart Association raises awareness of high blood pressure and promotes prevention of it through overlapping community approaches. |
| Target: BP | A national initiative formed by the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Medical Association (AMA) in response to the high prevalence of uncontrolled blood pressure (BP). |
To learn more about CardX and the Hypertension Management Use Case visit: